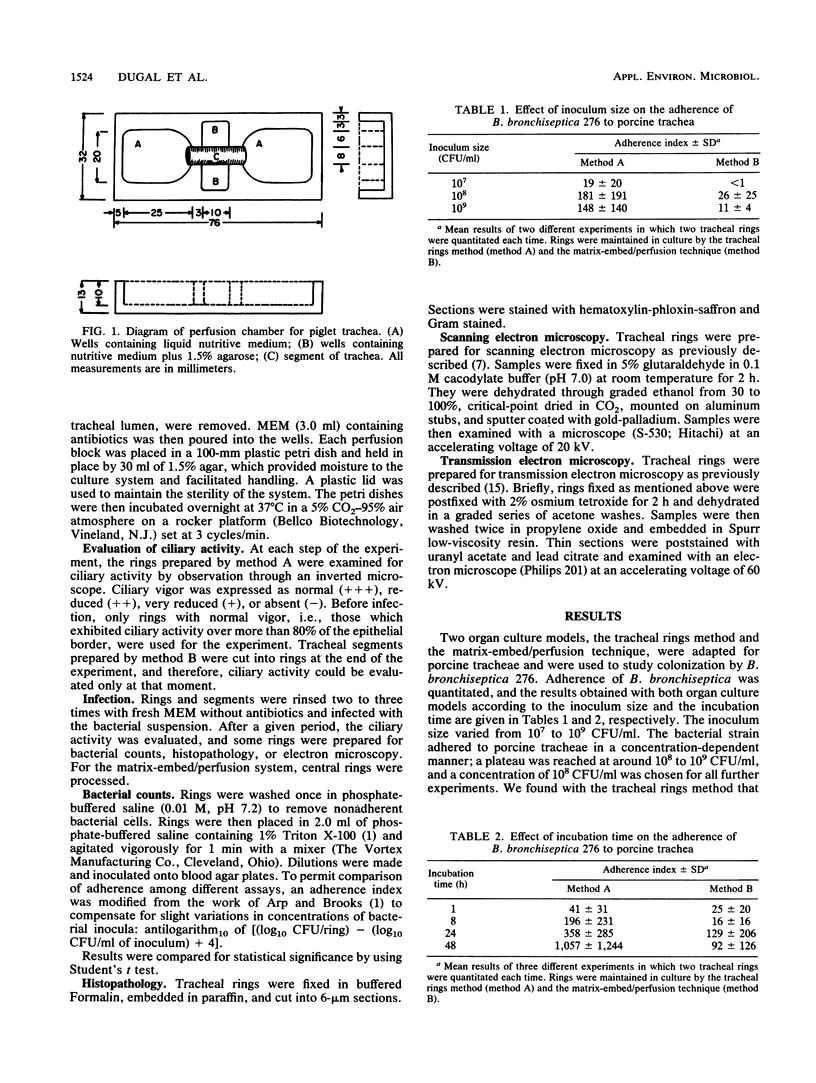
Abstract
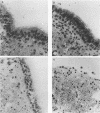
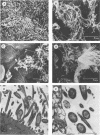
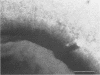
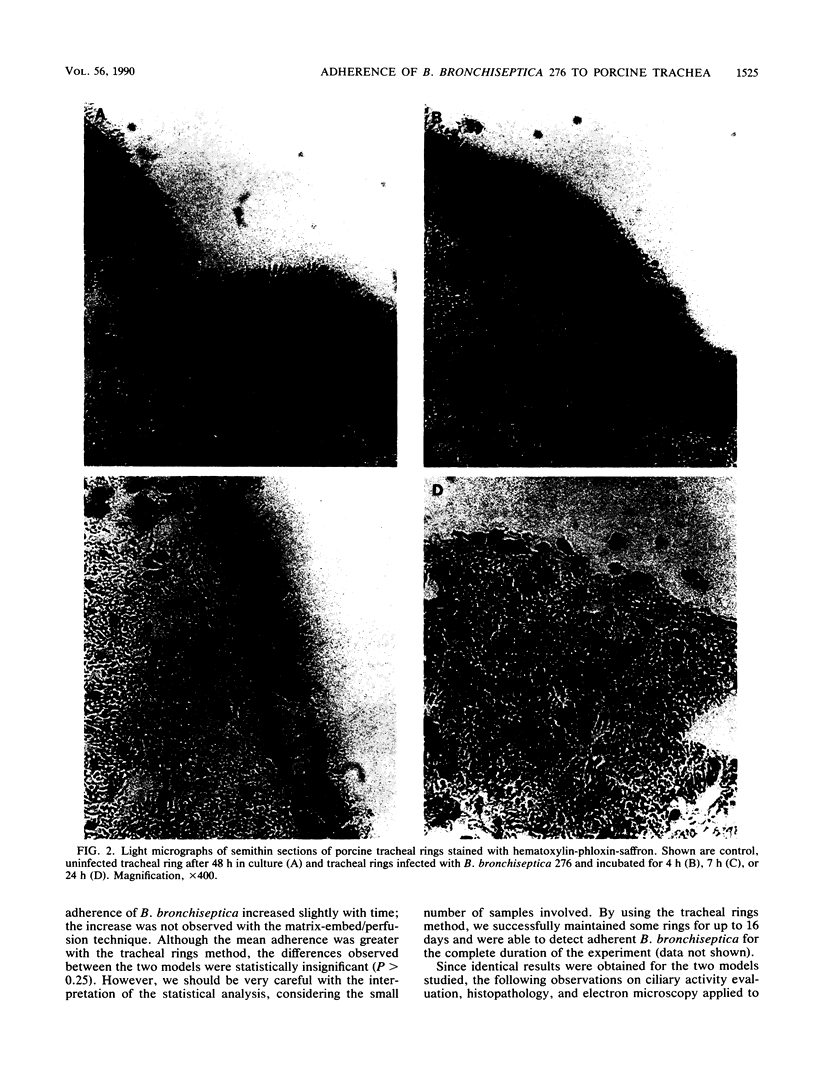
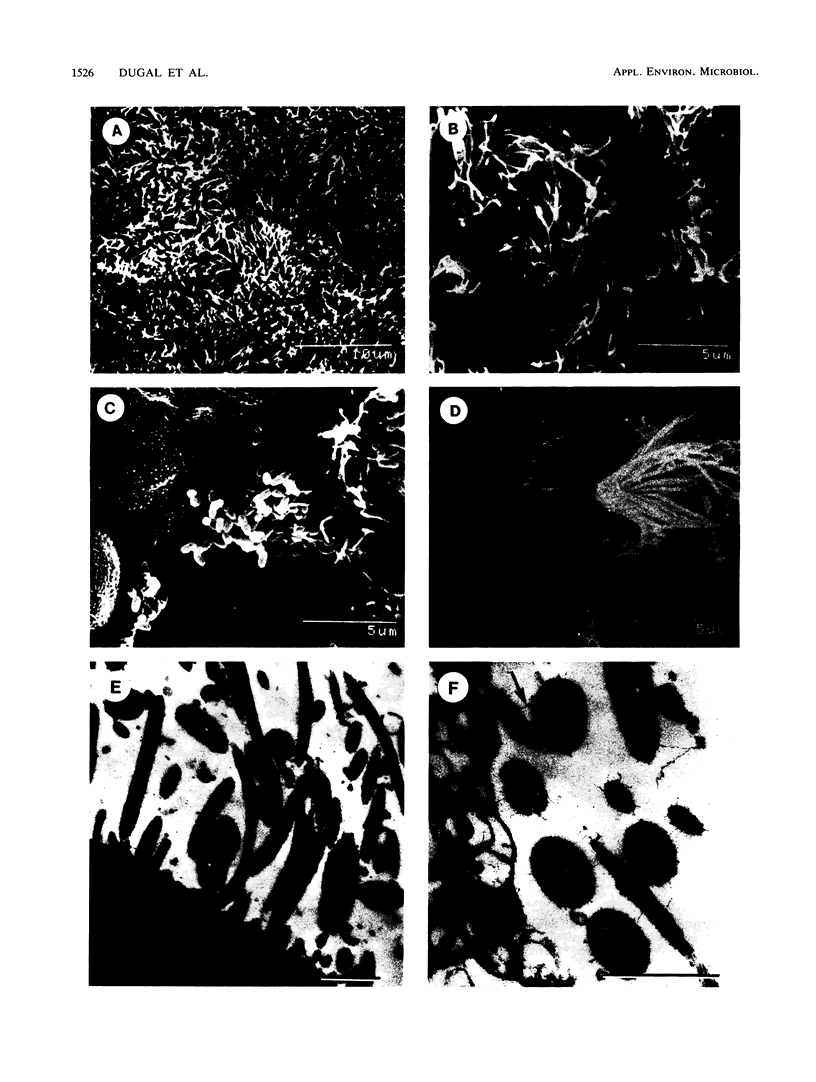
Two organ culture models have been adapted for porcine tracheae in order to study colonization by Bordetella bronchiseptica. Rings or segments excised from tracheae of newborn piglets were incubated overnight at 37 degrees C in a nutrient medium under 5% CO2-95% air conditions. Tracheal segments were infected with B bronchiseptica 276, and after different incubation times, bacterial counts were done. B. bronchiseptica adhered well to tracheae maintained in culture, and no statistically significant differences between the two models were observed. Noninfected tracheal mucosae maintained a normal appearance for several days, whereas infected mucosae showed typical damage caused by B. bronchiseptica, namely, loss of ciliary activity and cilia and sloughing of ciliated cells. Our data indicated that porcine tracheal organ culture could be advantageously used to study in vitro colonization by B. bronchiseptica.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arp L. H., Brooks E. E. An in vivo model for the study of Bordetella avium adherence to tracheal mucosa in turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Dec;47(12):2614–2617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakaletz L. O., Rheins M. S. A whole-organ perfusion model of Bordetella pertussis adherence to mouse tracheal epithelium. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1985 Jun;21(6):314–320. doi: 10.1007/BF02691578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bemis D. A., Kennedy J. R. An improved system for studying the effect of Bordetella bronchiseptica on the ciliary activity of canine tracheal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):349–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bemis D. A., Wilson S. A. Influence of potential virulence determinants on Bordetella bronchiseptica-induced ciliostasis. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.35-42.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broes A., Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Jacques M., Johnson W. M. Virulence properties of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O8: KX105 strains isolated from diarrheic piglets. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):241–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.241-246.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Peterson L. P., Baseman J. B. Pathogenesis of infection with Bordetella pertussis in hamster tracheal organ culture. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S196–S203. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabridge M. G., Hoglund L. E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection of intact guinea pig tracheas cultured in a unique matrix-embed/perfusion system. In Vitro. 1981 Oct;17(10):847–858. doi: 10.1007/BF02618279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow R. A. Biology of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):722–738. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.722-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Isayama Y. Bovine erythrocyte-agglutinin as a possible adhesin of Bordetella bronchiseptica responsible for binding to porcine nasal epithelium. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(3):205–209. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-3-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Isayama Y. Effect of antigenic modulation and phase variation on adherence of Bordetella bronchiseptica to porcine nasal epithelial cells. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Dec;48(12):1689–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Isayama Y. Evidence for sialyl glycoconjugates as receptors for Bordetella bronchiseptica on swine nasal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1607–1609. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1607-1609.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Foiry B. Electron microscopic visualization of capsular material of Pasteurella multocida types A and D labeled with polycationic ferritin. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3470–3472. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3470-3472.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Parent N., Foiry B. Adherence of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida to porcine nasal and tracheal epithelial cells. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):283–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Woods M. L., Jr Use of organ cultures in microbiological research. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:291–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Kume K., Yoshikawa H., Oyamada T., Yoshikawa T. Adherence of Pasteurella multocida or Bordetella bronchiseptica to the swine nasal epithelial cell in vitro. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.234-240.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin B. J., Bemis D. A. Adherence of Bordetella bronchiseptica to hamster lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):697–702. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.697-702.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Veit H. P., Sinsky R. J., Veit S. P., Hewlett E. L., Kornegay E. T. Virulence factors of Bordetella bronchiseptica associated with the production of infectious atrophic rhinitis and pneumonia in experimentally infected neonatal swine. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):217–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.217-222.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M. Atrophic rhinitis in swine. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1985;29:239–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Francis L. M., Sansom B. F. Virulence of Bordetella bronchiseptica from pigs with or without atrophic rhinitis. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):105–116. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya K., Futaesaku Y., Nakase Y. Electron microscopic observations on tracheal epithelia of mice infected with Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(5):461–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E. I., Nedelman J., Hendley J. O., Hewlett E. L. Species specificity of Bordetella adherence to human and animal ciliated respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):692–695. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.692-695.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo Y., Shimizu T. Adherence of Bordetella bronchiseptica to swine nasal epithelial cells and its possible role in virulence. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]