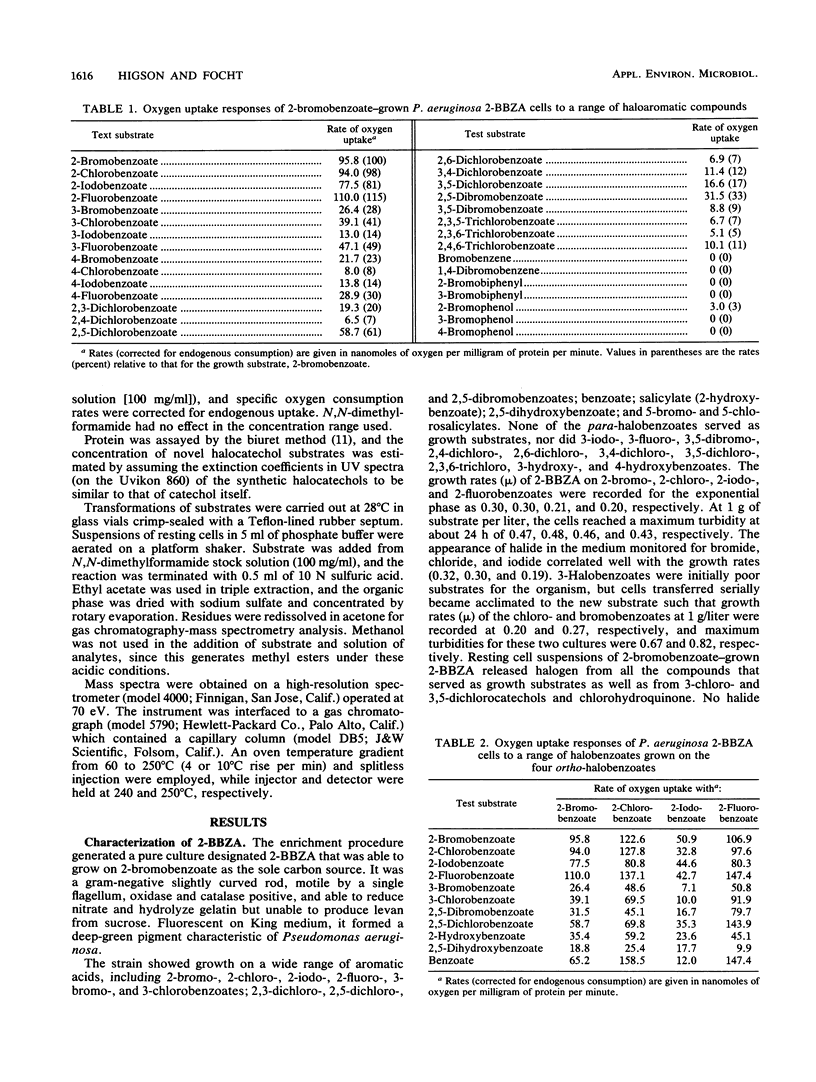
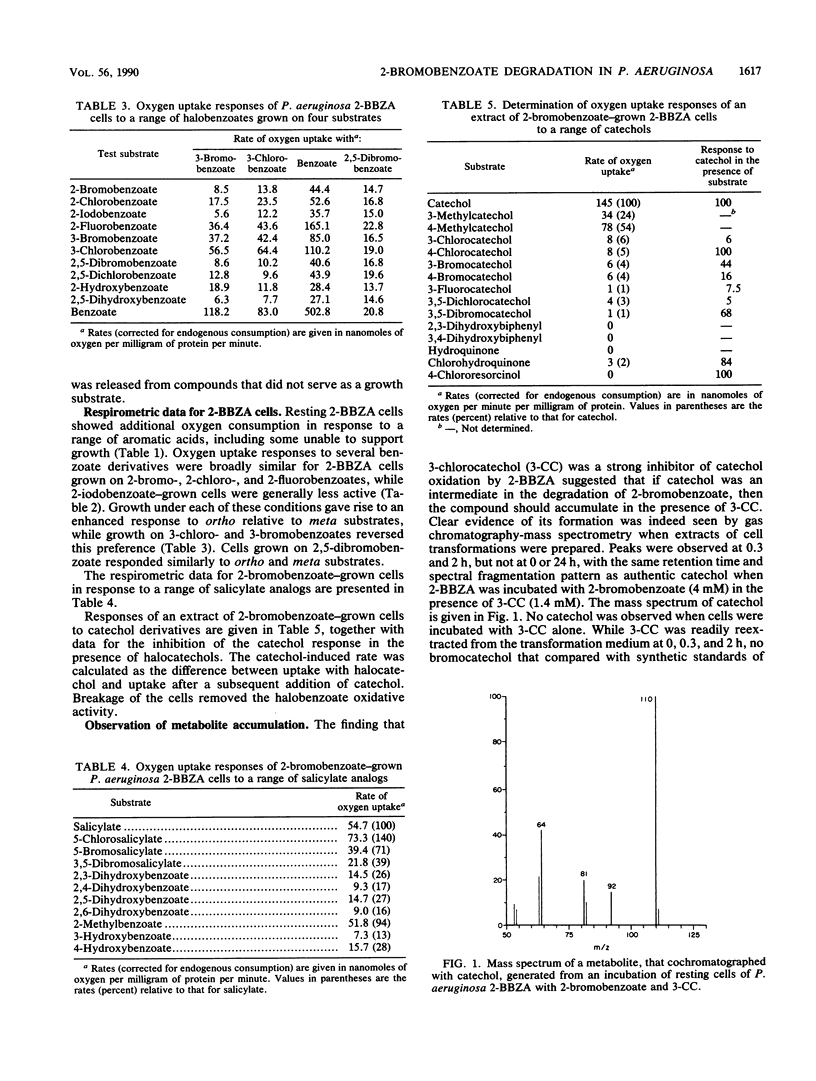
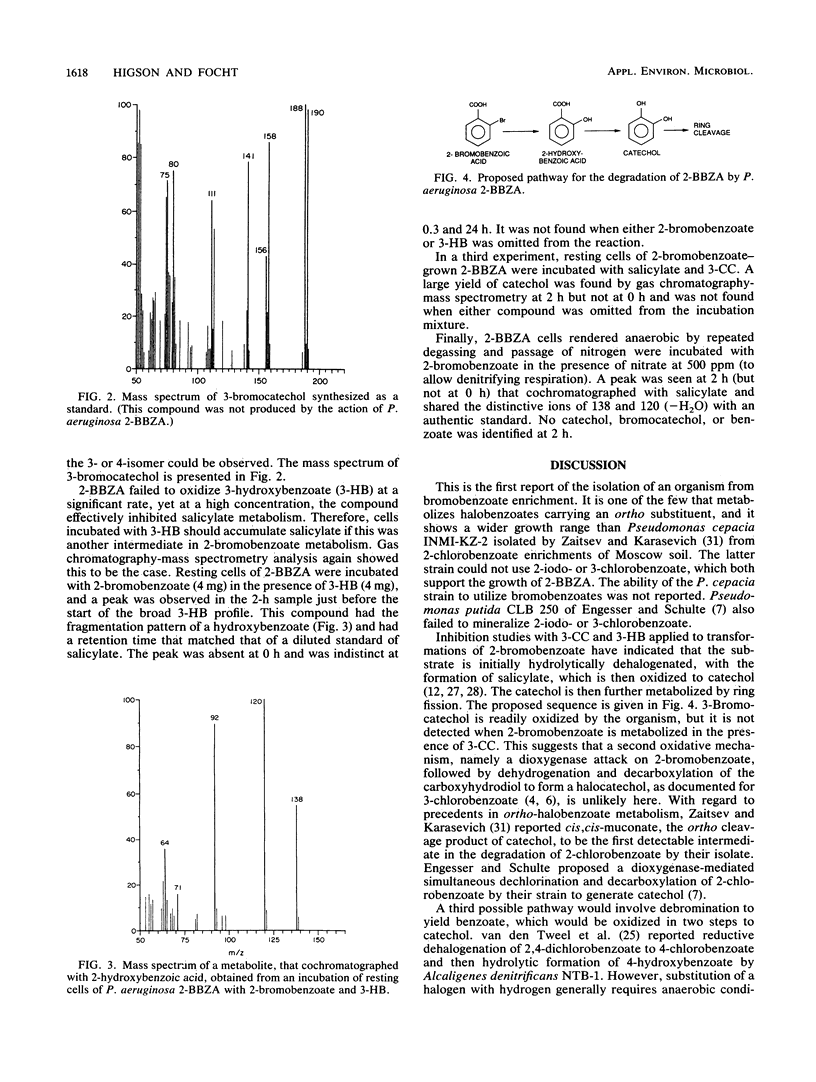
Abstract
A strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing 2-bromobenzoic acid, designated 2-BBZA, was isolated by enrichment culture from municipal sewage. It degraded all four 2-halobenzoates as well as certain 3-halo- and dihalobenzoates, though none of the 4-halobenzoates supported growth of this organism. 3-Hydroxybenzoate and 3-chlorocatechol were respective inhibitors of salicylate and catechol oxidation: when each was added separately to resting cells incubated with 2-bromobenzoate, salicylate and catechol were found. Oxygen uptake data suggest that the same dehalogenase may be involved in the oxidation of 2-bromo-, 2-chloro-, and 2-iodobenzoates.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando K., Kato A., Suzuki S. Isolation of 2.4-dichlorophenol from a soil fungus and its biological significance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1104–1107. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90672-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Kellogg S. T., Hamada S., Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmid specifying total degradation of 3-chlorobenzoate by a modified ortho pathway. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.639-646.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Weightman A. J., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Transposon mutagenesis and cloning analysis of the pathways for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 3-chlorobenzoate in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134(pJP4). J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.85-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Hellwig M., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00696222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3-chlorobenzoate-grown pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):73–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1740073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesser K. H., Schulte P. Degradation of 2-bromo-, 2-chloro- and 2-fluorobenzoate by Pseudomonas putida CLB 250. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. Aerobic cometabolism of DDT analogues by Hydrogenomonas sp. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):20–22. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tonomura K., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the biodegradability of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):223–227. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.223-227.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah R. Y., Tu S. C. Determination of the position of monooxygenation in the formation of catechol catalyzed by salicylate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6392–6394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higson F. K., Focht D. D. Bacterial metabolism of hydroxylated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):946–952. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.946-952.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D. Human health effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs). Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröckel L., Focht D. D. Construction of chlorobenzene-utilizing recombinants by progenitive manifestation of a rare event. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2470-2475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruisinger S., Klages U., Lingens F. Abbau der 4-chlorbenzoesäure durch eine Arthrobacter-Species. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00690235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siuda J. F., DeBernardis J. F. Naturally occurring halogenated organic compounds. Lloydia. 1973 Jun;36(2):107–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvestre M., Mailhiot K., Ahmad D., Massé R. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a 2-chlorobenzoate degrading Pseudomonas. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Apr;35(4):439–443. doi: 10.1139/m89-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe I., Kashimoto T., Tatsukawa R. Brominated phenols and anisoles in river and marine sediments in Japan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1985 Aug;35(2):272–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01636509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White-Stevens R. H., Kamin H., Gibson Q. H. Studies of a flavoprotein, salicylate hydroxylse. I. Enzyme mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2371–2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White-Stevens R. H., Kamin H. Studies of a flavoprotein, salicylate hydroxylase. I. Preparation, properties, and the uncoupling of oxygen reduction from hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2358–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Ribbons D. W. p-Cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: selective enrichment of defective mutants by using halogenated substrate analogs. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):816–824. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.816-824.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev G. M., Karasevich Iu N. Utilizatsiia 4-khlorbenzoinoi kisloty Arthrobacter globiformis. Mikrobiologiia. 1981 Jan-Feb;50(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Tweel W. J., Kok J. B., de Bont J. A. Reductive dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorobenzoate to 4-chlorobenzoate and hydrolytic dehalogenation of 4-chloro-, 4-bromo-, and 4-iodobenzoate by Alcaligenes denitrificans NTB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):810–815. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.810-815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


