Abstract
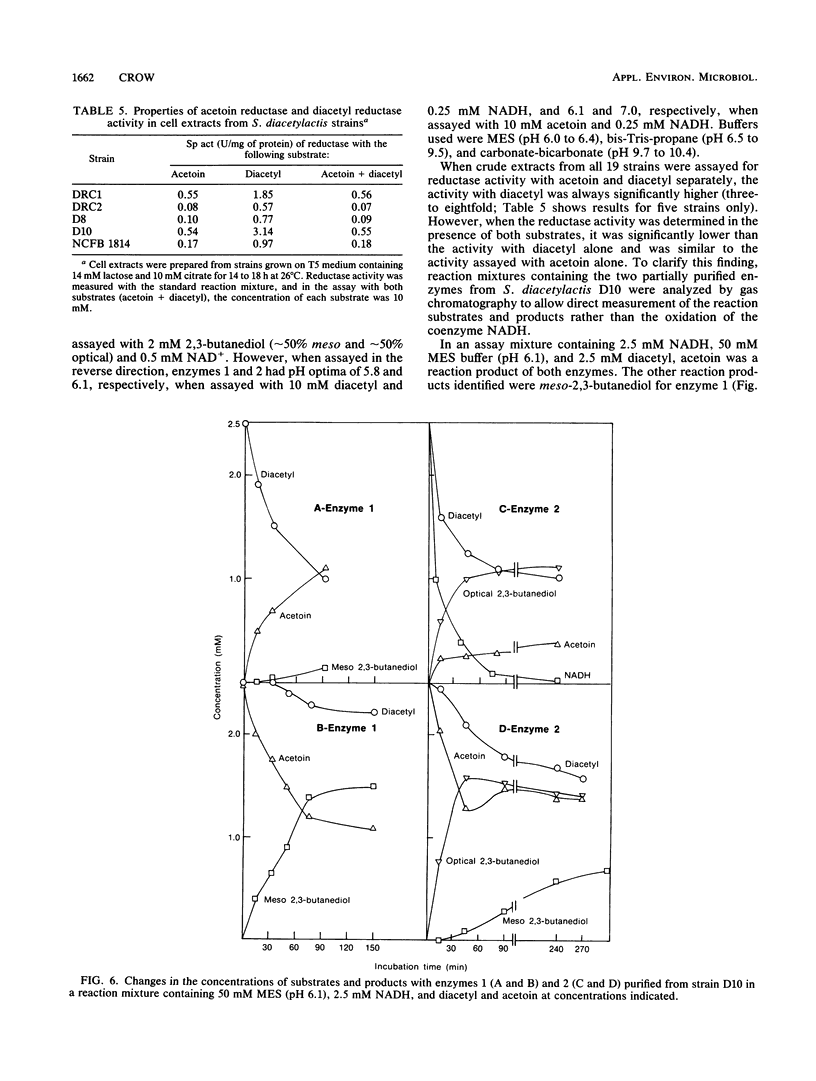
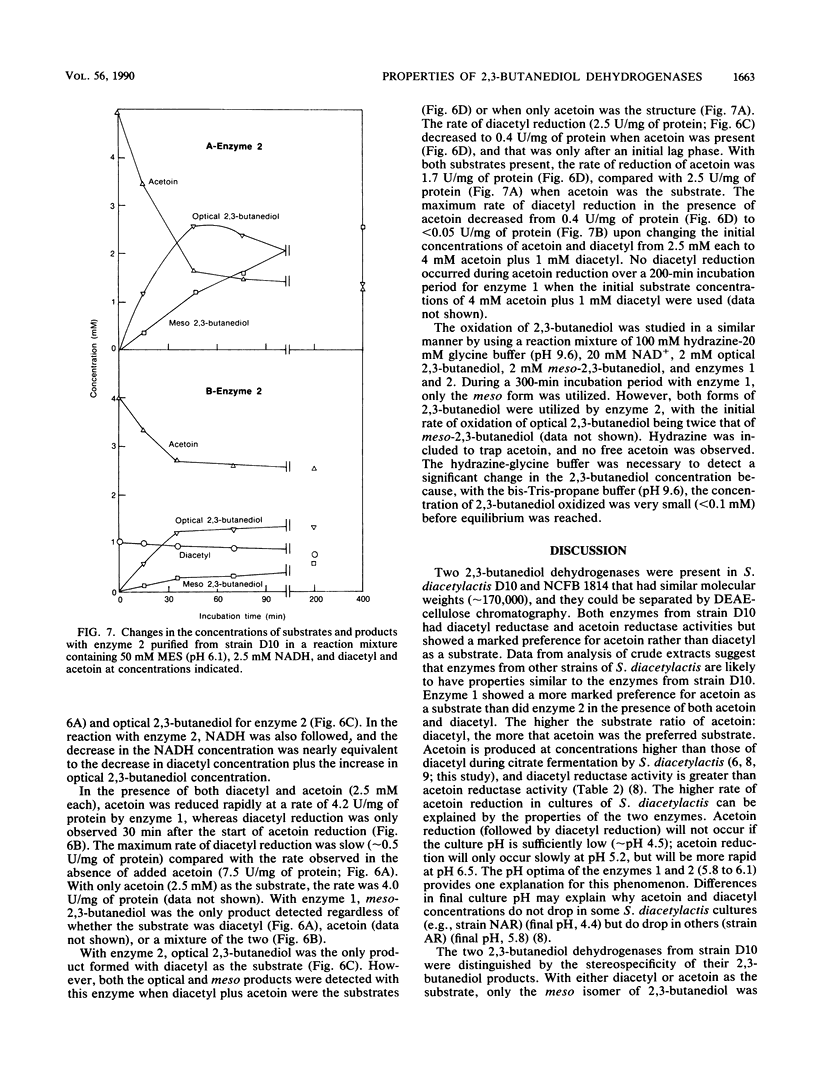
Two 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenases (enzymes 1 and 2; molecular weight of each, 170,000) have been partially purified from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (Streptococcus diacetylactis) D10 and shown to have reductase activity with either diacetyl or acetoin as the substrate. However, the reductase activity with 10 mM diacetyl was far greater for both enzymes (7.0- and 4.7-fold for enzymes 1 and 2, respectively) than with 10 mM acetoin as the substrate. In contrast, when acetoin and diacetyl were present together, acetoin was the preferred substrate for both enzymes, with enzyme 1 showing the more marked preference for acetoin. meso-2,3-Butanediol was the only isomeric product, with enzyme 1 independent of the substrate combinations. For enzyme 2, both the meso and optical isomers of 2,3-butanediol were formed with acetoin as the substrate, but only the optical isomers were produced with diacetyl as the substrate. With batch cultures of strain D10 at or near the point of citrate exhaustion, the main isomers of 2,3-butanediol present were the optical forms. If the pH was sufficiently high (>pH 5), acetoin reduction occurred over time and was followed by diacetyl reduction, and meso-2,3-butanediol became the predominant isomer. Interconversion of the optical isomers into the meso isomer did occur. The properties of 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenases are consistent with diacetyl and acetoin removal and the appearance of the isomers of 2,3-butanediol.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branen A. L., Keenan T. W. Diacetyl reductase of Lactobacillus casei. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Oct;16(10):947–951. doi: 10.1139/m70-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryn K., Hetland O., Stormer F. C. The reduction of diacetyl and acetoin in Aerobacter aerogenes. Evidence for one enzyme catalyzing both reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan 1;18(1):116–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan T. M. Citrate utilization in milk by Leuconostoc cremoris and Streptococcus diacetilactis. J Dairy Res. 1975 Feb;42(1):139–146. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900015168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins E. B., Bruhn J. C. Roles of acetate and pyruvate in the metabolism of Streptococcus diacetilactis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):541–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.541-546.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins E. B., Speckman R. A. Evidence for cellular control in the synthesis of acetoin or alpha-ketoisovaleric acid by microorganisms. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Jun;20(6):805–811. doi: 10.1139/m74-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordyce A. M., Crow V. L., Thomas T. D. Regulation of product formation during glucose or lactose limitation in nongrowing cells of Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):332–337. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.332-337.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. J., COLLINS E. B. Role of citritase in acetoin formation by Streptococcus diacetilactis and Leuconostoc citrovorum. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:954–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.954-959.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Seiriki K., Nakayama T., Sawada H. Discrimination of multiforms of diacetyl reductase in hamster liver. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;174:291–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetland O., Bryn K., Stormer F. C. Diacetyl (Acetoin) reductase from Aerobacter aerogenes. Evidence for multiple forms of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 28;20(2):206–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempler G. M., McKay L. L. Characterization of Plasmid Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis: Evidence for Plasmid-Linked Citrate Utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):316–323. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.316-323.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempler G. M., McKay L. L. Genetic Evidence for Plasmid-Linked Lactose Metabolism in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):1041–1043. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.1041-1043.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Stormer F. C. Diacetyl (acetoin) reductase from Aerobacter aerogenes. Kinetic mechanism and regulation by acetate of the reversible reduction of acetoin to 2,3-butanediol. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):100–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speckman R. A., Collins E. B. Diacetyl biosynthesis in Streptococcus diacetilactis and Leuconostoc citrovorum. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.174-180.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR M. B., JUNI E. Stereoisomeric specificities of 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:448–457. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D., Jarvis B. D., Skipper N. A. Localization of proteinase(s) near the cell surface of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):329–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.329-333.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



