Abstract
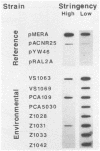
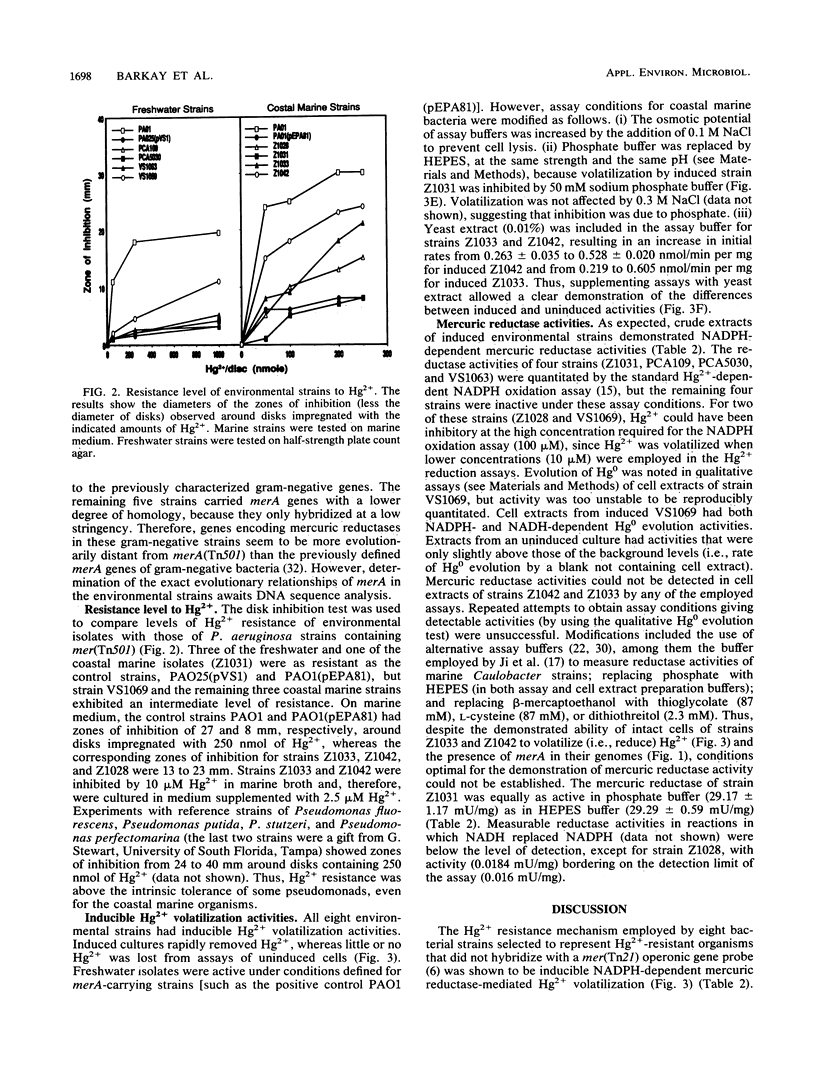
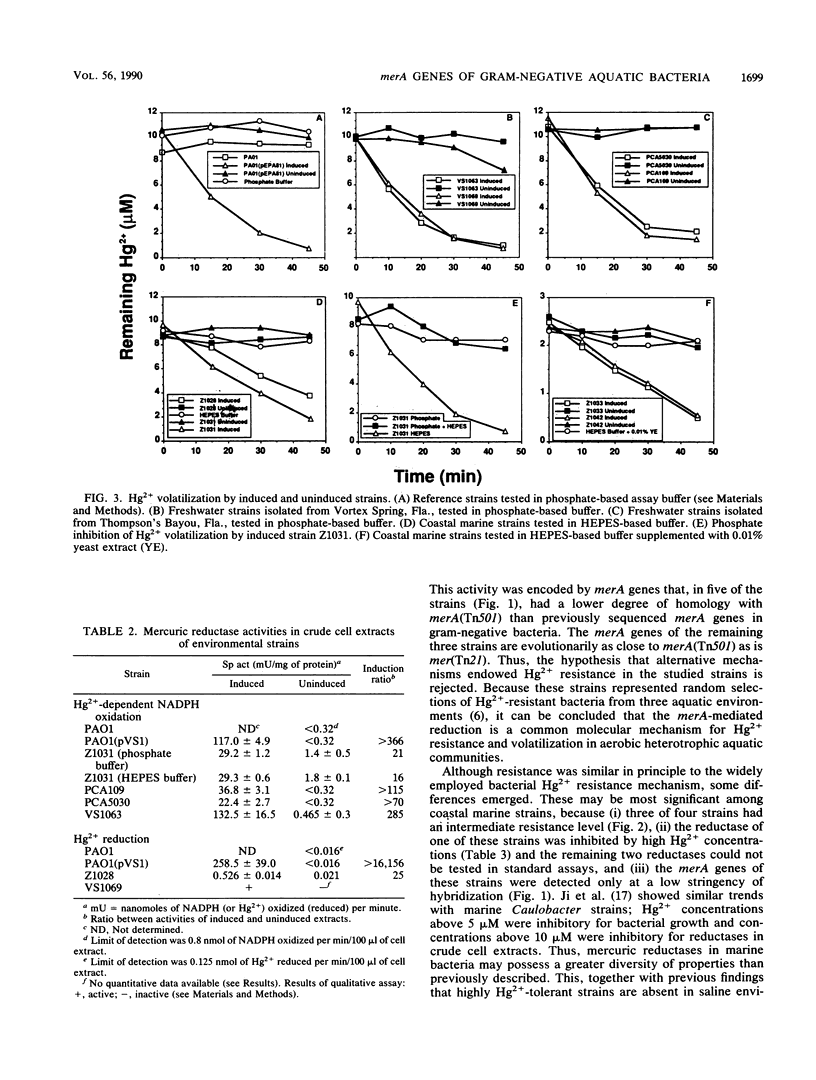
An investigation of the Hg2+ resistance mechanism of four freshwater and four coastal marine bacteria that did not hybridize with a mer operonic probe was conducted (T. Barkay, C. Liebert, and M. Gillman, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55:1196-1202, 1989). Hybridization with a merA probe, the gene encoding the mercuric reductase polypeptide, at a stringency of hybridization permitting hybrid formation between evolutionarily distant merA genes (as exists between gram-positive and -negative bacteria), detected merA sequences in the genomes of all tested strains. Inducible Hg2+ volatilization was demonstrated for all eight organisms, and NADPH-dependent mercuric reductase activities were detected in crude cell extracts of six of the strains. Because these strains represented random selections of bacteria from three aquatic environments, it is concluded that merA encodes a common molecular mechanism for Hg2+ resistance and volatilization in aerobic heterotrophic aquatic communities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts J. J., Schindler J. E., Miller R. W., Nutter D. E., Jr Elemental mercury evolution mediated by humic Acid. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):895–897. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T. Adaptation of aquatic microbial communities to hg stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2725–2732. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2725-2732.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Fouts D. L., Olson B. H. Preparation of a DNA gene probe for detection of mercury resistance genes in gram-negative bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):686–692. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.686-692.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Liebert C., Gillman M. Environmental significance of the potential for mer(Tn21)-mediated reduction of Hg2+ to Hg0 in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1196–1202. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1196-1202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Liebert C., Gillman M. Hybridization of DNA probes with whole-community genome for detection of genes that encode microbial responses to pollutants: mer genes and Hg2+ resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1574–1577. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1574-1577.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrineau P., Gilbert P., Jackson W. J., Jones C. S., Summers A. O., Wisdom S. The DNA sequence of the mercury resistance operon of the IncFII plasmid NR1. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):601–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz G. A., Jacobs K. A., Eickbush T. H., Cherbas P. T., Kafatos F. C. Isolation of multigene families and determination of homologies by filter hybridization methods. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:266–285. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienvenue E., Boudou A., Desmazes J. P., Gavach C., Georgescauld D., Sandeaux J., Seta P. Transport of mercury compounds across bimolecular lipid membranes: effect of lipid composition, pH and chloride concentration. Chem Biol Interact. 1984 Jan;48(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(84)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Ford S. J., Pridmore R. D., Fritzinger D. C. Nucleotide sequence of a gene from the Pseudomonas transposon Tn501 encoding mercuric reductase. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4089–4095. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcott P. H. Transient loss of plasmid-mediated mercuric ion resistance after stress in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1348–1354. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1348-1354.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald W. F., Gill G. A., Kim J. P. An equatorial pacific ocean source of atmospheric mercury. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):597–599. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4649.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B., Walsh C. T. Mercuric reductase. Purification and characterization of a transposon-encoded flavoprotein containing an oxidation-reduction-active disulfide. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2498–2503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji G. Y., Salzberg S. P., Silver S. Cell-free mercury volatilization activity from three marine caulobacter strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):523–525. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.523-525.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. P., Fitzgerald W. F. Sea-air partitioning of mercury in the equatorial pacific ocean. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1131–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4742.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laddaga R. A., Chu L., Misra T. K., Silver S. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the mercurial-resistance operon from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5106–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara H., Schottel J. L., Yamada T., Miyakawa Y., Asakawa M., Harville J., Silver S. Mercuric reductase enzymes from Streptomyces species and group B Streptococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1053–1059. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Nakahara H. Simplified X-ray film method for detection of bacterial volatilization of mercury chloride by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2871–2873. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2871-2873.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni'Bhriain N. N., Silver S., Foster T. J. Tn5 insertion mutations in the mercuric ion resistance genes derived from plasmid R100. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):690–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.690-703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan-Hou H. S., Imura N. Involvement of mercury methylation in microbial mercury detoxication. Arch Microbiol. 1982 Mar;131(2):176–177. doi: 10.1007/BF01054003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan-Hou H. S., Imura N. Role of hydrogen sulfide in mercury resistance determined by plasmid of Clostridium cochlearium T-2. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Mar;129(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00417179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan-Hou H. S., Nishimoto M., Imura N. Possible role of membrane proteins in mercury resistance of Enterobacter aerogenes. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Oct;130(2):93–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00411057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schottel J. L. The mercuric and organomercurial detoxifying enzymes from a plasmid-bearing strain of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4341–4349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori T., Inoue C., Sugawara K., Kusano T., Kitagawa Y. Cloning and expression of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans mercury ion resistance genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3458–3464. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3458-3464.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Misra T. K. Plasmid-mediated heavy metal resistances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:717–743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A. Interaction between an R factor and an element conferring resistance to mercuric ions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Feb 6;128(3):201–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00267109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Nelson J. D., Jr, Wan L. W., Colwell R. R. Effects of mercuric chloride on growth and morphology of selected strains of mercury-resistant bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):275–286. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.275-286.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Mahler I., Levinson H. S., Halvorson H. O. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of chromosomal mercury resistance genes from a Bacillus sp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4848–4851. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4848-4851.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Moore M., Levinson H. S., Silver S., Walsh C., Mahler I. Nucleotide sequence of a chromosomal mercury resistance determinant from a Bacillus sp. with broad-spectrum mercury resistance. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):83–92. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.83-92.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Murphy S. D., Silver S. Mercury and organomercurial resistances determined by plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):197–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.197-208.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte W., Green L., Misra T. K., Silver S. Resistance to mercury and to cadmium in chromosomally resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):663–669. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]