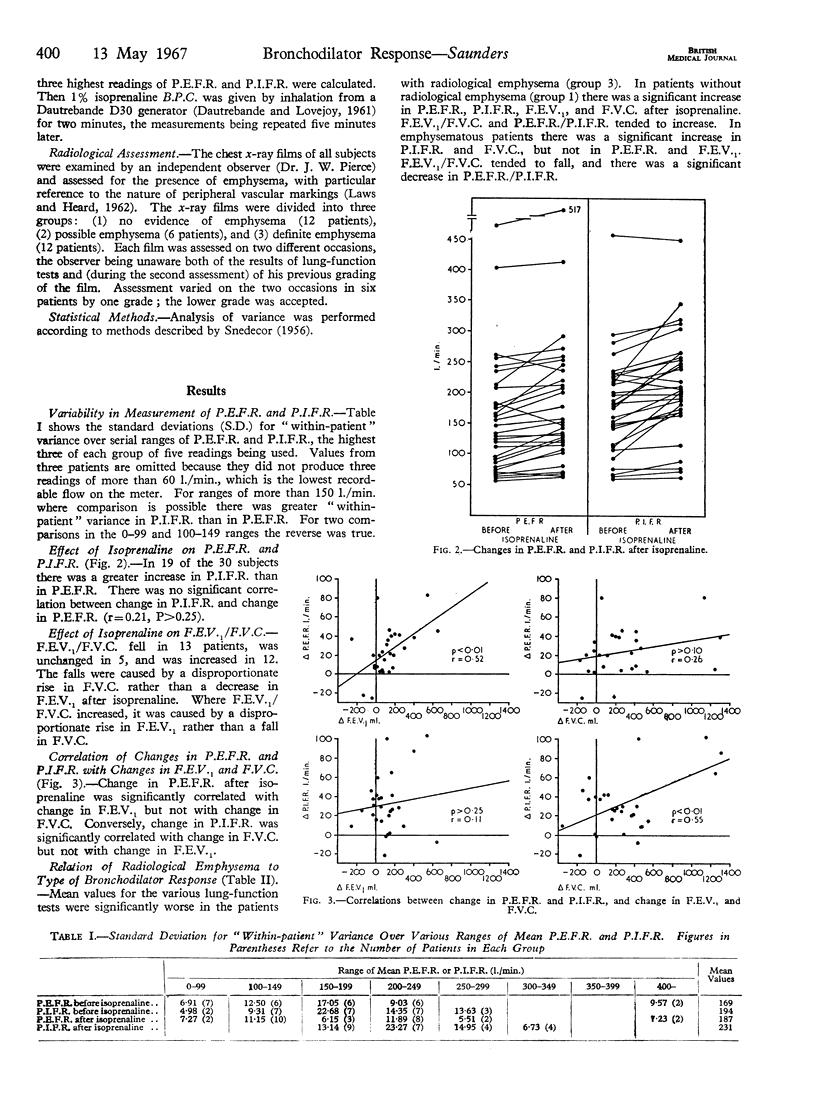
Full text
PDF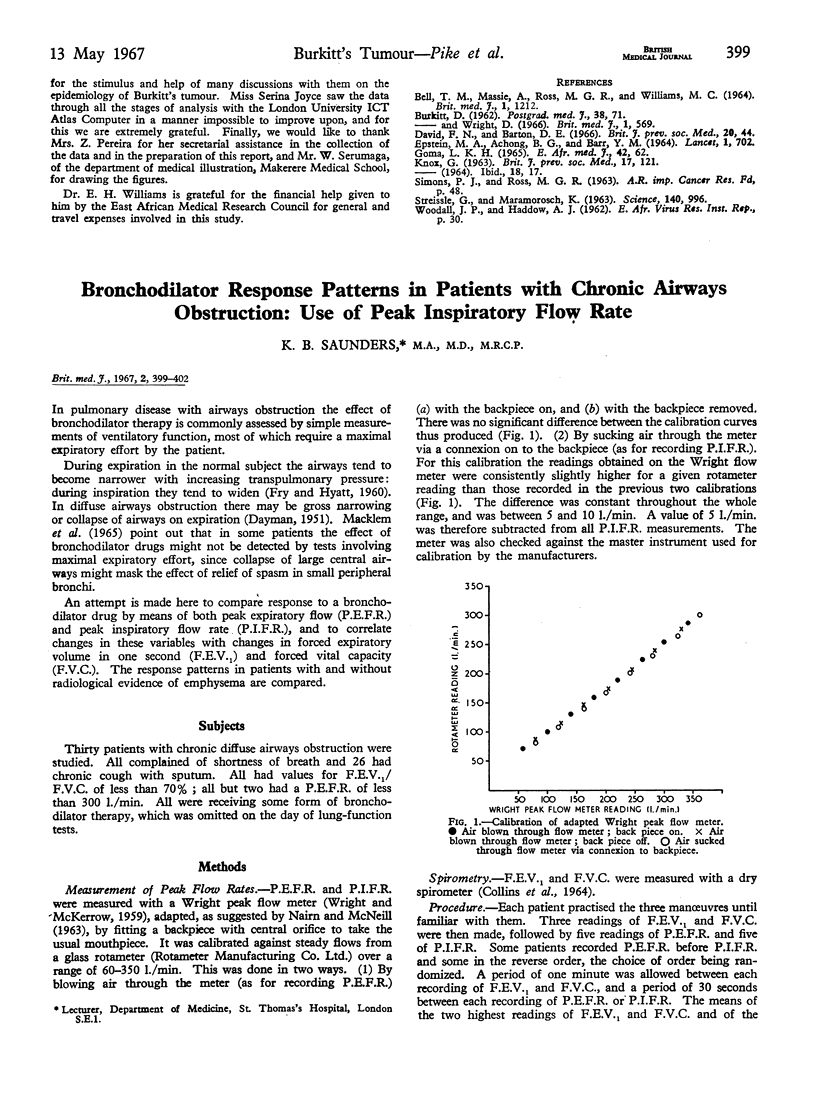


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burrows B., Fletcher C. M., Heard B. E., Jones N. L., Wootliff J. S. The emphysematous and bronchial types of chronic airways obstruction. A clinicopathological study of patients in London and Chicago. Lancet. 1966 Apr 16;1(7442):830–835. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J., MARTIN H. B., RILEY R. L. Mechanisms of airway obstruction. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Dec;101(6):329–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUTREBANDE L., LOVEJOY F. W., Jr New studies on aerosols. XII. A study of the number of breaths of sympathomimetic microaerosols necessary to obtain a maximal response in airway resistance. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1961 Apr 1;131:230–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAYMAN H. Mechanics of airflow in health and in emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1951 Nov;30(11):1175–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI102537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEKKER E., GROEN J. Asthmatic wheezing; compression of the trachea and major bronchi as a cause. Lancet. 1957 May 25;272(6978):1064–1068. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHANA L. M., ARONOVITCH M., PLACE R. A comparative study of the clinical and functional pattern in emphysematous patients with and without chronic respiratory failure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1963 May;87:699–716. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1963.87.5.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKLEM P. T., FRASER R. G., BROWN W. G. BRONCHIAL PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS IN EMPHYSEMA AND BRONCHITIS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jun;44:897–905. doi: 10.1172/JCI105206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIRN J. R., McNEILL R. S. Adaptation of the Wright peak flow meter to measure inspiratory flow. Br Med J. 1963 May 18;1(5341):1321–1323. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5341.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT B. M., McKERROW C. B. Maximum forced expiratory flow rate as a measure of ventilatory capacity: with a description of a new portable instrument for measuring it. Br Med J. 1959 Nov 21;2(5159):1041–1046. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5159.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


