Abstract
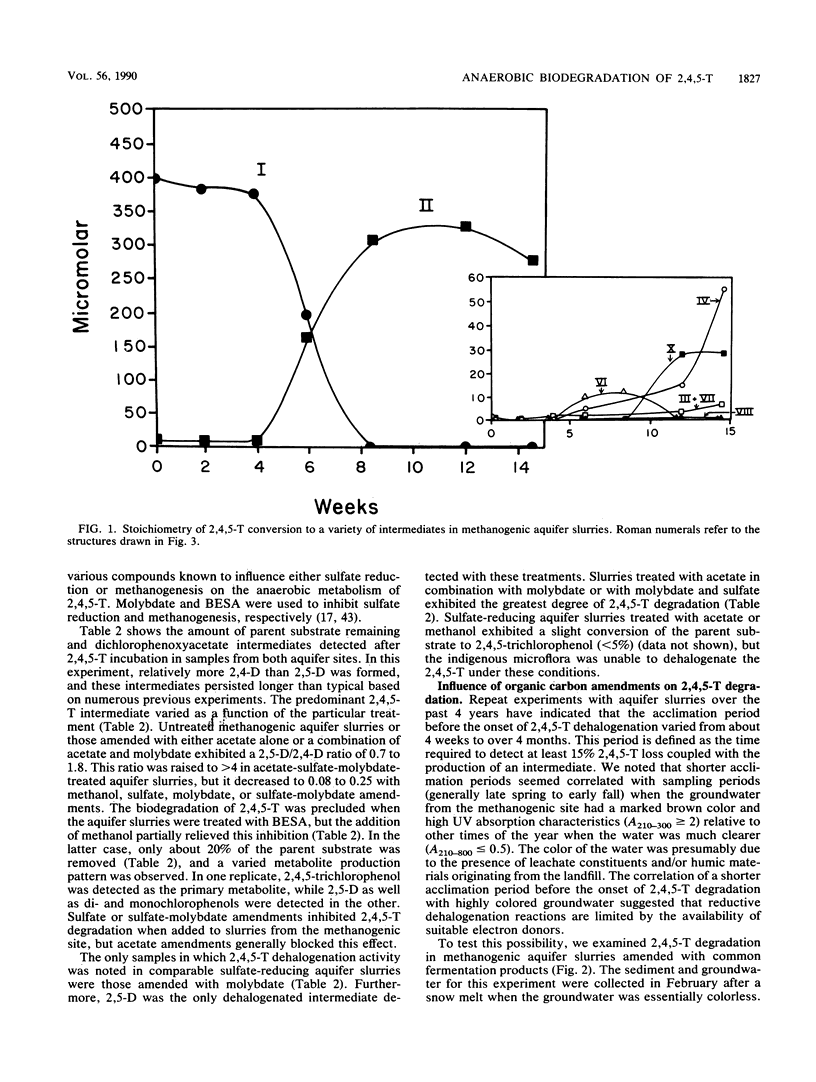
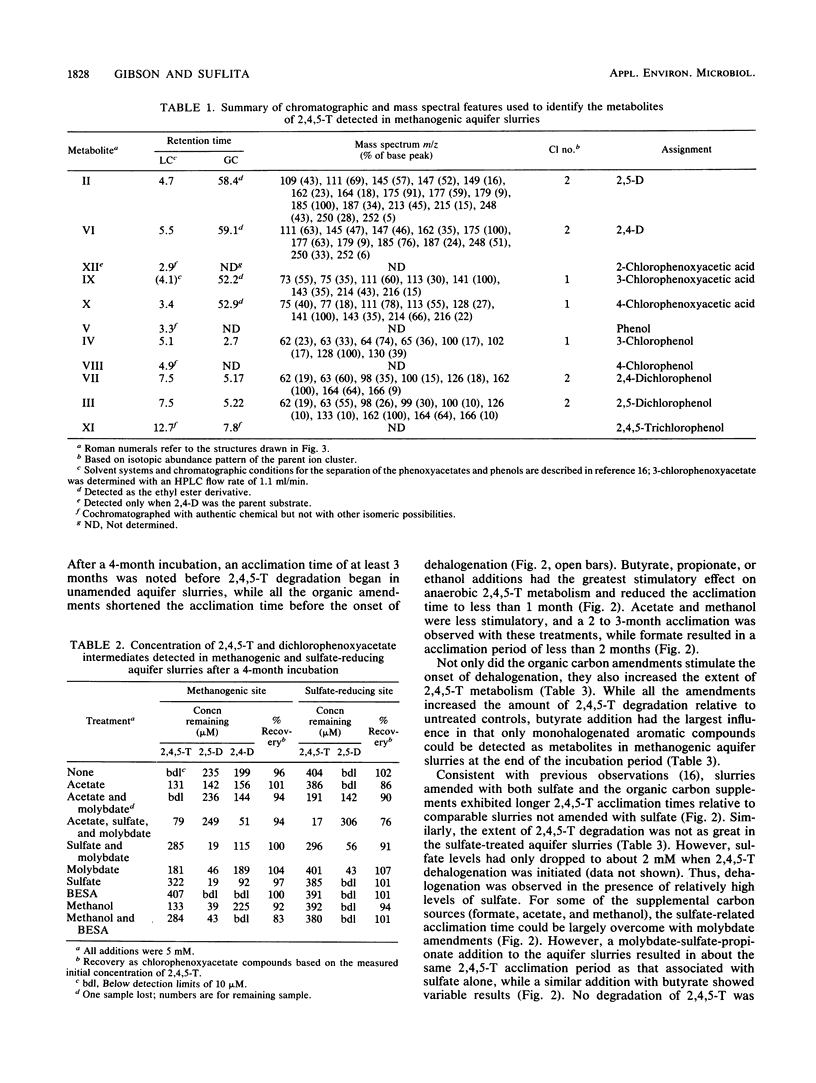
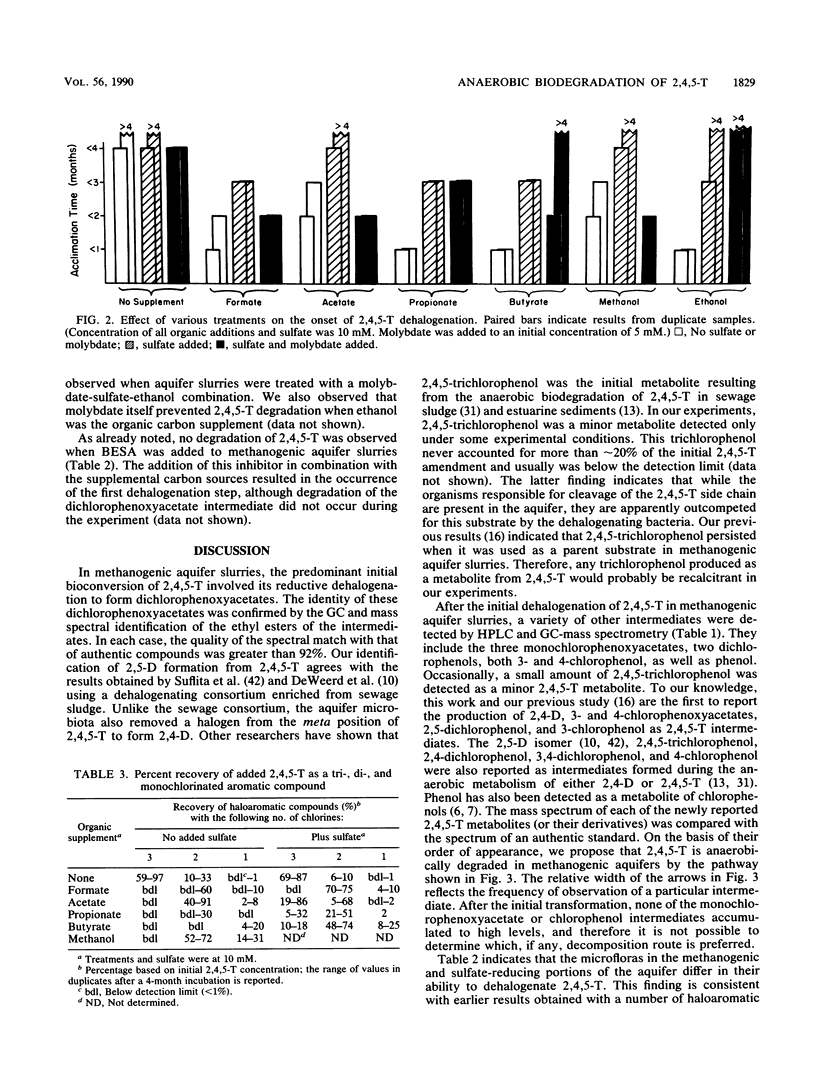
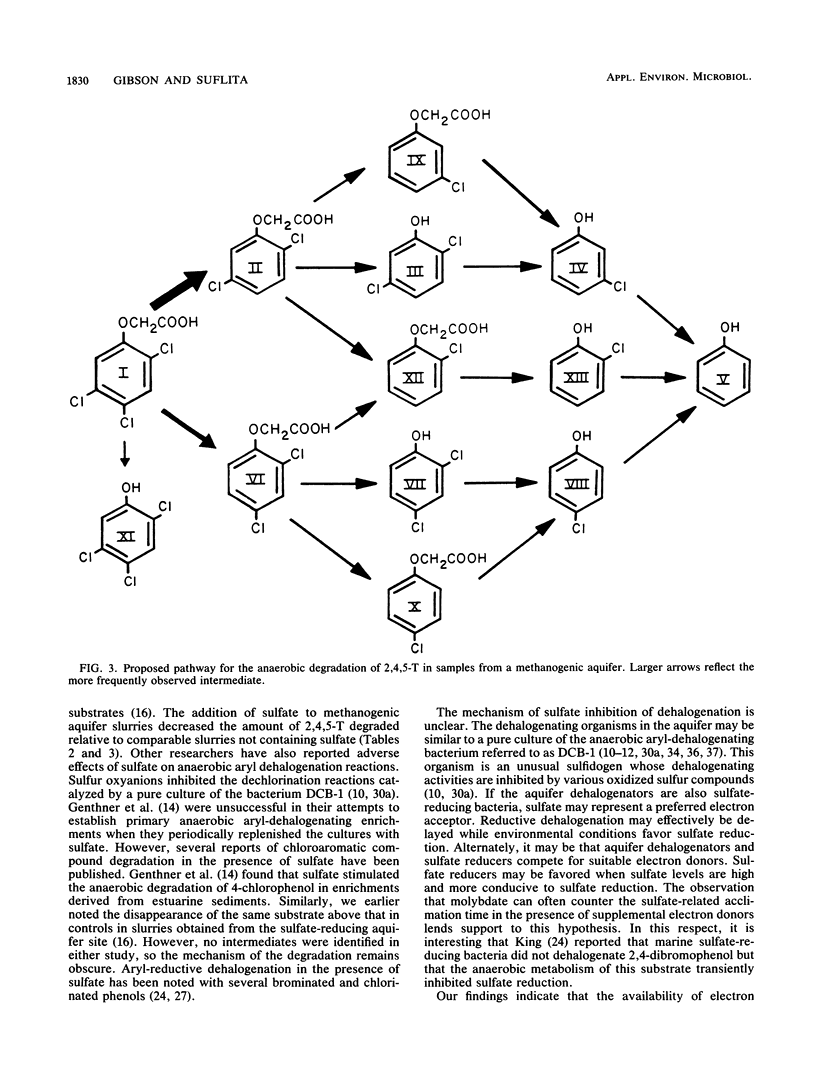
The herbicide 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) was dehalogenated in samples from a methanogenic aquifer to form 2,4- and 2,5-dichlorophenoxyacetic acids as the first detected intermediates. Further incubation of the aquifer slurries resulted in the formation of several intermediates including monochlorophenoxyacetic acids, di- and monochlorophenols, as well as phenol. No transformation of the parent substrate or production of intermediates was detected in autoclaved controls. The pattern of intermediate formation suggested that the anaerobic degradation of 2,4,5-T proceeded by a series of sequential dehalogenation steps with side-chain cleavage reactions occurring at some point before ring cleavage. The addition of short-chain organic acids or alcohols stimulated the onset and rate of 2,4,5-T dehalogenation and decreased the amount of parent substrate still detectable as halogenated intermediates at the end of the experiment. Sulfate addition had the opposite effect on dehalogenation regardless of whether supplemental carbon was added to the aquifer slurries. The inhibitory effect of sulfate on dehalogenation could sometimes be relieved with molybdate, although this effect seemed to be related to the supplemental carbon compound that was used.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attaway H. H., 3rd, Paynter M. J., Camper N. D. Degradation of selected phenylurea herbicides by anaerobic pond sediment. J Environ Sci Health B. 1982;17(6):683–699. doi: 10.1080/03601238209372350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belay N., Daniels L. Production of ethane, ethylene, and acetylene from halogenated hydrocarbons by methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1604–1610. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1604-1610.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R., Berry D., Tiedje J. M. Anaerobic biodegradation of phenolic compounds in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.50-54.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. F., Jr, Bedard D. L., Brennan M. J., Carnahan J. C., Feng H., Wagner R. E. Polychlorinated biphenyl dechlorination in aquatic sediments. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.236.4802.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Tiedje J. M. Growth yield increase linked to reductive dechlorination in a defined 3-chlorobenzoate degrading methanogenic coculture. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00425073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathepure B. Z., Tiedje J. M., Boyd S. A. Reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene to tri- and dichlorobenzenes in anaerobic sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):327–330. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.327-330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Anaerobic Degradation of Chloroaromatic Compounds in Aquatic Sediments under a Variety of Enrichment Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1466–1471. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1466-1471.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Characterization of anaerobic dechlorinating consortia derived from aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1472-1476.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Extrapolation of biodegradation results to groundwater aquifers: reductive dehalogenation of aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):681–688. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.681-688.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A., Suflita J. M., Tiedje J. M. Reductive dehalogenations of halobenzoates by anaerobic lake sediment microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1459-1465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M. Dehalogenation in marine sediments containing natural sources of halophenols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3079–3085. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3079-3085.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohring G. W., Rogers J. E., Wiegel J. Anaerobic biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater lake sediments at different temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):348–353. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.348-353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohring G. W., Zhang X. M., Wiegel J. Anaerobic dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments in the presence of sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2735–2737. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2735-2737.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. P., Zeyer J., Eicher P., Schwarzenbach R. P. Anaerobic degradation of alkylated benzenes in denitrifying laboratory aquifer columns. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.490-496.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkfield T. G., Tiedje J. M. Characterization of the requirements and substrates for reductive dehalogenation by strain DCB-1. J Ind Microbiol. 1990 Jan;5(1):9–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01569601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quensen J. F., 3rd, Tiedje J. M., Boyd S. A. Reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls by anaerobic microorganisms from sediments. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):752–754. doi: 10.1126/science.242.4879.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteria in an anaerobic consortium that mineralizes 3-chlorobenzoic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):840–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.840-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. O., Linkfield T. G., Tiedje J. M. Physiological characterization of strain DCB-1, a unique dehalogenating sulfidogenic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2938–2943. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2938-2943.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. O., Tiedje J. M. Carbon dioxide fixation and mixotrophic metabolism by strain DCB-1, a dehalogenating anaerobic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2944–2948. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2944-2948.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struijs J., Rogers J. E. Reductive dehalogenation of dichloroanilines by anaerobic microorganisms in fresh and dichlorophenol-acclimated pond sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2527–2531. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2527-2531.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Robinson J. A., Tiedje J. M. Kinetics of microbial dehalogenation of haloaromatic substrates in methanogenic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1466–1473. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1466-1473.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


