Abstract
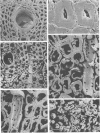
Isolates of six species of Ganoderma in the G. lucidum complex were evaluated for their ability to decay wood of Quercus hypoleucoides A. Camus and Abies concolor (Gord. and Glend.) Lindl. ex. Hildebr. by using in vitro agar block decay tests. Morphological, ultrastructural, and chemical studies of decayed wood were used to determine the extent of delignification or simultaneous decay caused by each species of Ganoderma. All species decayed both white fir and oak wood; however, less percent weight loss (%WL) occurred in white fir than oak. In white fir, isolates of two undescribed Ganoderma species (RLG16161, RLG16162, JEA615, and JEA625) caused significantly higher%WL (21 to 26%) than that in G. colossum, G. oregonense, G. meredithiae, and G. zonatum (10 to 16%). Only Ganoderma sp. isolates JEA615 and JEA625 caused delignification, with JEA615 causing a lignin-to-glucose gram loss ratio of 1.6:1. Morphological and ultrastructural studies confirmed delignification by this fungus and showed that some delignification had occurred by all of the species, although areas of delignification were limited to small regions adjacent to simultaneously decayed cells. In oak, G. colossum caused significantly less%WL (22 to 35%) than the other species (38 to 52%). All of the species, except G. meredithiae, caused delignification with lignin-to-glucose gram loss ratios ranging from 1.4 to 4.9:1. Extensive delignification by isolates of G. colossum and G. oregonense was observed; moderate delignification was caused by the other species. Ganoderma meredithiae caused a simultaneous decay, with only small localized regions of cells delignified, while delignification by G. zonatum was irregular, with specific zones within the cell wall delignified. The thermophilic and chlamydosporic G. colossum has the capacity to cause extensive delignification and appears ideally suited for use in lignin degradation studies and biotechnological applications of lignin-degrading fungi.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchette R. A., Abad A. R., Farrell R. L., Leathers T. D. Detection of lignin peroxidase and xylanase by immunocytochemical labeling in wood decayed by basidiomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1457-1465.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette R. A., Reid I. D. Ultrastructural Aspects of Wood Delignification by Phlebia (Merulius) tremellosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):239–245. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.239-245.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette R. A. Screening wood decayed by white rot fungi for preferential lignin degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):647–653. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.647-653.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill I., Kraepelin G. Palo Podrido: Model for Extensive Delignification of Wood by Ganoderma applanatum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1305–1312. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1305-1312.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faison B. D., Kirk T. K. Factors Involved in the Regulation of a Ligninase Activity in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):299–304. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.299-304.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Farrell R. L. Enzymatic "combustion": the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:465–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otjen L., Blanchette R. A. Xylobolus frustulatus Decay of Oak: Patterns of Selective Delignification and Subsequent Cellulose Removal. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):670–676. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.670-676.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhnau K., Wegner A. Evidence for direct binding of vinculin to actin filaments. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw NM, Blanis D, Bodek A, Budd H, Coombes R, Eno S, Fry CA, Harada H, Ho YH, Kim YK. Search for unstable heavy neutral leptons in e+e- annihilations at sqrt s from 50 to 60.8 GeV. Phys Rev Lett. 1989 Sep 25;63(13):1342–1345. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]