Abstract
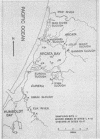
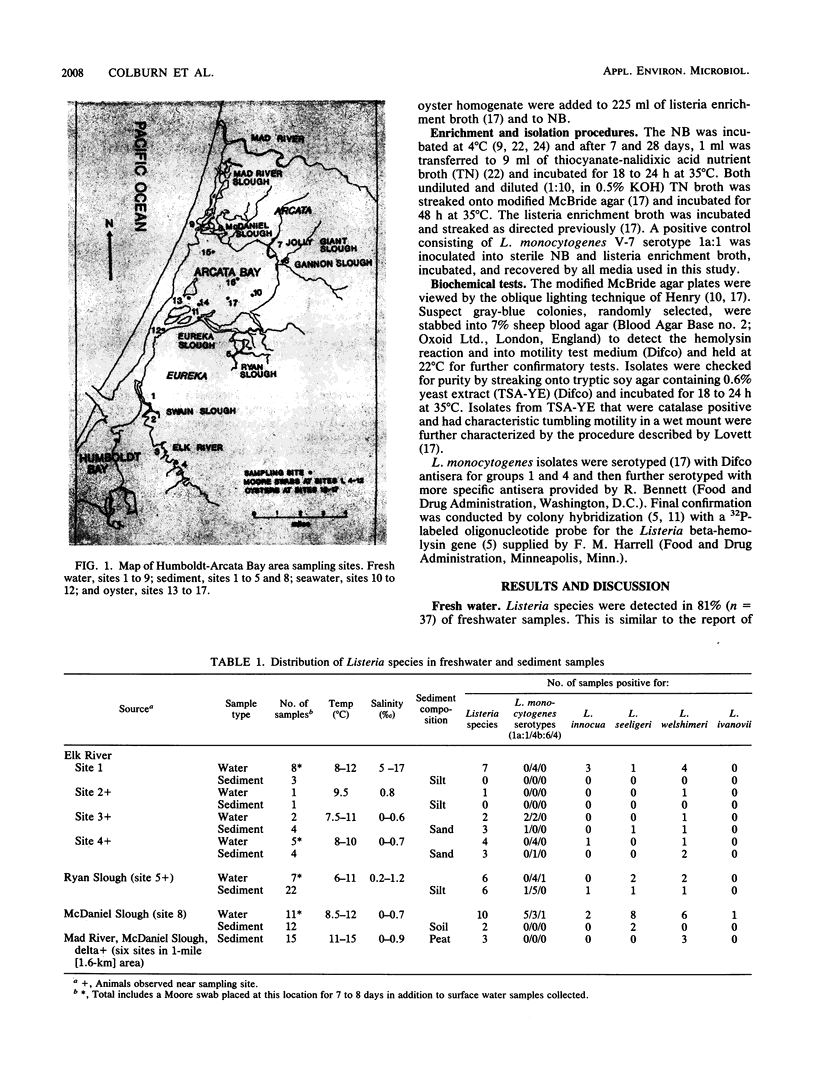
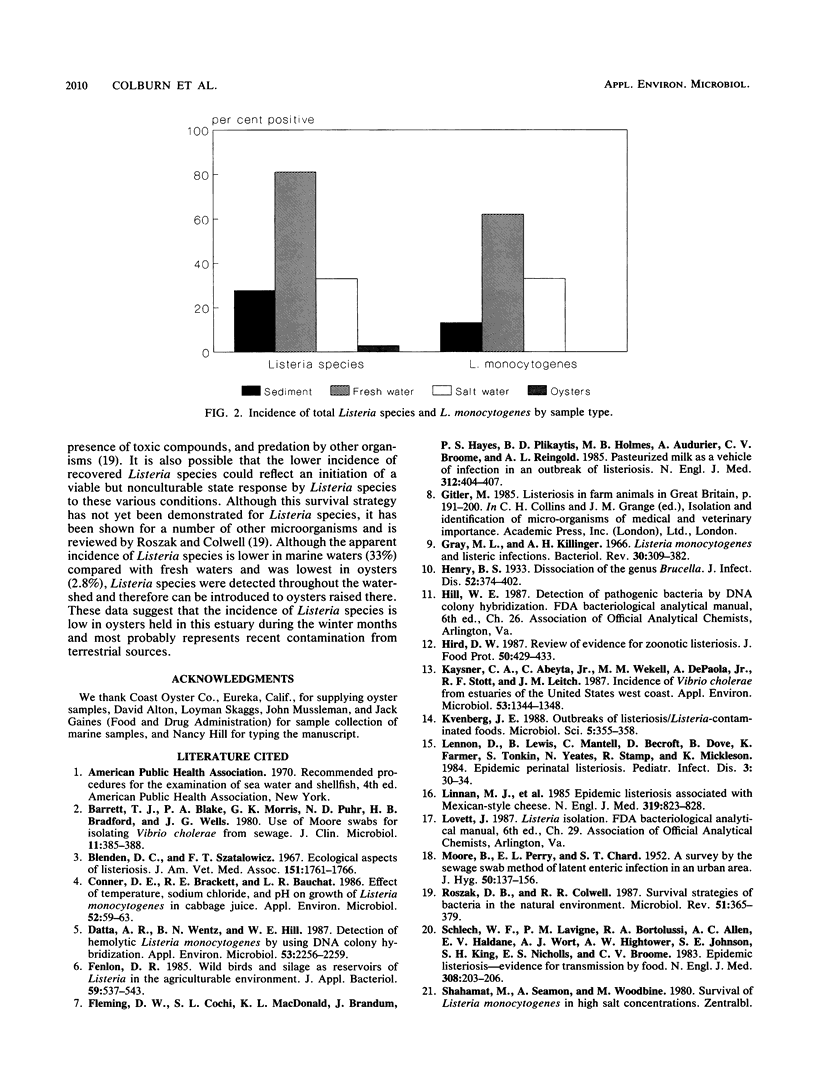
Listeria species and L. monocytogenes were found in 81 and 62%, respectively, of fresh or low-salinity waters (37 samples) in tributaries draining into Humboldt-Arcata Bay, Calif., during a winter (January-February) sampling period. The incidence of Listeria species and L. monocytogenes in sediment (46 samples) from the same sites where water was sampled was 30.4 and 17.4%, respectively. One of three bay water samples contained Listeria species (including L. monocytogenes), while of 35 samples of oysters examined, only 1 was found positive for Listeria species (L. innocua). A given species or L. monocytogenes serogroup appeared to predominate in fresh water when domesticated animals (cows, horses) were nearby, whereas greater variety with no species predominance was observed in areas with no direct animal influence.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett T. J., Blake P. A., Morris G. K., Puhr N. D., Bradford H. B., Wells J. G. Use of Moore swabs for isolating Vibrio cholerae from sewage. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.385-388.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner D. E., Brackett R. E., Beuchat L. R. Effect of temperature, sodium chloride, and pH on growth of Listeria monocytogenes in cabbage juice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):59–63. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.59-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. R., Wentz B. A., Hill W. E. Detection of hemolytic Listeria monocytogenes by using DNA colony hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2256–2259. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2256-2259.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenlon D. R. Wild birds and silage as reservoirs of Listeria in the agricultural environment. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;59(6):537–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb03357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaysner C. A., Abeyta C., Jr, Wekell M. M., DePaola A., Jr, Stott R. F., Leitch J. M. Incidence of Vibrio cholerae from estuaries of the United States West Coast. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1344–1348. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1344-1348.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvenberg J. E. Outbreaks of listeriosis/Listeria-contaminated foods. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Dec;5(12):355–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon D., Lewis B., Mantell C., Becroft D., Dove B., Farmer K., Tonkin S., Yeates N., Stamp R., Mickleson K. Epidemic perinatal listeriosis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;3(1):30–34. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198401000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnan M. J., Mascola L., Lou X. D., Goulet V., May S., Salminen C., Hird D. W., Yonekura M. L., Hayes P., Weaver R. Epidemic listeriosis associated with Mexican-style cheese. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 29;319(13):823–828. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809293191303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE B., PERRY E. L., CHARD S. T. A survey by the sewage swab method of latent enteric infection in an urban area. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Jun;50(2):137–156. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Lavigne P. M., Bortolussi R. A., Allen A. C., Haldane E. V., Wort A. J., Hightower A. W., Johnson S. E., King S. H., Nicholls E. S. Epidemic listeriosis--evidence for transmission by food. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):203–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSHIMER H. J. Survival of Listeria monocytogenes in soil. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80:316–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.316-320.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J., Sleath K. P. Isolation and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes from Sewage, Sewage Sludge and River Water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;50(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J., Seeliger H. P. Incidence of Listeria monocytogenes in nature. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jul;30(1):29–32. doi: 10.1128/am.30.1.29-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]