Abstract
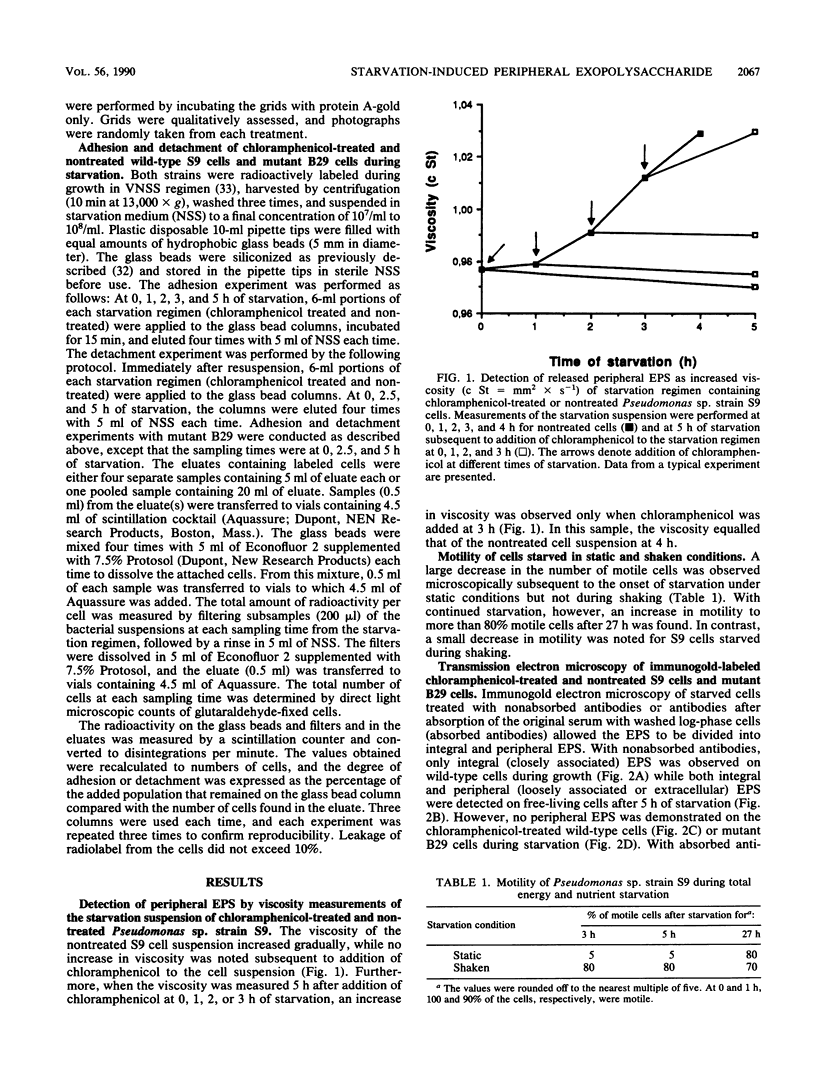
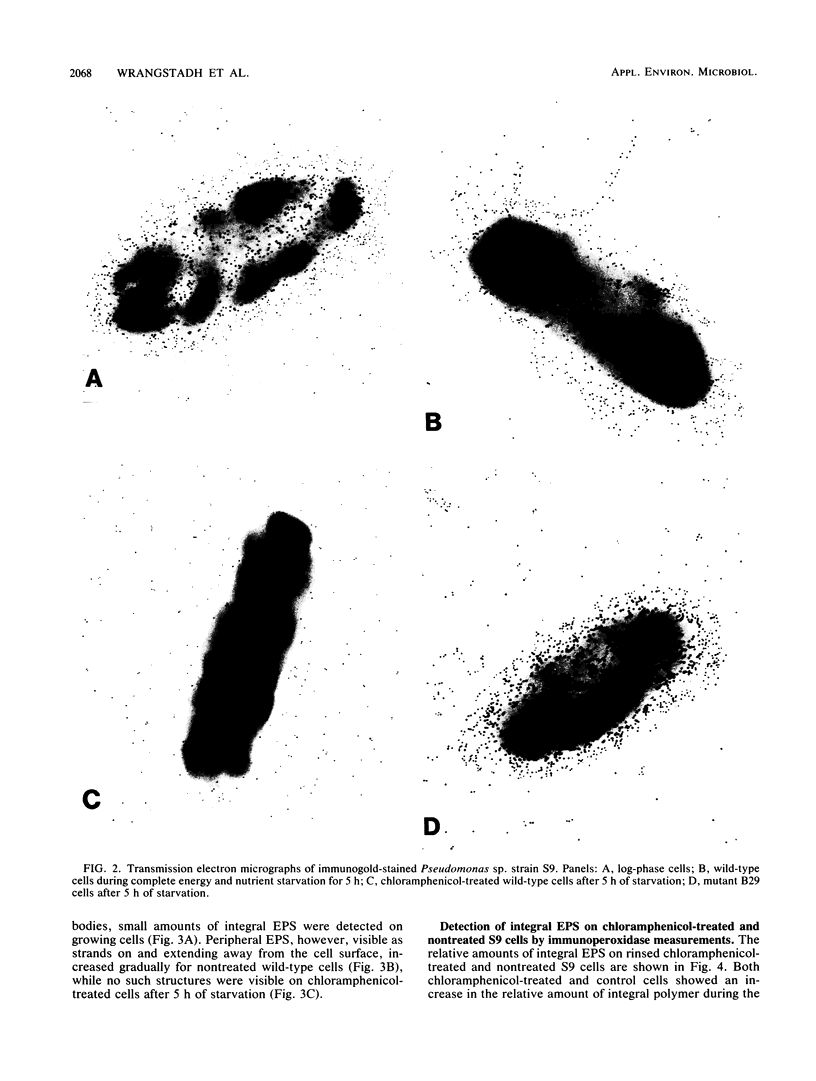
The marine bacterium Pseudomonas sp. strain S9 produces exopolysaccharides (EPS) during both growth and total energy source and nutrient starvation. Transmission electron microscopy of immunogold-labeled cells demonstrated that the EPS is closely associated with the cell surface during growth (integral EPS), while both the integral form and a loosely associated extracellular (peripheral) form were observed during starvation. Formation and release of the latter rendered the starvation medium viscous. In addition, after 3 h of starvation in static conditions, less than 5% of the cells were motile, compared with 100% at the onset of starvation and approximately 80% subsequent to release of the peripheral EPS at 27 h of starvation. Inhibition of protein synthesis with chloramphenicol added before 3 h of starvation caused no increase in viscosity. However, addition of chloramphenicol at 3 h did not prevent the subsequent increase in viscosity displayed by S9 cells. The amount of integral EPS increased for both nontreated and chloramphenicol-treated S9 cells during the first hour of starvation, with a subsequent equal decrease. The chloramphenicol-treated cells, as well as cells of a transposon-generated mutant strain deficient in peripheral EPS formation, remained adhesive to a hydrophobic inanimate surface during the initial 5 h of starvation, whereas nontreated wild-type cells had progressively decreased adhesion capacity. During the initial 5 h of starvation, most of the nontreated cells but only a small fraction of the chloramphenicol-treated and mutant cells detached from the hydrophobic substratum.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertson N. H., Nyström T., Kjelleberg S. Exoprotease Activity of Two Marine Bacteria during Starvation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):218–223. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.218-223.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. J., McCrae S. K., May B. E. Attached and free-floating bacterioplankton in howe sound, british columbia, a coastal marine fjord-embayment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):614–621. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.614-621.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Simon M., Silverman M. Regulation of lateral flagella gene transcription in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):210–218. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.210-218.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson M., Jones G. W., Kjelleberg S. Frequency of antibiotic and heavy metal resistance, pigmentation, and plasmids in bacteria of the marine air-water interface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2338–2342. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2338-2342.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Guckert J. B., White D. C., Deck F. Effect of nutrient deprivation on lipid, carbohydrate, DNA, RNA, and protein levels in Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):788–793. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.788-793.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Humphrey B. A., Marshall K. C. Effect of interfaces on small, starved marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1166–1172. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1166-1172.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Auger E. A., Blum P. H., Schultz J. E. Genetic basis of starvation survival in nondifferentiating bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:293–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström T., Albertson N., Kjelleberg S. Synthesis of membrane and periplasmic proteins during starvation of a marine Vibrio sp. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1645–1651. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter J. S. The caulobacters: ubiquitous unusual bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Mar;45(1):123–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.1.123-179.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Gottlieb A., Rosenberg M. Inhibition of bacterial adherence to hydrocarbons and epithelial cells by emulsan. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1024–1028. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1024-1028.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrangstadh M., Conway P. L., Kjelleberg S. The production and release of an extracellular polysaccharide during starvation of a marine Pseudomonas sp. and the effect thereof on adhesion. Arch Microbiol. 1986 Aug;145(3):220–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00443649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Huber P. S., Meyer A. E., Slots J., Fornalik M. S., Baier R. E. In situ identification of bacterial species in marine microfouling films by using an immunofluorescence technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1214–1220. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1214-1220.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]