Abstract
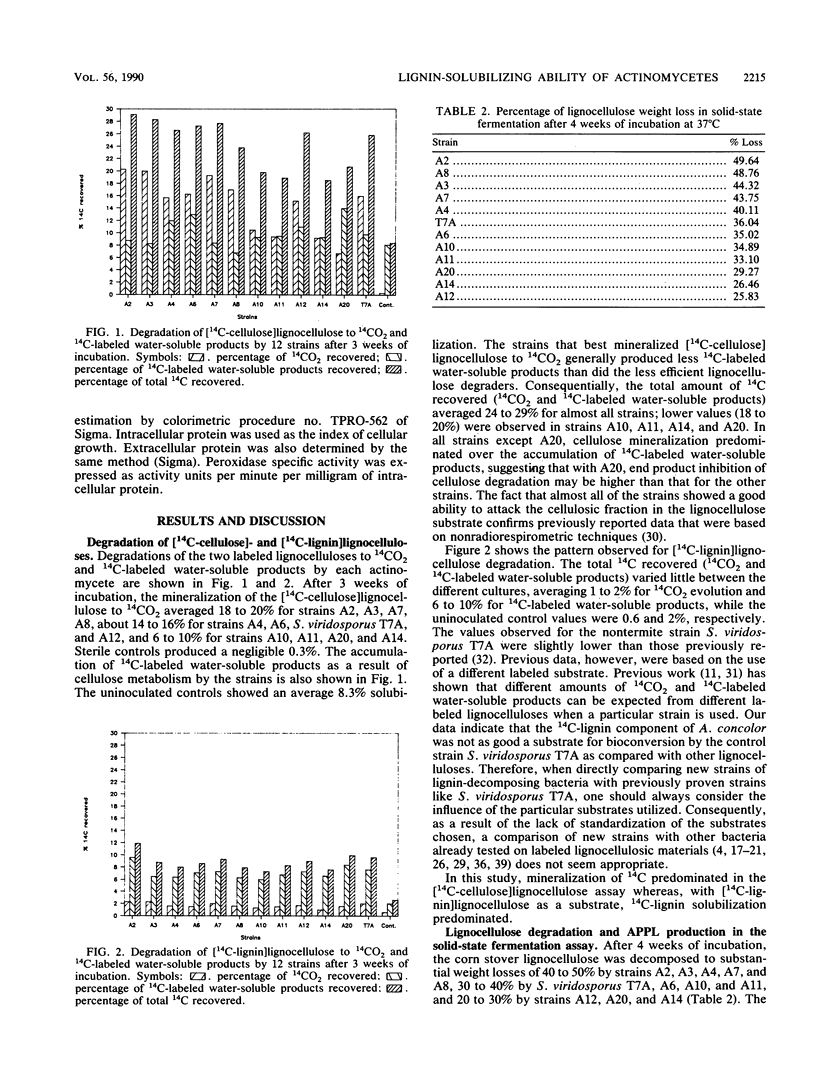
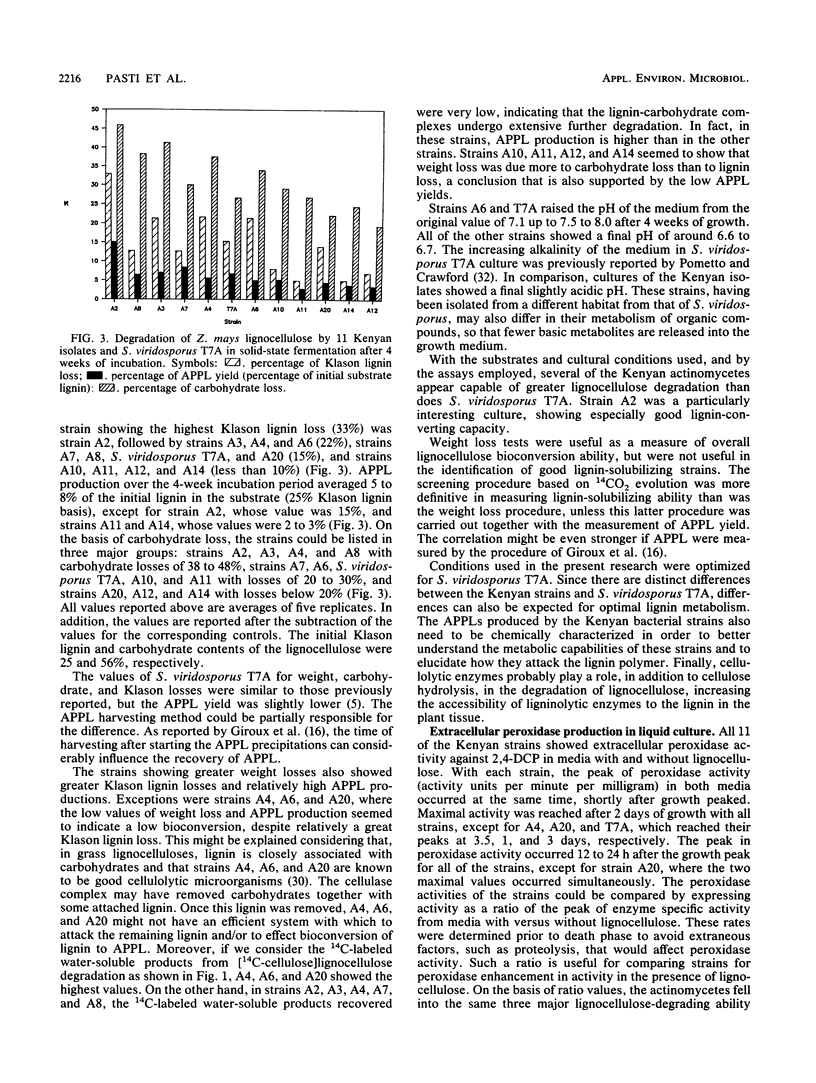
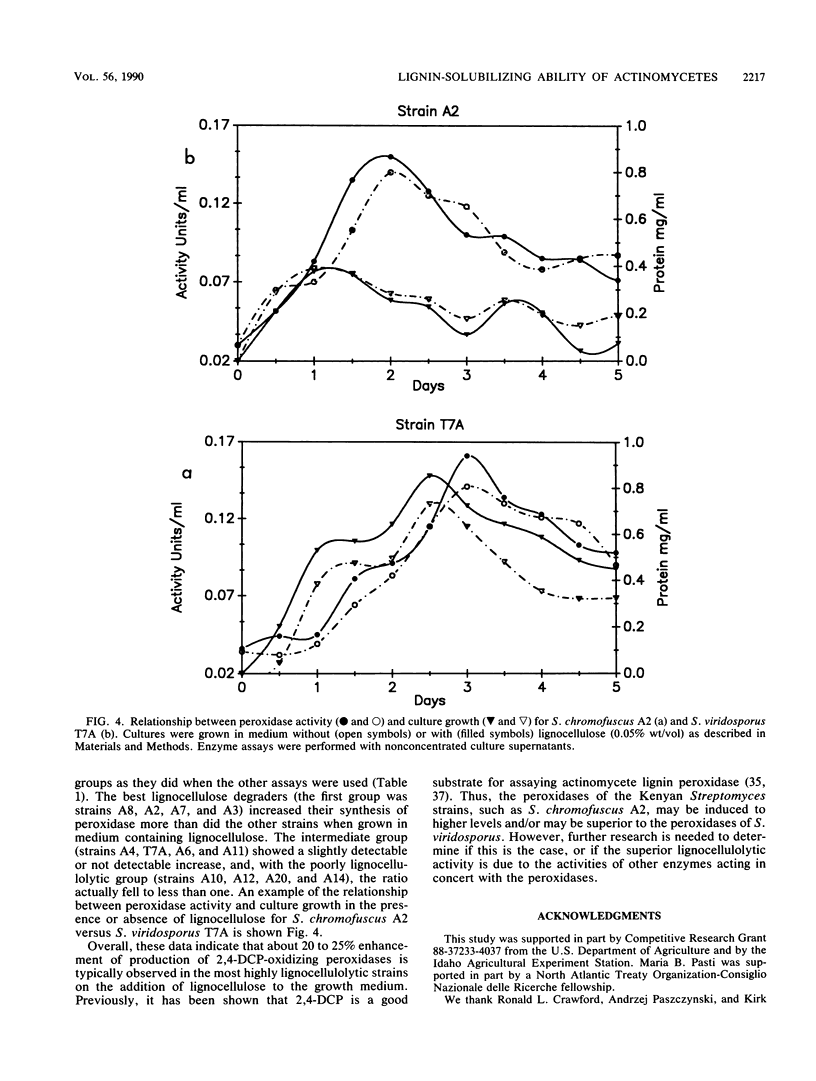
The lignocellulose-degrading abilities of 11 novel actinomycete strains isolated from termite gut were determined and compared with that of the well-characterized actinomycete, Streptomyces viridosporus T7A. Lignocellulose bioconversion was followed by (i) monitoring the degradation of [14C]lignin- and [14C]cellulose-labeled phloem of Abies concolor to 14CO2 and 14C-labeled water-soluble products, (ii) determining lignocellulose, lignin, and carbohydrate losses resulting from growth on a lignocellulose substrate prepared from corn stalks (Zea mays), and (iii) quantifying production of a water-soluble lignin degradation intermediate (acid-precipitable polymeric lignin). The actinomycetes were all Streptomyces strains and could be placed into three groups, including a group of five strains that appear superior to S. viridosporus T7A in lignocellulose-degrading ability, three strains of approximately equal ability, and three strains of lesser ability. Strain A2 was clearly the superior and most effective lignocellulose decomposer of those tested. Of the assays used, total lignocellulose weight loss was most useful in determining overall bioconversion ability but not in identifying the best lignin-solubilizing strains. A screening procedure based on 14CO2 evolution from [14C-lignin]lignocellulose combined with measurement of acid-precipitable polymeric lignin yield was the most effective in identifying lignin-solubilizing strains. For the termite gut strains, the pH of the medium showed no increase after 3 weeks of growth on lignocellulose. This is markedly different from the pattern observed with S. viridosporus T7A, which raises the medium pH considerably. Production of extracellular peroxidases by the 11 strains and S. viridosporus T7A was followed for 5 days in liquid cultures.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhi T. P., Korus R. A., Crawford D. L. Production of Major Extracellular Enzymes during Lignocellulose Degradation by Two Streptomycetes in Agitated Submerged Culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1165–1168. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1165-1168.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antai S. P., Crawford D. L. Degradation of softwood, hardwood, and grass lignocelluloses by two streptomyces strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):378–380. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.378-380.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball A. S., Betts W. B., McCarthy A. J. Degradation of lignin-related compounds by actinomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1642–1644. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1642-1644.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Hodson R. E. Thermophilic anaerobic biodegradation of [C]lignin, [C]cellulose, and [C]lignocellulose preparations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):971–976. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.971-976.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgmeyer J. R., Crawford D. L. Production and Characterization of Polymeric Lignin Degradation Intermediates from Two Different Streptomyces spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):273–278. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.273-278.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L., Crawford R. L. Microbial degradation of lignocellulose: the lignin component. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):714–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.714-717.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L., Crawford R. L., Pometto A. L. Preparation of specifically labeled C-(lignin)- and C-(cellulose)-lignocelluloses and their decomposition by the microflora of soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jun;33(6):1247–1251. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.6.1247-1251.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L. Lignocellulose decomposition by selected streptomyces strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1041–1045. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1041-1045.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L., Pometto A. L., Crawford R. L. Lignin Degradation by Streptomyces viridosporus: Isolation and Characterization of a New Polymeric Lignin Degradation Intermediate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):898–904. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.898-904.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroux H., Vidal P., Bouchard J., Lamy F. Degradation of Kraft Indulin Lignin by Streptomyces viridosporus and Streptomyces badius. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3064–3070. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3064-3070.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradziel K., Haider K., Kochmańska J., Malarczyk E., Trojanowski J. Bacterial decomposition of synthetic 14C-labeled lignin and lignin monomer derivatives. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1978;27(2):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider K., Trojanowski J., Sundman V. Screening for lignin degrading bacteria by means of 14C-labelled lignins. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):103–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00407936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern H. W. Bacterial degradation of dehydropolymers of coniferyl alcohol. Arch Microbiol. 1984 May;138(1):18–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00425401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr T. J., Kerr R. D., Benner R. Isolation of a bacterium capable of degrading peanut hull lignin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1201–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1201-1206.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Farrell R. L. Enzymatic "combustion": the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:465–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odier E., Janin G., Monties B. Poplar lignin decomposition by gram-negative aerobic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):337–341. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.337-341.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. B., Crawford D. L., Pometto A. L., 3rd Isolation of lignocellulose-decomposing actinomycetes and degradation of specifically 14C-labeled lignocelluloses by six selected Streptomyces strains. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1270–1276. doi: 10.1139/m79-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pometto A. L., Crawford D. L. Effects of pH on Lignin and Cellulose Degradation by Streptomyces viridosporus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):246–250. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.246-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pridham T. G., Gottlieb D. The Utilization of Carbon Compounds by Some Actinomycetales as an Aid for Species Determination. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.1.107-114.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandra M., Crawford D. L., Hertel G. Characterization of an extracellular lignin peroxidase of the lignocellulolytic actinomycete Streptomyces viridosporus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3057–3063. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3057-3063.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandra M., Crawford D. L., Pometto A. L. Extracellular Enzyme Activities during Lignocellulose Degradation by Streptomyces spp.: A Comparative Study of Wild-Type and Genetically Manipulated Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2754–2760. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2754-2760.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. M., Bleakley B. H., Crawford D. L., Hertel G., Rafii F. Cloning and expression of a lignin peroxidase gene from Streptomyces viridosporus in Streptomyces lividans. J Biotechnol. 1990 Feb;13(2-3):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(90)90099-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Goodfellow M., Wellington E. M., Vickers J. C., Alderson G., Sneath P. H., Sackin M. J., Mortimer A. M. A probability matrix for identification of some Streptomycetes. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jun;129(6):1815–1830. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-6-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



