Abstract
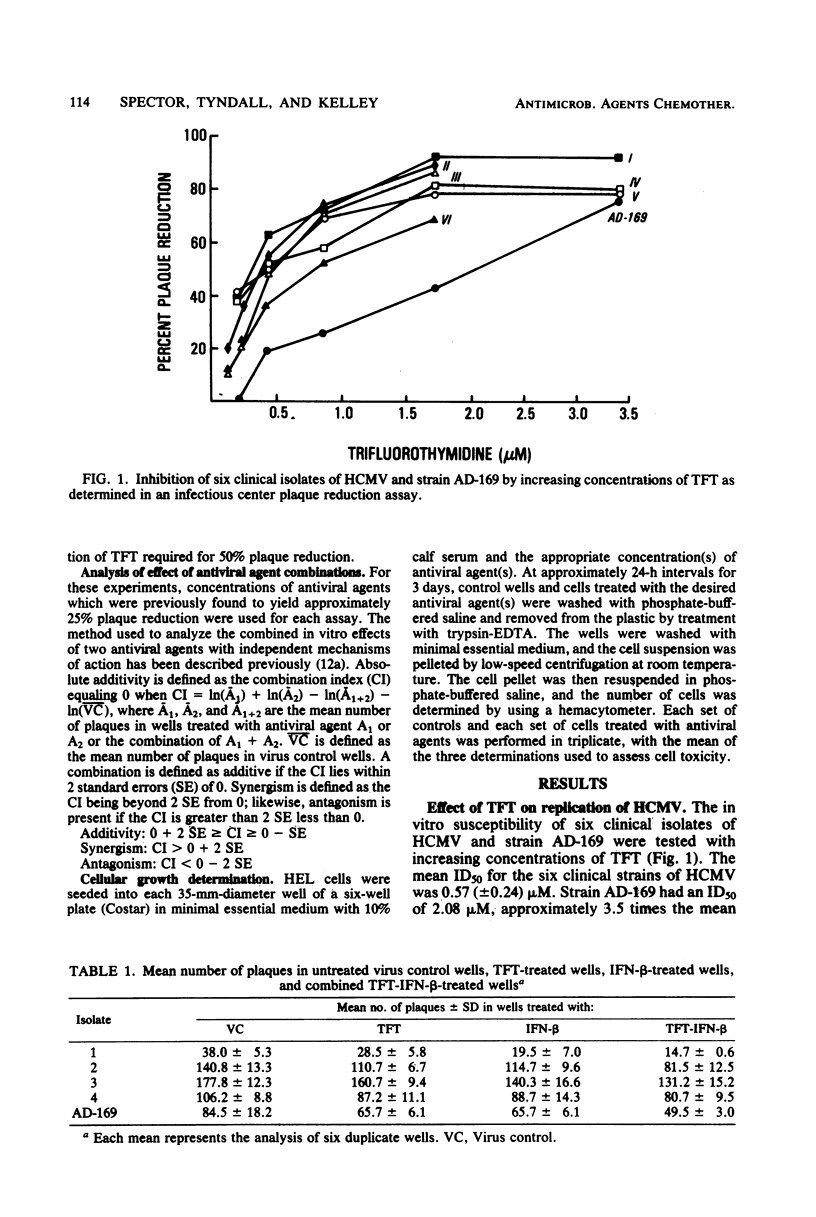
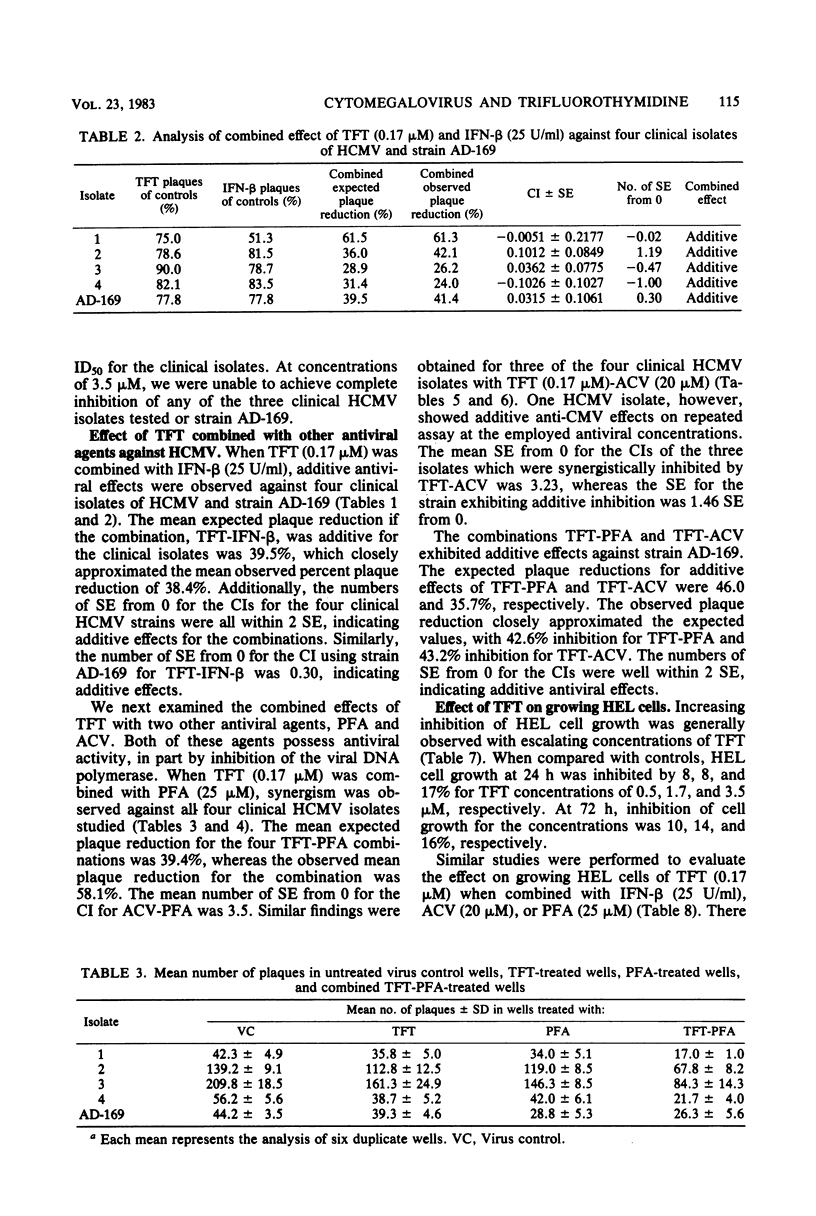
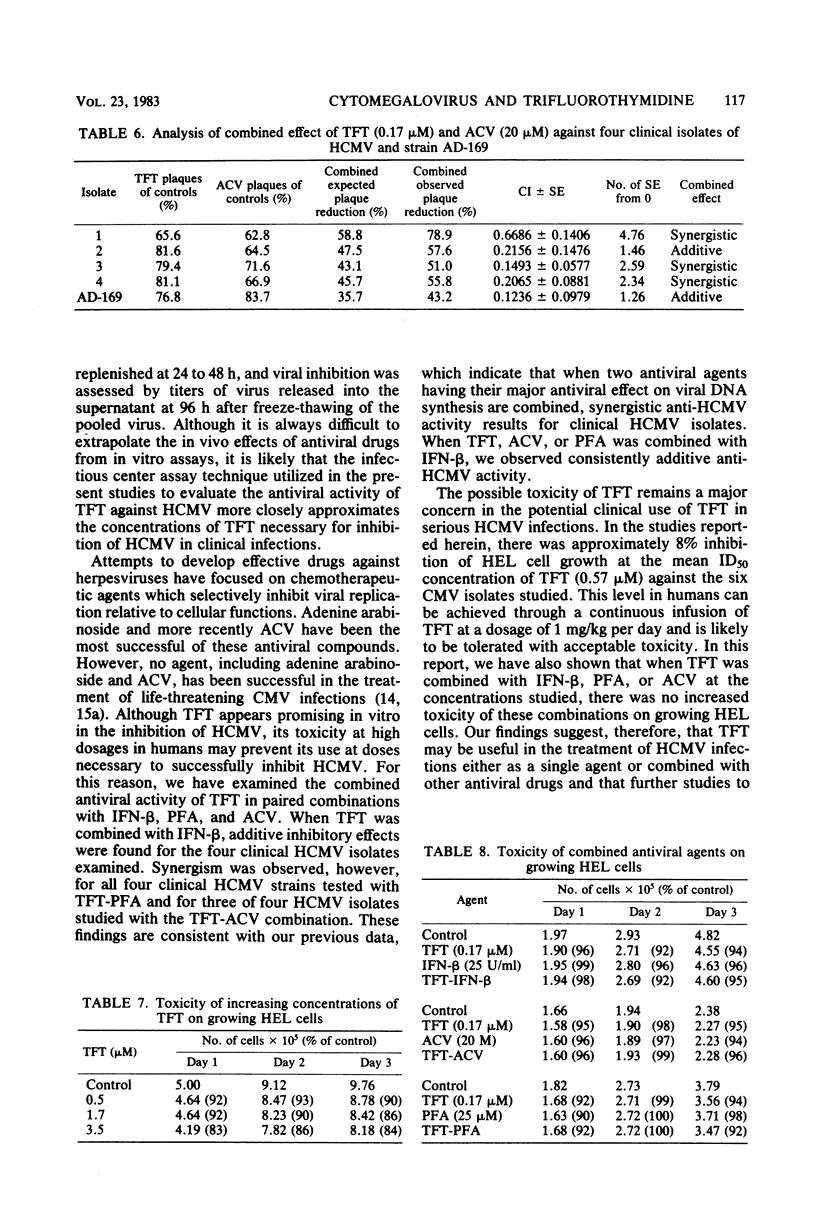
The antiviral activity of trifluorothymidine (TFT) singly and in combination with other antiviral agents against human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) was evaluated by using an infectious center plaque reduction assay. The 50% inhibitory dose of TFT against six different patient HCMV strains was 0.57 (+/- 0.24, standard deviation) microM and ranged from 0.32 to 0.97 microM. The 50% inhibitory dose for the laboratory-adapted HCMV strain, AD-169, was 2.1 microM. When TFT (0.17 microM) was combined with human fibroblast interferon (25 U/ml), the combination was additive against all four HCMV isolates evaluated. Synergism was observed when TFT (0.17 microM) was combined with phosphonoformic acid (25 microM) for all strains studied or with acyclovir (20 microM) for three of the four clinical HCMV strains tested. Each of the three antiviral agents, when combined with TFT, exhibited additive effects against strain AD-169. TFT at concentrations of 0.5, 1.7, and 3.5 microM had an increasing inhibitory effect on uninfected human embryonic lung fibroblast (HEL) cell growth over 72 h, with 16% growth inhibition at 3.5 microM after 3 days. There was no increased toxicity to growing HEL cells when the paired antiviral agent combinations were evaluated. These findings suggest that TFT may be useful singly or in combination with other antiviral agents in treating HCMV infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bresnick E., Williams S. S. Effects of 5-trifluoromethyldeoxyuridine upon deoxythymidine kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Mar;16(3):503–507. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coster D. J., McKinnon J. R., McGill J. I., Jones B. R., Fraunfelder F. T. Clinical evaluation of adenine arabinoside and trifluorothymidine in the treatment of corneal ulcers caused by herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A173–A177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter D. L., Wolberg W. H., Ansfield F. J., Helson L., Heidelberger C. The clinical pharmacology of 5-trifluoromethyl-2'-deoxyuridine. Cancer Res. 1972 Feb;32(2):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger C. On the molecular mechanism of the antiviral activity of trifluorothymidine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Aug 8;255:317–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. G., Neiman P. E., Reeves W. C., Thomas E. D. Prophylactic adenine arabinoside following marrow transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. D., Spencer H. C., Jr, Watts J. C., Gregg M. B., Stewart J. A., Troupin R. H., Thomas E. D. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia after human marrow transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Feb;82(2):181–188. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P., Wasserman P. B., Wentworth B. B., Kao G. F., Lerner K. G., Storb R., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Fefer A., Fass L. Interstitial pneumonia and cytomegalovirus infection as complications of human marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1973 May;15(5):478–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E. Cytomegalovirus: pathogenicity, immunity, and vaccine initiatives. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):618–630. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst J. R., Danenberg P. V., Heidelberger C. Growth inhibition of cells in cultures and of vaccinia virus infected HeLa cells by derivatives of trifluorothymidine. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(3-4):221–231. doi: 10.1159/000221929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Stubbs K. G., Dahle A. J., Livingston M. M., Saxon S. S., Alford C. A. Inapparent congenital cytomegalovirus infection with elevated cord IgM levels. Casual relation with auditory and mental deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 7;290(6):291–296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402072900601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. H., Russell P. S., Levin M., Cohen C. From the National Institutes of Health. Summary of a workshop on cytomegalovirus infections during organ transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):728–734. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Tyndall M., Kelley E. Effects of acyclovir combined with other antiviral agents on human cytomegalovirus. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):36–39. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr J. G., Bart R. D., Jr, Gold E. Inapparent congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics in early infancy. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 7;282(19):1075–1078. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005072821905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda M., Heidelberger C. Comparative studies of fluorinated pyrimidines with various cell lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Dec;28(12):2529–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda M., Heidelberger C. Fluorinated pyrimidines. XXXI. Mechanisms of inhibition of vaccinia virus replication in HeLa cells by pyrimidine nucleosides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):24–29. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Hintz M., McGuffin R., Springmeyer S. C., Connor J. D., Meyers J. D. Treatment of cytomegalovirus pneumonia with high-dose acyclovir. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings P. C., Awdry P. N., Bors F. H., Jones B. R., Brown D. C., Kaufman H. E. Clinical evaluation of trifluorothymidine in the treatment of herpes simplex corneal ulcers. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Jun;73(6):932–942. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90463-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B. L., Parkhurst J. R. HEp-2 cell- and herpes simplex virus type 1- induced deoxythymidine kinases: inhibition by derivatives of 5-trifluoromethyl-2'-deoxyuridine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):470–475. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingard J. R., Stuart R. K., Saral R., Burns W. H. Activity of trifluorothymidine against cytomegalovirus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):286–290. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


