Abstract
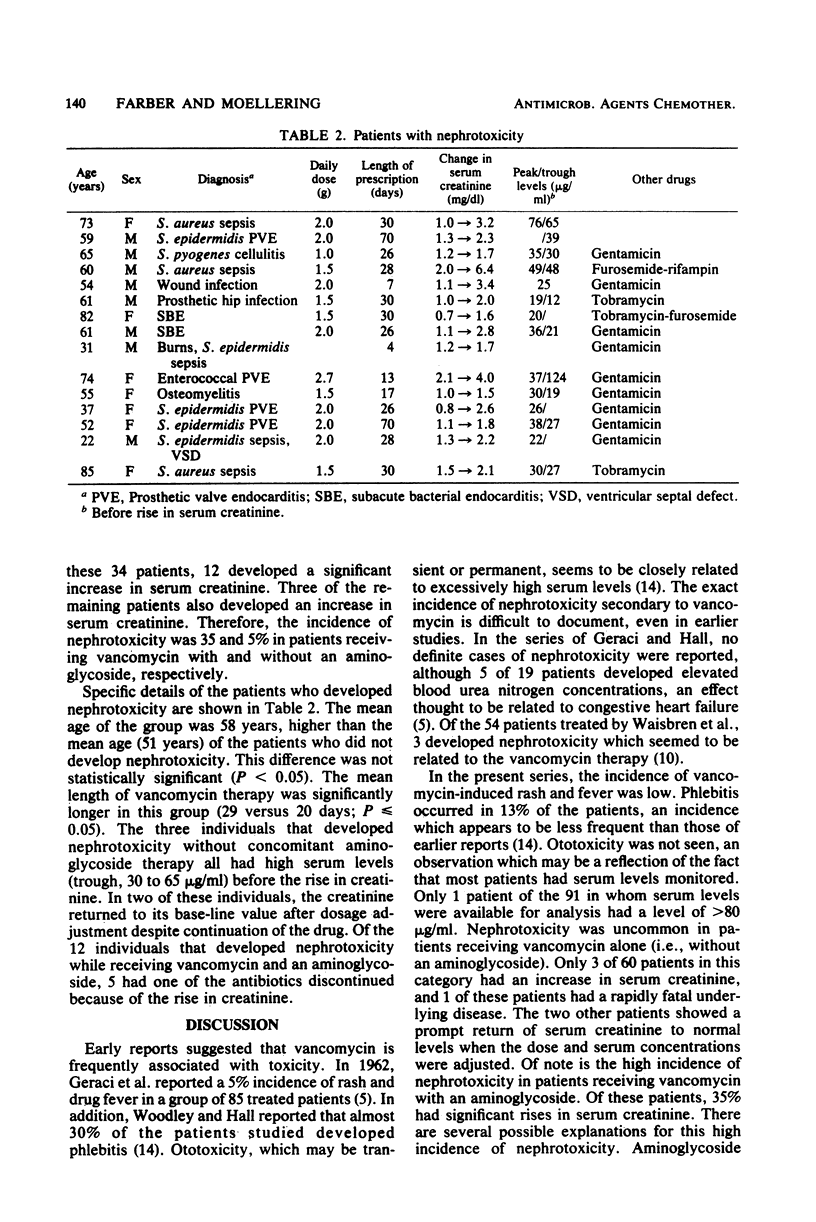
A retrospective chart review of 98 patients treated with 100 courses of intravenous vancomycin was undertaken to better define its toxicity. Most of the patients carried diagnoses of Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis infection. Auditory toxicity was not seen, and fever and rash occurred in only 1 to 3% of the subjects. Phlebitis was noted in 13% of the cases and required discontinuation of therapy in 2%. Therapy was complicated by neutropenia (polymorphonuclear leukocyte count, less than or equal to 1,000 cells per cm3) in 2% of the patients but was rapidly reversible. Nephrotoxicity was uncommon (5%) and reversible in subjects receiving vancomycin alone, even when the therapy was continued. However, 35% of the patients receiving vancomycin with an aminoglycoside developed significant elevations in serum creatinine. Although this high incidence may have been due to the patient population selected or to the aminoglycoside therapy alone, the possibility of additive toxicity between vancomycin and the aminoglycosides should be considered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff G. R., Sloan R. S., Dinwiddie C. B., Jr, Glant M. D., Fineberg N. S., Luft F. C. Effects of vancomycin on renal function in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):306–308. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borland C. D., Farrar W. E. Reversible neutropenia from vancomycin. JAMA. 1979 Nov 30;242(22):2392–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook F. V., Farrar W. E., Jr Vancomycin revisited. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jun;88(6):813–818. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-6-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley K., Loesch D., Landesman B., Mead K., Chern M., Strate R. An outbreak of infections caused by strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin and aminoglycosides. I. Clinical studies. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):273–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERACI J. E., NICHOLS D. R., WELLMAN W. E. Vancomycin in serious staphylococcal infections. Arch Intern Med. 1962 May;109:507–515. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620170005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W., Dismukes W. E., Buckley M. J., Austen W. G. Late prosthetic valve endocarditis: clinical features influencing therapy. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek J. J., Marsik F. J., Bartlett R. C., Weir B., Shea P., Quintiliani R. Clinical, epidemiologic and bacteriologic observations of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a large community hospital. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Moellering R. C., Jr, Greenblatt D. J. Single-dose kinetics of intravenous vancomycin. J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;20(4 Pt 1):197–201. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1980.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Lipsky J. J., Laskin O. L., Hellmann D. B., Mellits E. D., Longstreth J., Lietman P. S. Double-blind comparison of the nephrotoxicity and auditory toxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 15;302(20):1106–1109. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005153022002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODLEY D. W., HALL W. H. The treatment of severe staphylococcal infections with vancomycin. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Aug;55:235–249. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Gentry L. O. A randomized, comparative study of tobramycin and gentamicin in treatment of acute urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134 (Suppl):S146–S149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.supplement_1.s146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West B. C. Vancomycin-induced neutropenia. South Med J. 1981 Oct;74(10):1255–1256. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198110000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold J. S., Turnipseed S. A. Toxicology of vancomycin in laboratory animals. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3 Suppl:S224–S229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


