Abstract
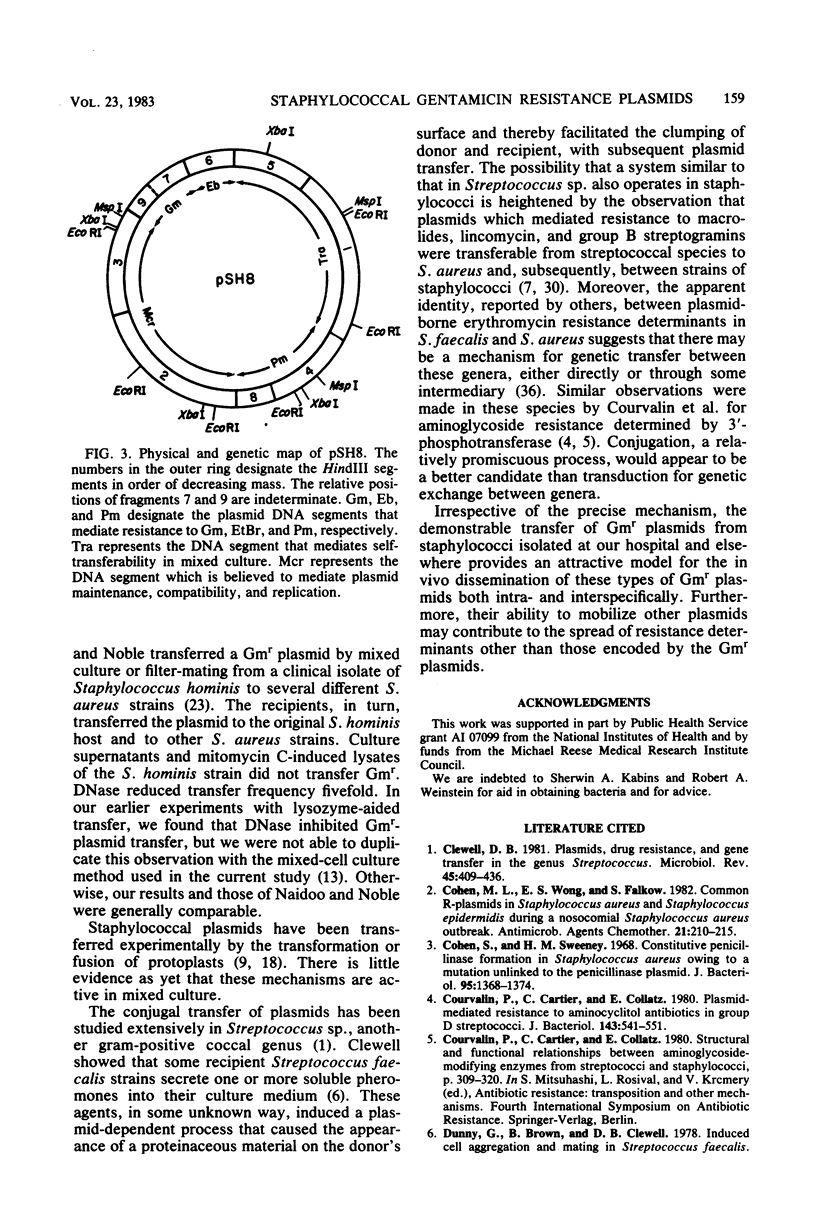
We have previously reported the transfer of gentamicin resistance (Gmr) plasmids in a mixed culture inter- and intraspecifically between strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated at Michael Reese Hospital (Jaffe et al., Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 21:773-779, 1982). We have now shown that representatives of these plasmids were transferred between apparently nonlysogenic strains of S. aureus either in mixed culture in broth or by filter-mating on agar medium. The mechanism of transfer appeared to be conjugation. A transferable Gmr plasmid (pSH8) mobilized or cotransferred a tetracycline R-plasmid and a chloramphenicol R-plasmid that were not independently transferable. The transfer of Gmr plasmids was accompanied by a high incidence of deletion mutations with varied loss of plasmid resistance determinants and, with some mutants, loss of the ability to effect self-transfer. Restriction endonuclease digestion of pSH8 and its deletion mutants made it possible to assign the property of self-transfer to a specific segment of the pSH8 genome and provided the basis for a physical and genetic map of that plasmid. Similar Gmr plasmids from S. aureus strains isolated in locations remote from Michael Reese Hospital had resistance determinants and transfer properties comparable to those of pSH8. Our observations provide evidence for the conjugal transfer of some staphylococcal plasmids, apparently independent of the presence of phage. This mechanism may be of significance in the intra- and interspecific dissemination of resistance to aminoglycosides and other antibiotics in Staphylococcus spp.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wong E. S., Falkow S. Common R-plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis during a nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus outbreak. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):210–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Sweeney H. M. Constitutive penicillinase formation in Staphylococcus aureus owing to a mutation unlinked to the penicillinase plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1368–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1368-1374.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Carlier C., Collatz E. Plasmid-mediated resistance to aminocyclitol antibiotics in group D streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):541–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.541-551.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel H. W., Soedirman N., Rost J. A., van Leeuwen W. J., van Embden J. D. Transferability of macrolide, lincomycin, and streptogramin resistances between group A, B, and D streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.407-413.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves D. J. Interspecific relationships of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus sp.: isolation and comparison of plasmids determining tetracycline resistance in S. aureus and S. epidermidis. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Dec;25(12):1468–1475. doi: 10.1139/m79-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Ahrné S., Lindberg M. Plasmid transfer and genetic recombination by protoplast fusion in staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.74-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordanescu S., Surdeanu M., Della Latta P., Novick R. Incompatibility and molecular relationships between small Staphylococcal plasmids carrying the same resistance marker. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):468–479. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Sweeney H. M., Nathan C., Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Cohen S. Identity and interspecific transfer of gentamicin-resistance plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):738–747. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Sweeney H. M., Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Cohen S. Structural and phenotypic varieties of gentamicin resistance plasmids in hospital strains of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):773–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. Antibiotic resistance plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus and their clinical importance. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.1-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. Evidence for two mechanisms of plasmid transfer in mixed cultures of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Aug;119(2):423–435. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-2-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. High-frequency transfer of neomycin resistance between naturally occurring strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Feb;4(1):73–84. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijers J. A., Winkler K. C., Stobberingh E. E. Resistance transfer in mixed cultures of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):21–39. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Rosenblum E. D. Plasmid for tetracycline resistance in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidoo J., Noble W. C. Transfer of gentamicin resistance between coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive staphylococci on skin. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):183–187. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidoo J., Noble W. C. Transfer of gentamicin resistance between strains of Staphylococcus aureus on skin. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Aug;107(2):391–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-107-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Morse S. I. In vivo transmission of drug resistance factors between strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):45–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Seed B. Two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis "SeaPlaque" agarose dimension. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):358–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyru G., Wexler L. F., Novick R. P. Naturally occurring penicillinase plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):215–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.215-221.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston S. M., Palmer T. J. Transduction of penicillinase production and other antibiotic-resistance markers in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):235–242. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendorf L. L., Kayser F. H. Transduction and plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid analysis in a multiply antibiotic-resistant strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):679–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.679-686.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Clewell D. B., Glatzer L. Conjugative transfer of R-plasmids from Streptococcus faecalis to Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):204–207. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Brodsky R. F. Characterization of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.28-36.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky A. M., Rabinovich P. M., Yakubov L. Z., Sineokaya I. V., Stepanov A. I., Gordeyev V. K. Direct selection of DNA inserts in plasmid gene of kanamycin-resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):487–488. doi: 10.1007/BF00425867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Vidal L., Baldwin J. N. Penicillin and tetracycline resistance plasmids in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):359–365. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Sweeney H. M., Jaffe H. W., Cohen S. Gentamicin-resistant staphylococci as hospital flora: epidemiology and resistance plasmids. J Infect Dis. 1982 Mar;145(3):374–382. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.3.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Holder S. B., Halling S. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence common to staphylococcal and streptococcal plasmids which specify erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):990–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.990-998.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Baldwin J. N. Intraspecific transduction in Staphylococcus epidermidis and interspecific transduction between Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jun;17(6):767–773. doi: 10.1139/m71-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]