Abstract
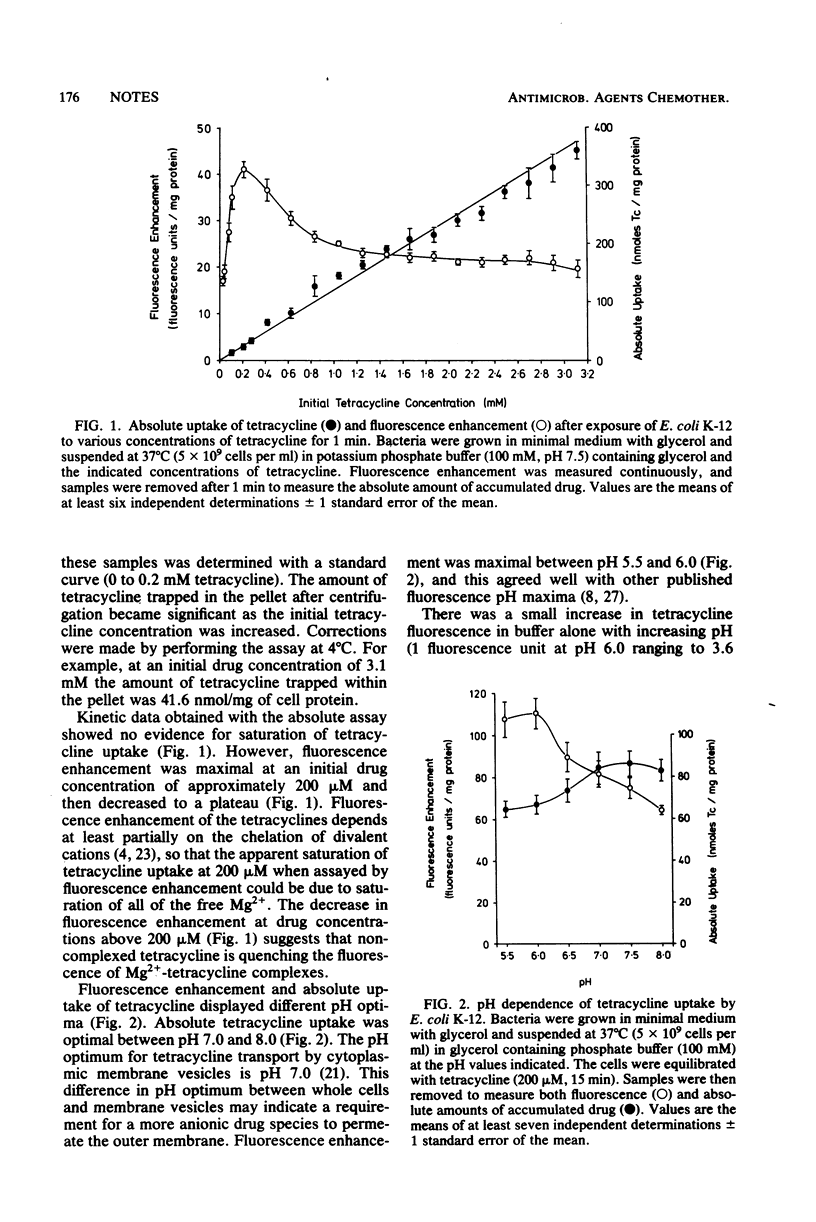
Transport of tetracycline into Escherichia coli was studied by two methods, one involving an absolute determination of accumulated drug and the other a fluorescence assay. Tetracycline uptake was nonsaturable when assayed by the absolute method, but fluorescence enhancement was maximal at an initial external tetracycline concentration of about 200 microM. The two transport assays also gave different results for the pH optimum of tetracycline transport. The absolute method indicated a pH optimum of 7.0 to 8.0, whereas the fluorescence method gave a value of 5.5 to 6.0. These data indicate that the fluorescence assay is of limited value in certain situations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball P. R., Chopra I., Eccles S. J. Accumulation of tetracyclines by Escherichia coli K-12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1500–1507. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball P. R., Shales S. W., Chopra I. Plasmid-mediated tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli involves increased efflux of the antibiotic. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell A. H., Hutchison J. D. Visualization of membrane bound cations by a fluorescent technique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Ball P. Transport of antibiotics into bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1982;23:183–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Howe T. G., Linton A. H., Linton K. B., Richmond M. H., Speller D. C. The tetracyclines: prospects at the beginning of the 1980s. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jul;8(1):5–21. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Shales S., Ball P. Tetracycline resistance determinants from groups A to D vary in their ability to confer decreased accumulation of tetracycline derivatives by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Apr;128(4):689–692. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockter M. E., Magnuson J. A. Characterization of the active transport of chlorotetracycline in staphylococcus aureus by a fluorescence technique. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(1):32–44. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockter M. E., Magnuson J. A. Membrane phase transitions and the transport of chlortetracycline. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 May;168(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockter M. E., Trumble W. R., Magnuson J. A. Membrane lateral phase separations and chlortetracycline transport by Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1319–1323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayolle F., Privitera G., Sebald M. Tetracycline transport in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):502–505. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Reiss M., Kersten H. Interaction of tetracylines with ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. A fluorometric investigation. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1160–1164. doi: 10.1021/bi00730a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Higginson B. Active accumulation of tetracycline by Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):287–297. doi: 10.1042/bj1160287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L. M., Cullinane J. C., Petrucci R. E., Jr, Levy S. B. Active uptake of tetracycline by membrane vesicles from susceptible Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):307–313. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L., Petrucci R. E., Jr, Levy S. B. Active efflux of tetracycline encoded by four genetically different tetracycline resistance determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3974–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shales S. W., Chopra I., Ball P. R. Evidence for more than one mechanism of plasmid-determined tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Nov;121(1):221–229. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-1-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. P., Cantor C. R. Role of magnesium in the binding of tetracycline to Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


