Abstract
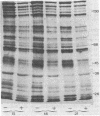
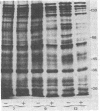
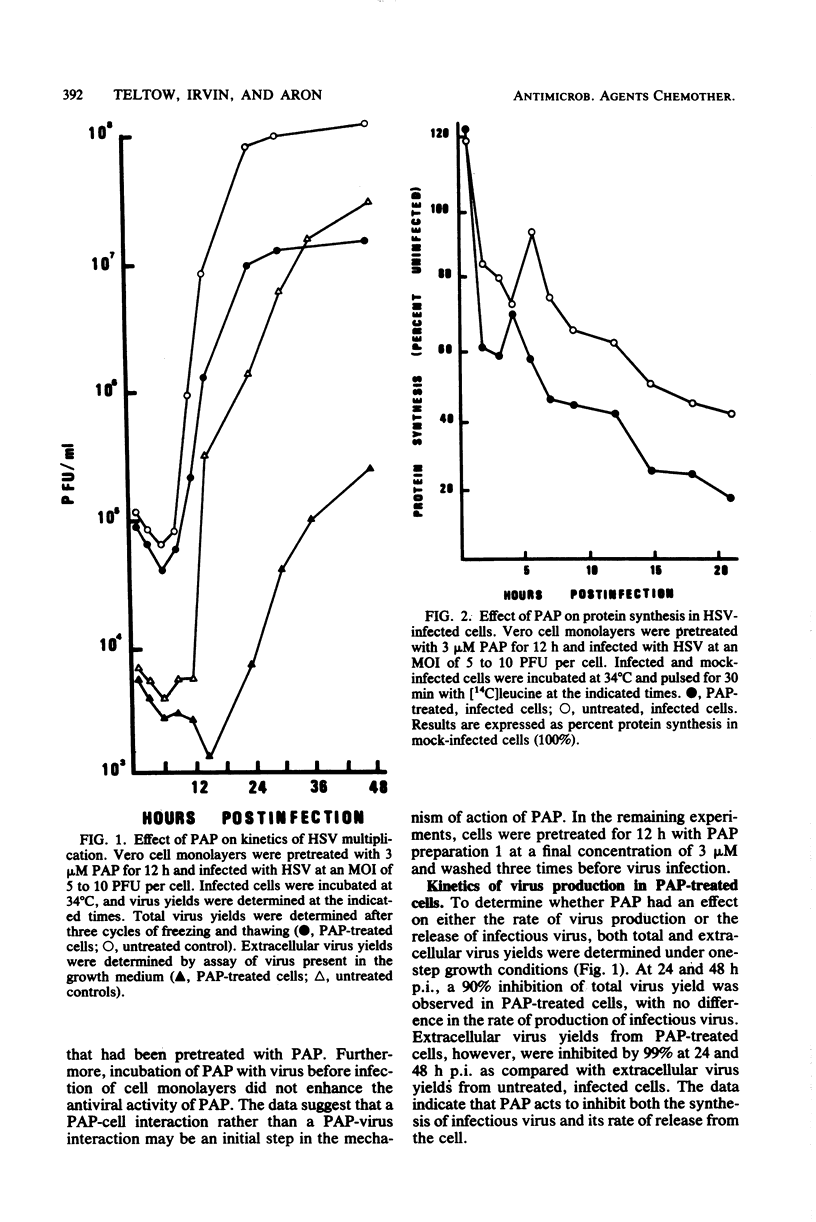
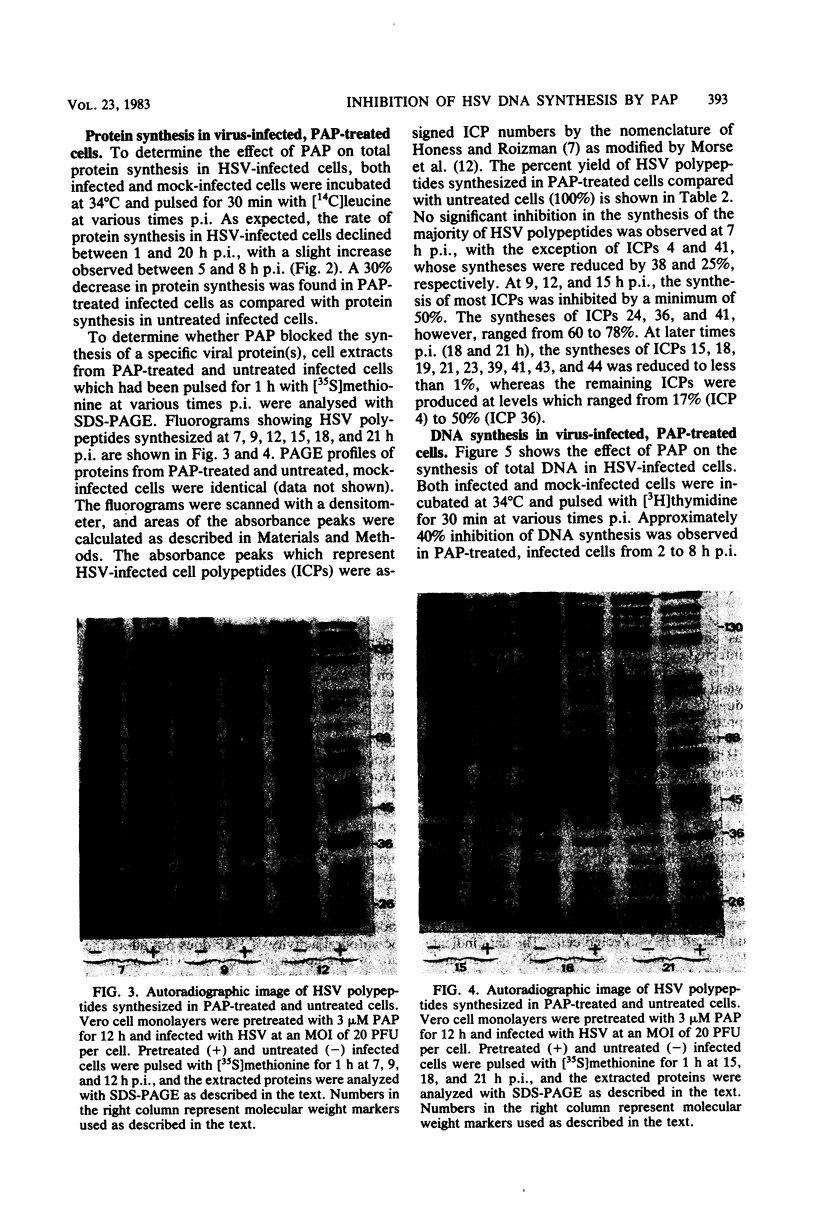
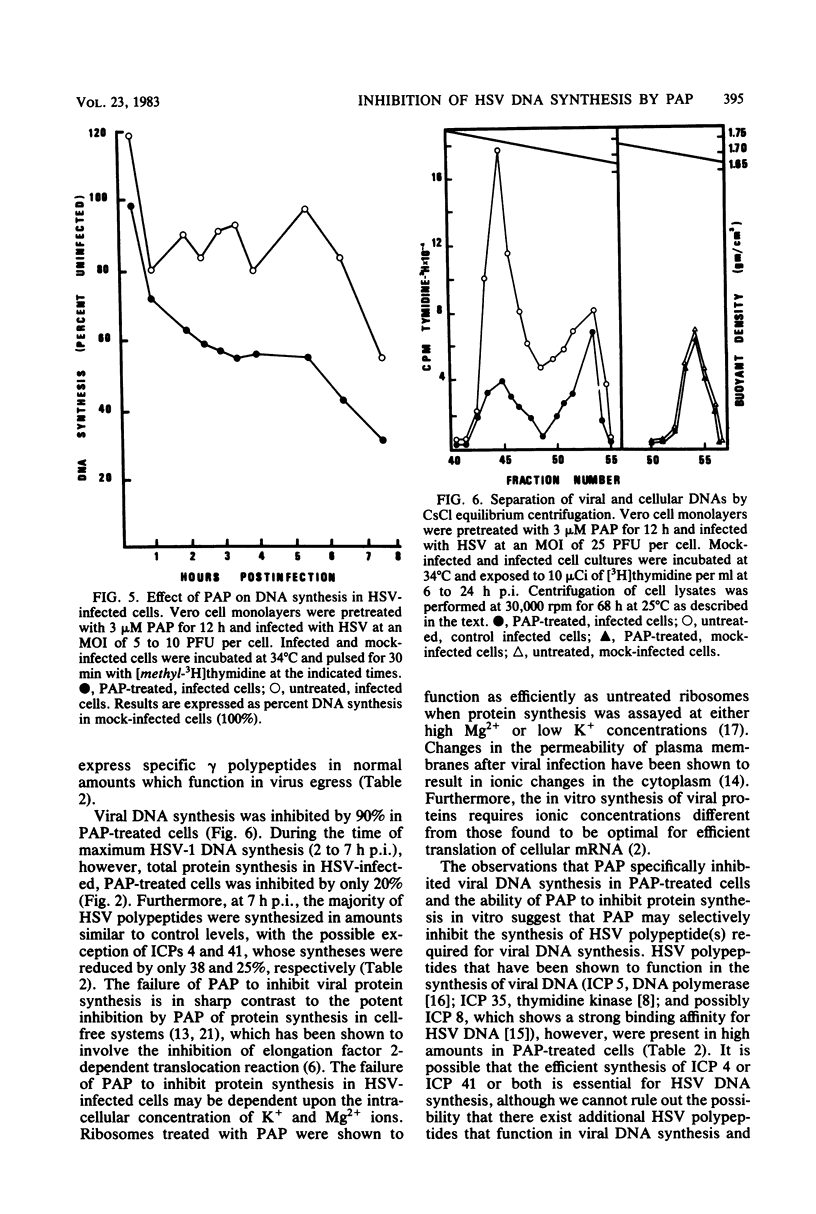
Pokeweed antiviral protein at a concentration of 3 microM inhibited both the synthesis and release of infectious herpes simplex virus type 1 in cell culture by 90 and 99%, respectively. Addition of pokeweed antiviral protein to Vero cell monolayers before virus infection was 10 to 15% more effective in reducing virus yields than was the simultaneous addition of the antiviral protein with virus inoculum. Viral DNA synthesis was inhibited by 90% in cells which had been exposed to the antiviral protein, whereas cellular DNA synthesis was unaffected. No significant inhibition in the synthesis of the majority of viral infected-cell polypeptides was observed early postinfection (7 h), with the exception of infected cell polypeptides 4 and 41, whose syntheses were reduced by 38 and 25%, respectively. At 9 to 21 h postinfection, however, the synthesis of individual infected cell polypeptides was reduced by 48 to greater than 99%.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aron G. M., Irvin J. D. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus multiplication by the pokeweed antiviral protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):1032–1033. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Smith A. E. Sodium ions and the shut-off of host cell protein synthesis by picornaviruses. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):807–809. doi: 10.1038/264807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Carrasco L. Selective inhibition of protein synthesis in virus-infected mammalian cells. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.114-122.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. A., Aswell J. F. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication by araT. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):294–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus-specific polypeptides studied by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of immune precipitates. J Gen Virol. 1974 Feb;22(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin J. D. Purification and partial characterization of the antiviral protein from Phytolacca americana which inhibits eukaryotic protein synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):522–528. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuho Y., Kishida K., Hara T. Targeting of the antiviral protein from Phytolacca americana with an antibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Irvin J. D., Hardesty B. The effect of an antiviral peptide on the ribosomal reactions of the peptide elongation enzymes, EF-I and EF-II. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Apr;155(2):278–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Altendorf K. H., Schweiger M., Hirsch-Kaufmann M., Pfennig-Yeh M. L., Herrlich P. E. coli membranes become permeable to ions following T7-virus-infection. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 8;149(2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00332882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Littler E., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. II. Major virus-specific DNa-binding protein. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):894–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.894-902.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. I. Purification of the induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):618–626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.618-626.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodes T. L., 3rd, Irvin J. D. Reversal of the inhibitory effects of the pokeweed antiviral protein upon protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 29;652(1):160–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spear P. G. Preparation of herpes simplex virus of high titer. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):83–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.83-84.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson J. A., Walker V. M., Flewett T. H., Barclay G. R. The inhibition of infection by cucumber mosaic virus and influenza virus by extracts from Phytolacca americana. J Gen Virol. 1974 Feb;22(2):225–232. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ussery M. A., Irvin J. D., Hardesty B. Inhibition of poliovirus replication by a plant antiviral peptide. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:431–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt S. D., Shepherd R. J. Isolation and characterization of a virus inhibitor from Phytolacca americana. Phytopathology. 1969 Dec;59(12):1787–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]