Abstract
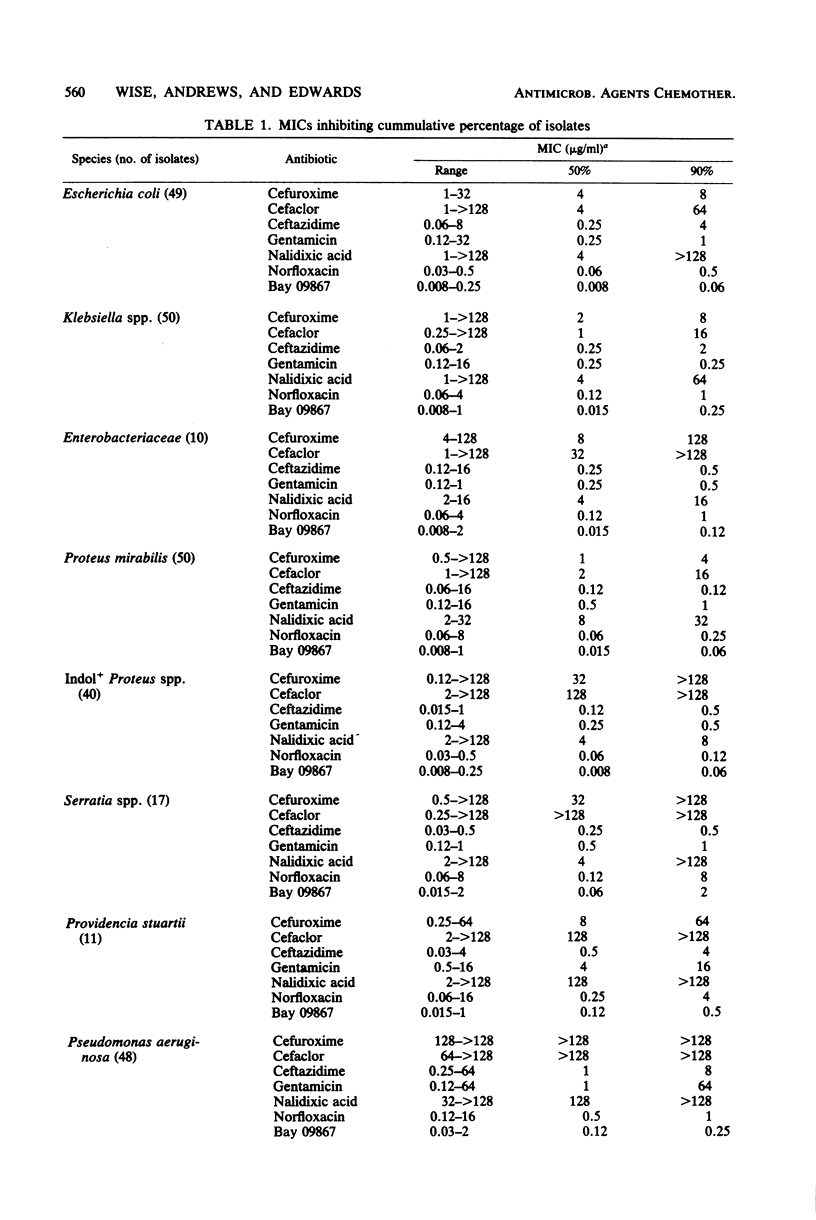
The in vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, was compared with those of norfloxacin, nalidixic acid, ceftazidime, cefaclor, cefuroxime, gentamicin, and other antimicrobial agents, when appropriate, against 410 recent clinical isolates. The minimal inhibitory concentrations of Bay 09867 for 90% of Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacteroides fragilis strains were between 0.008 and 2 micrograms/ml. Bay 09867 was considerably more active against the gram-negative bacteria tested than were other agents tested. Gentamicin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, P. aeruginosa, and methicillin-resistant S. aureus were highly susceptible to Bay 09867. Strains less susceptible to nalidixic acid and norfloxacin tended to be less susceptible to Bay 09867. The protein binding of Bay 09867 was about 20%.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Newsom S. W., Matthews J., Amphlett M., Warren R. E. Norfloxacin and the antibacterial gamma pyridone beta carboxylic acids. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jul;10(1):25–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Une T., Osada Y., Ogawa H., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of DL-8280, a new oxazine derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



