Abstract
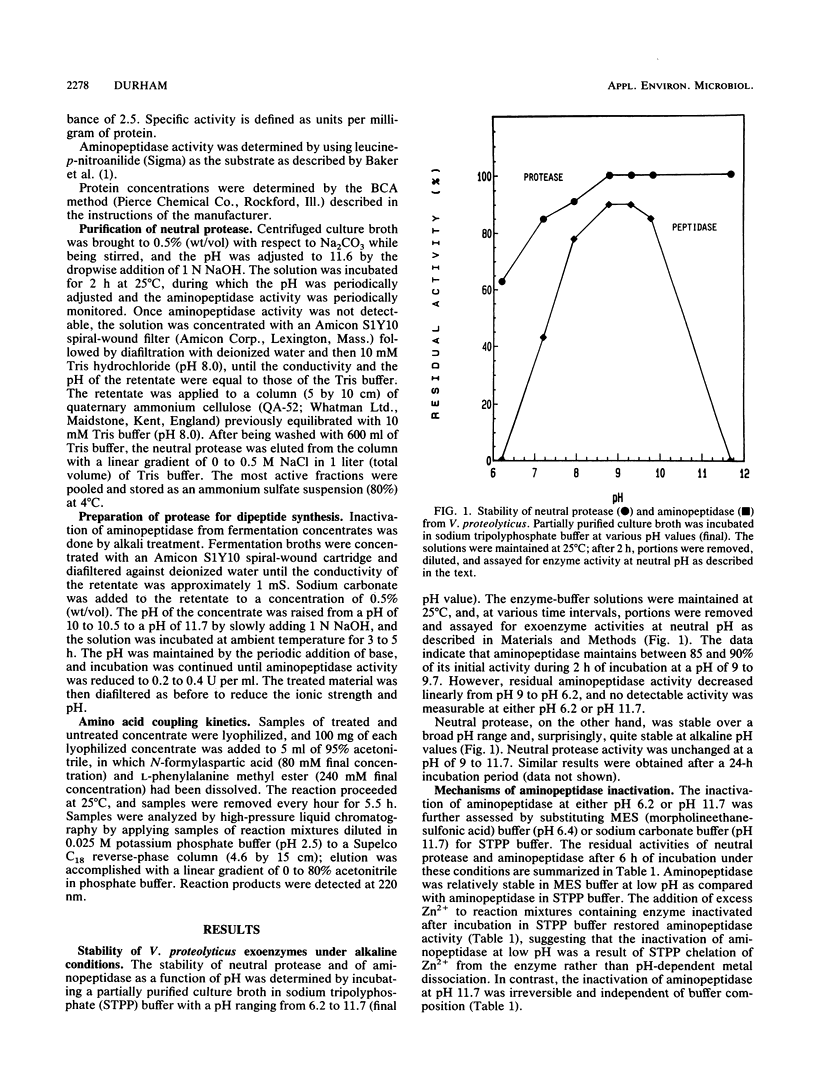
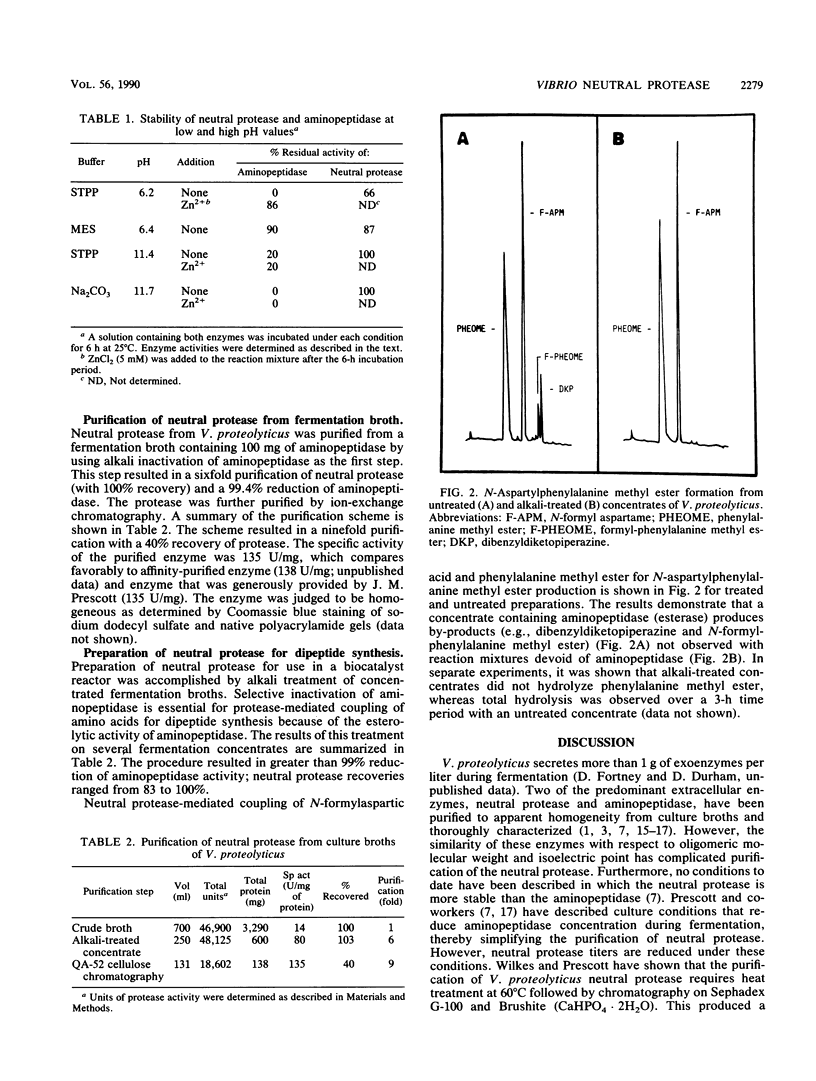
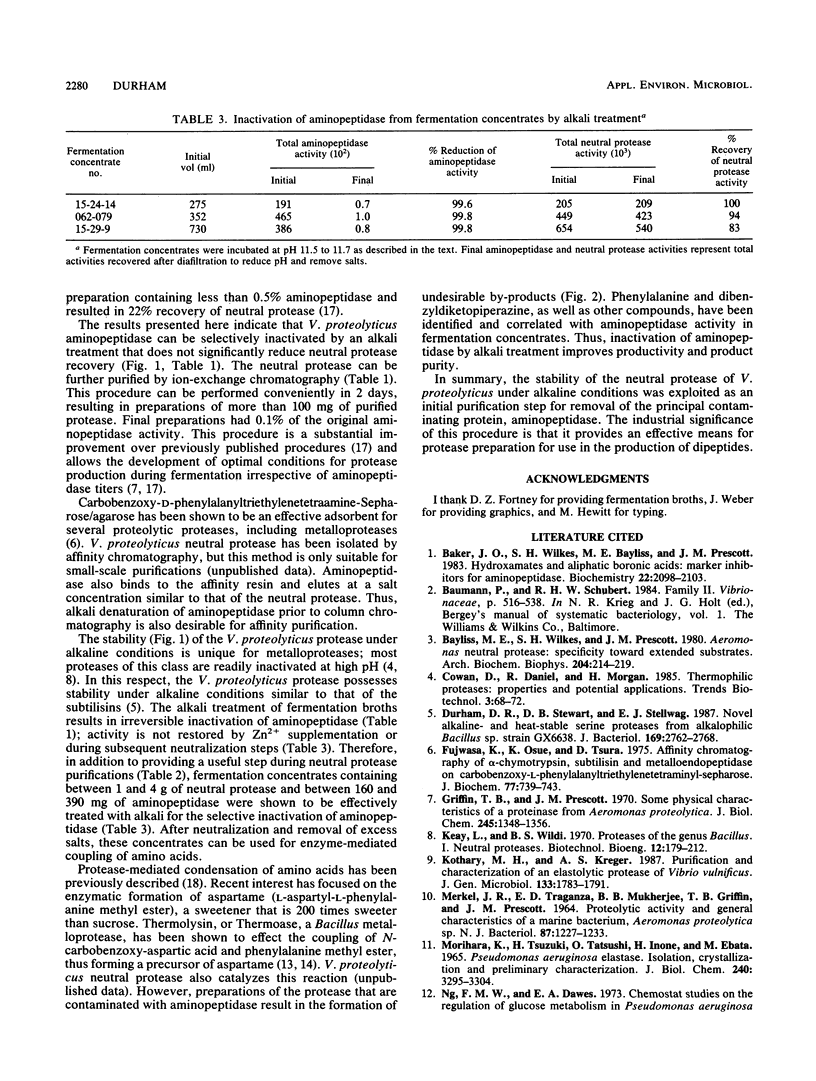
A procedure is described for the purification of a neutral protease from fermentation broths of Vibrio proteolyticus. The key feature of the purification scheme is the selective, irreversible inactivation of a contaminating exoenzyme, aminopeptidase, by alkali treatment, rather than removal of this enzyme by conventional chromatographic methods. Fermentation broths or concentrates were brought to pH 11.5 to 11.7 by Na2CO3-NaOH addition and incubated at 25 degrees C until aminopeptidase activity was diminished. The alkali treatment resulted in greater than 99% reduction of aminopeptidase activity with minimal loss of neutral protease activity. The neutral protease could be further purified to apparent homogeneity by QA-52 cellulose chromatography. The alkali treatment of fermentation concentrates was also useful for preparation of V. proteolyticus neutral protease to effect the coupling of N-protected aspartic acid and phenylalanine methyl ester for the production of N-aspartylphenylalanine methyl ester, a precursor for the sweetener aspartame.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. O., Wilkes S. H., Bayliss M. E., Prescott J. M. Hydroxamates and aliphatic boronic acids: marker inhibitors for aminopeptidase. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2098–2103. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. E., Wilkes S. H., Prescott J. M. Aeromonas neutral protease: specificity toward extended substrates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 1;204(1):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham D. R., Stewart D. B., Stellwag E. J. Novel alkaline- and heat-stable serine proteases from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain GX6638. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2762–2768. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2762-2768.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K., Osue K., Tsuru D. Affinity chromatography of alpha-chymotrypsin, subtilism, and metalloendopeptidases on carbobenzoxy-L-phenylalanyl-triehtylenetetraminyl-sepharose. J Biochem. 1975 Apr;77(4):739–743. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T. B., Prescott J. M. Some physical characteristics of a proteinase from Aeromonas proteolytica. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1348–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keay L., Wildi B. S. Proteases of the genus Bacillus. I. Neutral proteases. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Mar;12(2):179–212. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary M. H., Kreger A. S. Purification and characterization of an elastolytic protease of Vibrio vulnificus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1783–1791. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel J. R., Traganza E. D., Mukherjee B. B., Griffin T. B., Prescott J. M. Proteolytic activity and general characteristics of a marine bacterium, Aeromonas proteolytica sp. N. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1227–1233. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1227-1233.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng F. M., Dawes E. A. Chemostat studies on the regulation of glucose metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by citrate. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):129–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1320129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. M., Wilkes S. H. Aeromonas aminopeptidase. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:530–543. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes S. H., Bayliss M. E., Prescott J. M. Critical ionizing groups in Aeromonas neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1821–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H. Enzymatic catalysts in organic synthesis. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1145–1152. doi: 10.1126/science.2658059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



