Abstract
Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli strain collections harbor heterogeneous groups of bacteria in which two main types of strains may be distinguished, differing both in the symbiotic plasmid and in the chromosome. We have analyzed under laboratory conditions the competitive abilities of the different types of Rhizobium strains capable of nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris L. bean. R. leguminosarum bv. phaseoli type I strains (characterized by nif gene reiterations and a narrow host range) are more competitive than type II strains (that have a broad host range), and both types are more competitive than the promiscuous rhizobia isolated from other tropical legumes able to nodulate beans. Type I strains become even more competitive by the transfer of a non-Sym, 225-kilobase plasmid from type II strain CFN299. This plasmid has been previously shown to enhance the nodulation and nitrogen fixation capabilities of Agrobacterium tumefaciens transconjugants carrying the Sym plasmid of strain CFN299. Other type I R. leguminosarum bv. phaseoli transconjugants carrying two symbiotic plasmids (type I and type II) have been constructed. These strains have a diminished competitive ability. The increase of competitiveness obtained in some transconjugants seems to be a transient property.
Full text
PDF

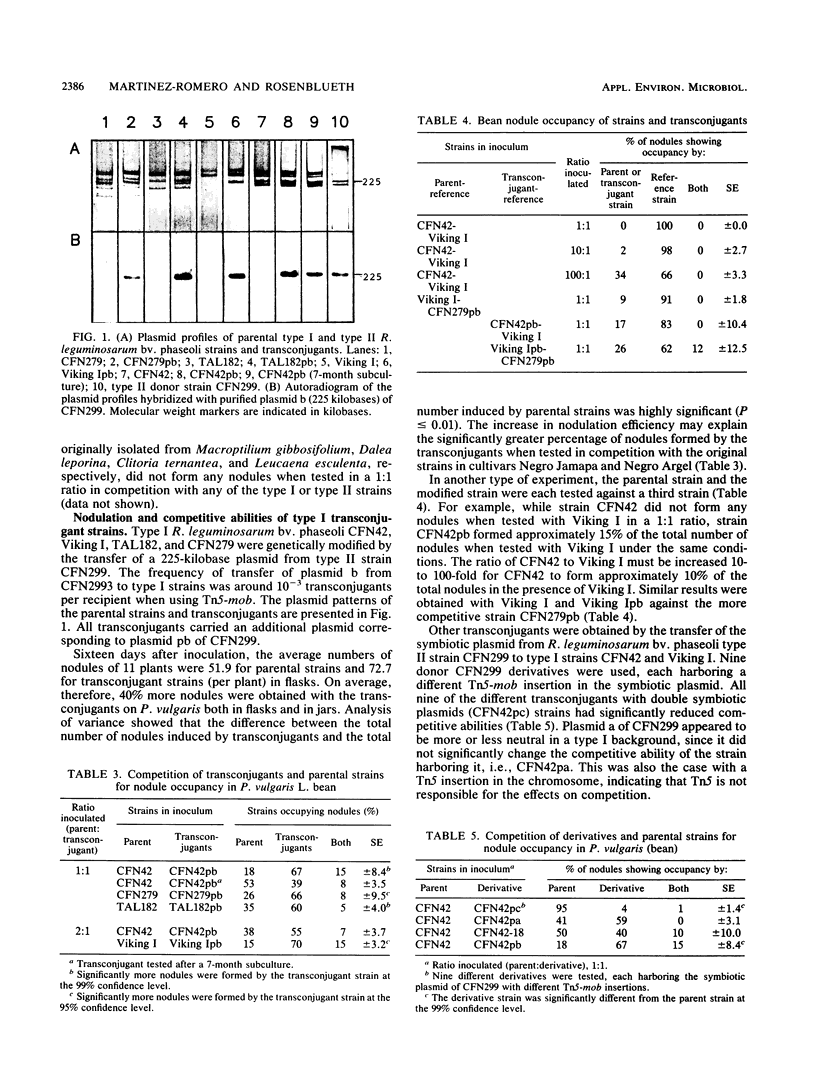


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo R. S., Maya-Flores J., Barnes-McConnell D., Yokoyama C., Dazzo F. B., Bliss F. A. Semienclosed Tube Cultures of Bean Plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) for Enumeration of Rhizobium phaseoli by the Most-Probable-Number Technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):954–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.954-956.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brom S., Martinez E., Dávila G., Palacios R. Narrow- and Broad-Host-Range Symbiotic Plasmids of Rhizobium spp. Strains That Nodulate Phaseolus vulgaris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1280–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1280-1283.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromfield E. S., Sinha I. B., Wolynetz M. S. Influence of Location, Host Cultivar, and Inoculation on the Composition of Naturalized Populations of Rhizobium meliloti in Medicago sativa Nodules. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.1077-1084.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Zurkowski W., Shine J., Rolfe B. G. Sym plasmid transfer to various symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium trifolii, R. leguminosarum, and R. meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1035–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1035-1045.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling D. N., Broughton W. J. Competition for nodulation of legumes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:131–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling D. N., Samrey U., Stanley J., Broughton W. J. Cloning of Rhizobium leguminosarum genes for competitive nodulation blocking on peas. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1345–1348. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1345-1348.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHRAEUS G. The infection of clover root hairs by nodule bacteria studied by a simple glass slide technique. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Apr;16(2):374–381. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-2-374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Brom S., Martínez E., Piñero D., Romero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Reiterated DNA sequences in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5782–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5782-5788.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Pardo M. A., Leija A., Martínez E., Romero D., Piñero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Genomic instability in Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1191–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1191-1196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handelsman J., Brill W. J. Erwinia herbicola isolates from alfalfa plants may play a role in nodulation of alfalfa by Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):818–821. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.818-821.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamicker B. J., Brill W. J. Methods To Alter the Recovery and Nodule Location of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Inoculant Strains on Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1737–1742. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1737-1742.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez E., Palacios R., Sánchez F. Nitrogen-fixing nodules induced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring Rhizobium phaseoli plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2828–2834. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2828-2834.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moawad H., Bohlool B. B. Competition Among Rhizobium spp. for Nodulation of Leucaena leucocephala in Two Tropical Soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.5-9.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinero D., Martinez E., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships among isolates of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2825–2832. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2825-2832.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert F. M., Schmidt E. L. Population Changes and Persistence of Rhizobium phaseoli in Soil and Rhizospheres. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.550-556.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton P. W., Tavares J. W. Inoculation response of legumes in relation to the number and effectiveness of indigenous Rhizobium populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):1013–1018. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.1013-1018.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett E. W., Barta T. M. Trifolitoxin Production and Nodulation Are Necessary for the Expression of Superior Nodulation Competitiveness by Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii Strain T24 on Clover. Plant Physiol. 1987 Oct;85(2):335–342. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett E. W. Isolation of genes involved in nodulation competitiveness from Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii T24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3810–3814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



