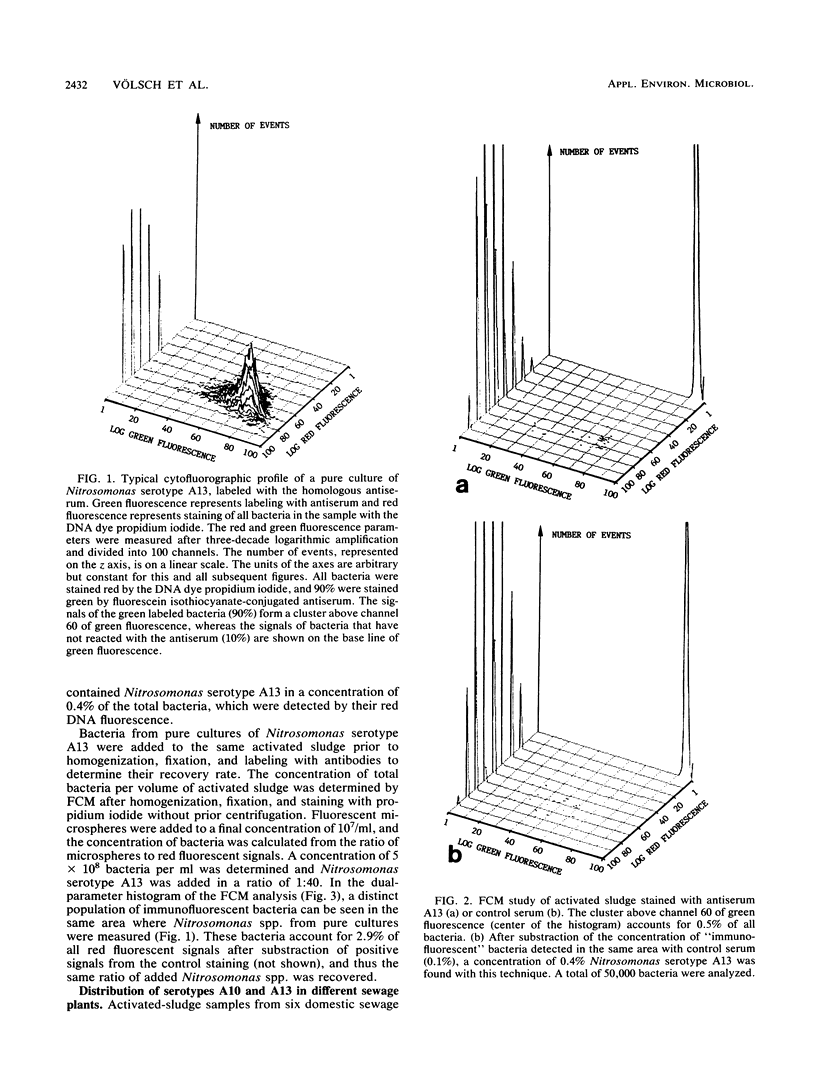
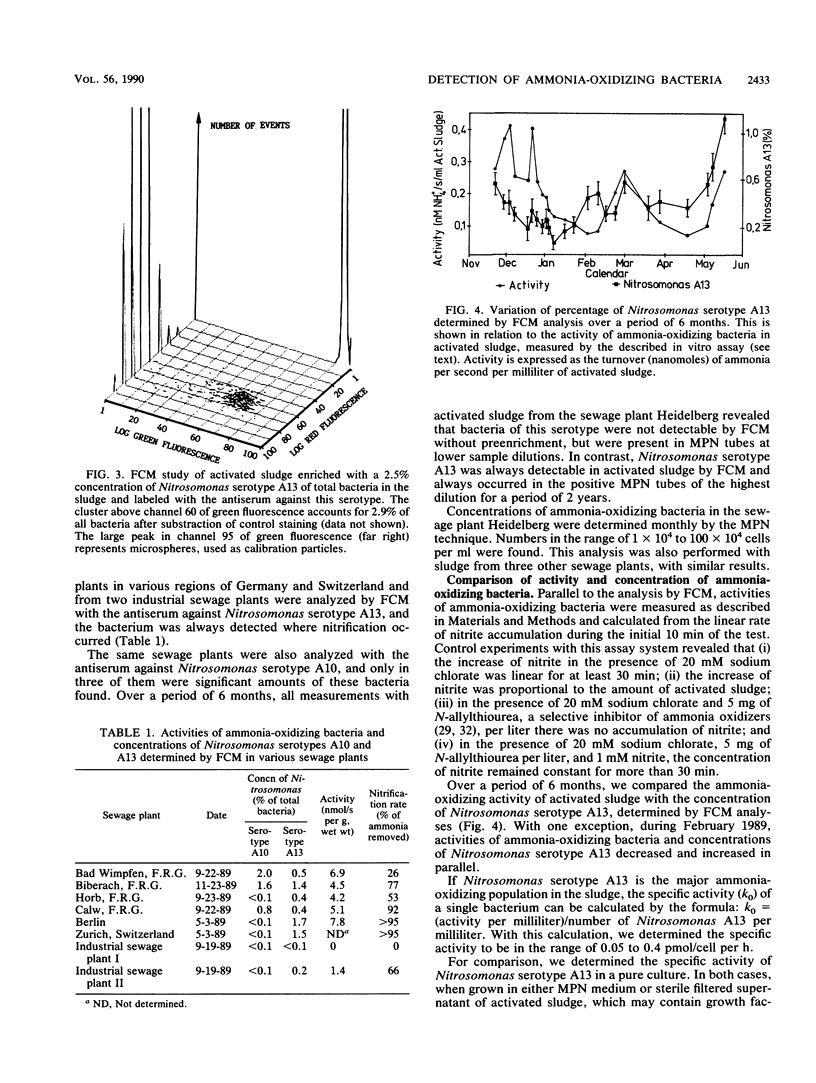
Abstract
Two different serotypes of the genus Nitrosomonas were isolated from samples of the sewage plant Heidelberg. These nitrifiers were enumerated in activated sludge of various other sewage plants after immunofluorescent labeling and staining with propidium iodide by flow cytometry. The concentrations of these serotypes of Nitrosomonas spp. were in the range of 0.1 to 2%. Also, a test for the determination of the activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria was developed. Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria were specifically inhibited with sodium chlorate, and the activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria could be calculated from the increase of nitrite. Concentrations and activities of ammonia oxidizers were measured for a period of 6 months in the sewage plant Heidelberg. With one exception, activities and concentrations of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria decreased and increased in parallel.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeliovich A. Nitrifying bacteria in wastewater reservoirs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):754–760. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.754-760.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belser L. W., Mays E. L. Specific inhibition of nitrite oxidation by chlorate and its use in assessing nitrification in soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):505–510. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.505-510.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belser L. W., Mays E. L. Use of nitrifier activity measurements to estimate the efficiency of viable nitrifier counts in soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):945–948. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.945-948.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belser L. W. Population ecology of nitrifying bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:309–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belser L. W., Schmidt E. L. Diversity in the ammonia-oxidizing nitrifier population of a soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):584–588. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.584-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belser L. W., Schmidt E. L. Serological diversity within a terrestrial ammonia-oxidizing population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):589–593. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.589-593.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Nonspecific staining: its control in immunofluorescence examination of soil. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1012–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruchhaus H., Geyer G. Studies on the alkaline hydrolysis of nucleic acid in tissue sections. V. Cytophotometric evaluation of the effect of an alkaline hydrolysis on the Feulgen reaction. Histochem J. 1974 Sep;6(5):579–581. doi: 10.1007/BF01003273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. B. Population ecology of nitrifiers in a stream receiving geothermal inputs of ammonium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1170-1177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. W., Baigent G. J. Method for flow cytometric detection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):689–695. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.689-695.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Autecological study of the chemoautotroph Nitrobacter by immunofluorescence. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.124-129.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. K., Knowles R. Inhibition of chemoautotrophic nitrification by sodium chlorate and sodium chlorite: a reexamination. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1178–1182. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1178-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram M., Cleary T. J., Price B. J., Price R. L., 3rd, Castro A. Rapid detection of Legionella pneumophila by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1982 Sep;3(2):134–137. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour J. D., Robson J. A., Arndt C. W., Schulte T. H. Detection of Escherichia coli in blood using flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1985 May;6(3):186–190. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matulewich V. A., Strom P. F., Finstein M. S. Length of incubation for enumerating nitrifying bacteria present in various environments. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):265–268. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.265-268.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Lee D., Cowles J. R. Comparison of nucleic acid content in populations of free-living and symbiotic Rhizobium meliloti by flow microfluorometry. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1156–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1156-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. P., Martin K. L. Evaluation of a microfluorometer in immunofluorescence assays of individual spores of Bacillus anthracis and Bacillus cereus. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Mar 26;49(3):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahar E., Lamed R., Ofek I. Rapid identification of Streptococcus pyogenes by flow cytometry. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;2(3):192–195. doi: 10.1007/BF02029514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano S., Walker N. Isolation of ammonia-oxidizing autotrophic bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;31(4):493–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen H. B., Boye E. Escherichia coli growth studied by dual-parameter flow cytophotometry. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1091–1094. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1091-1094.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson T. G., Boon A. G., Trotman C. N. Inhibition of nitrification in the activated sludge process of sewage disposal. J Appl Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;29(2):266–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1966.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. B., Carlucci A. F. Marine ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: serological diversity determined by immunofluorescence in culture and in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):194–201. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.194-201.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. B., Perry M. J. Immunofluorescent Assay for the Marine Ammonium-Oxidizing Bacterium Nitrosococcus oceanus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):913–918. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.913-918.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



