Abstract
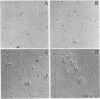
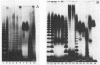
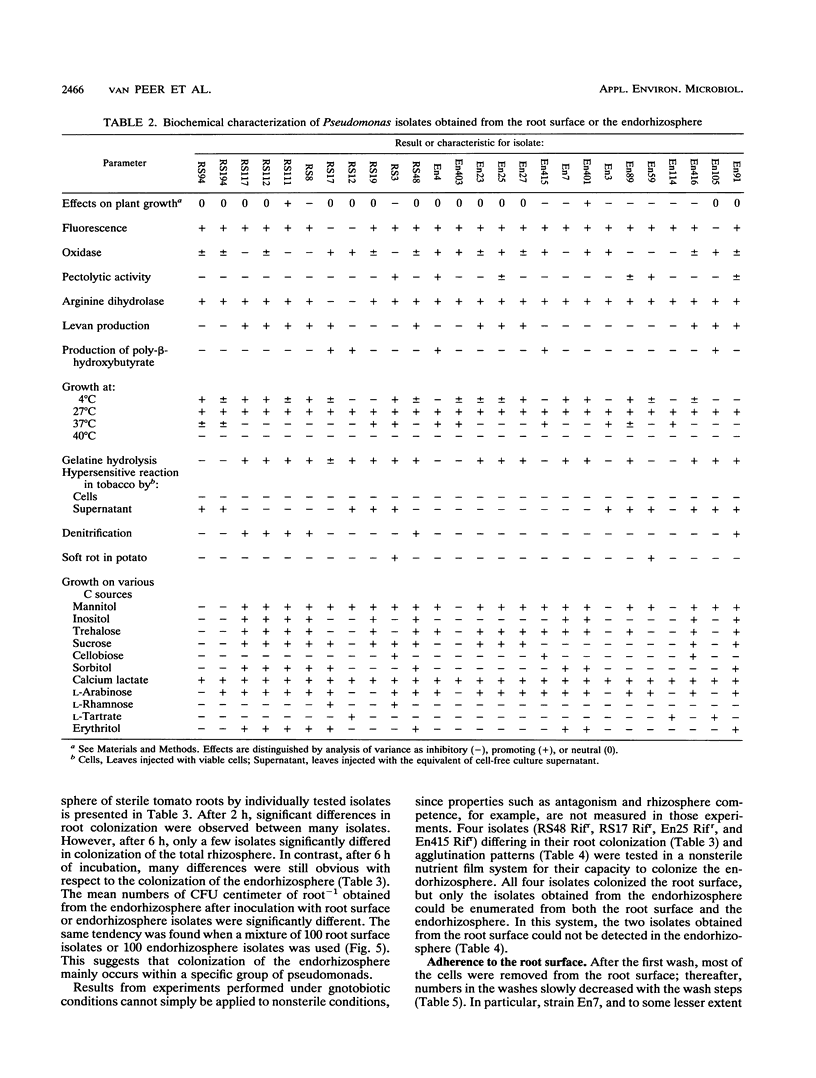
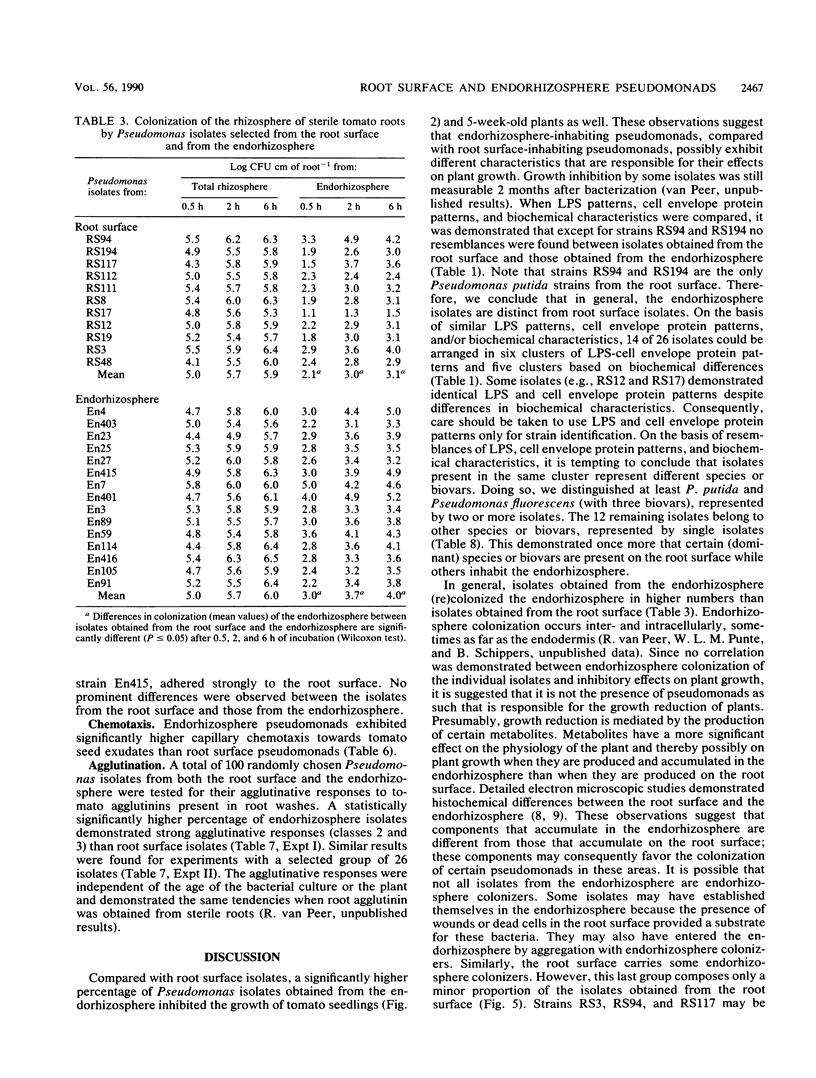
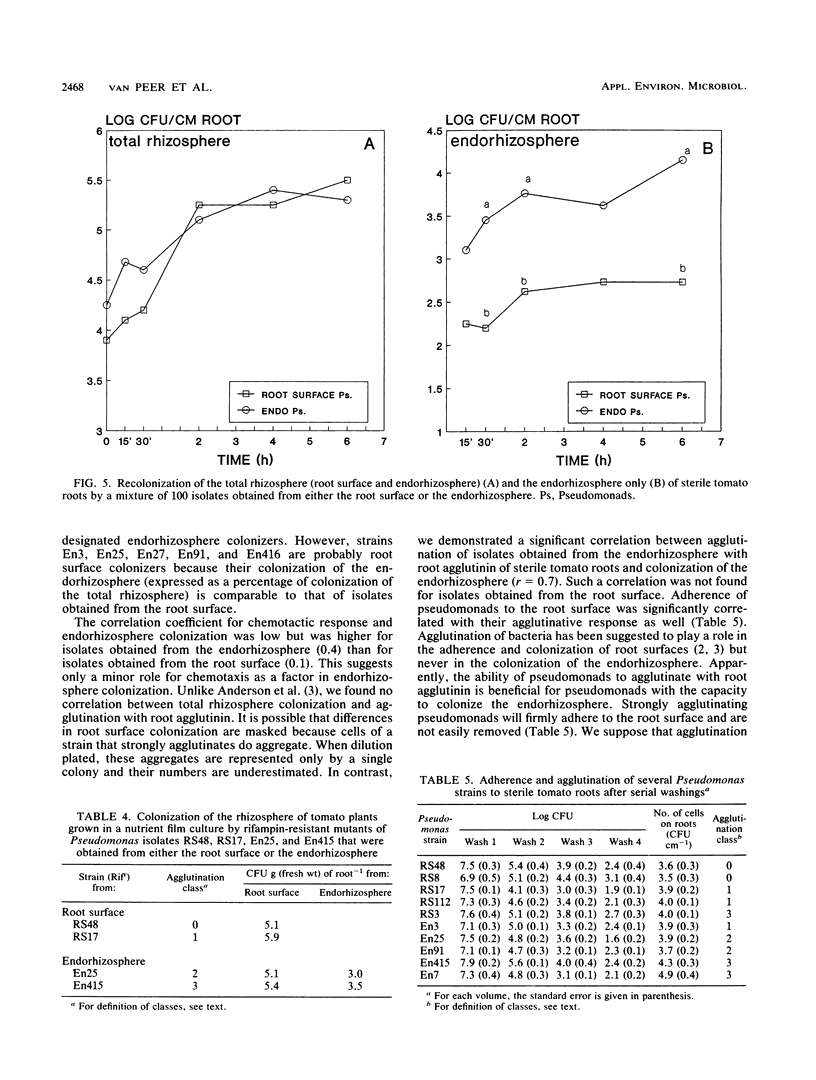
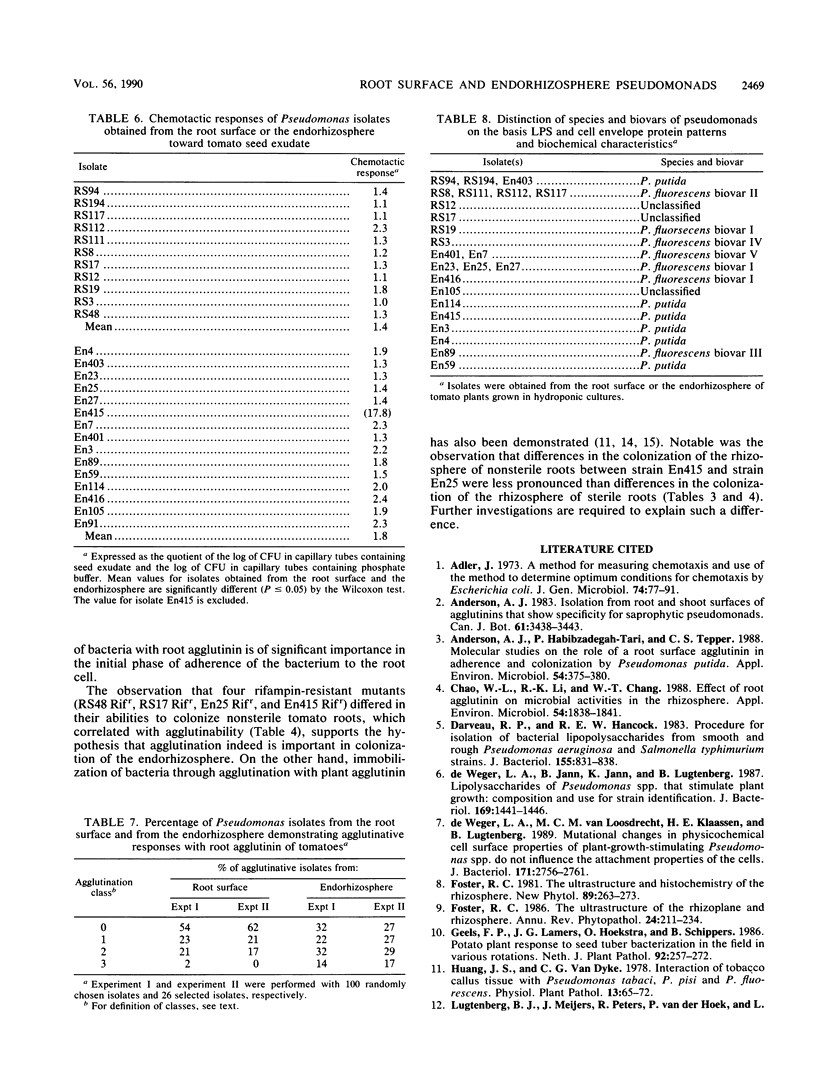
An extensive colonization of the endorhizosphere by fluorescent pseudomonads was observed in tomato plants grown on artificial substrates. These studies reveal that a significantly higher percentage of pseudomonads obtained from the endorhizosphere (30%) reduced plant growth than those obtained from the root surface (4%). Lipopolysaccharide patterns, cell envelope protein patterns, and other biochemical characteristics indicated that Pseudomonas isolates obtained from the endorhizosphere are distinct from Pseudomonas isolates obtained from the root surface. Isolates from the endorhizosphere especially were able to recolonize the endorhizosphere of both sterile and nonsterile tomato roots. The ability of the endorhizosphere isolates to colonize the endorhizosphere significantly correlated with their agglutination by tomato root agglutinin but did not correlate with chemotaxis to seed exudates of tomato. No correlation between colonization of the endorhizosphere and agglutination by root agglutinin could be demonstrated for the root surface isolates. We propose that agglutination of specific Pseudomonas strains by root agglutinin is of importance in the initial phase of adherence of bacteria to the root surface.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. J., Habibzadegah-Tari P., Tepper C. S. Molecular Studies on the Role of a Root Surface Agglutinin in Adherence and Colonization by Pseudomonas putida. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):375–380. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.375-380.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W. L., Li R. K., Chang W. T. Effect of root agglutinin on microbial activities in the rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1838–1841. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1838-1841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., Jann B., Jann K., Lugtenberg B. Lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas spp. that stimulate plant growth: composition and use for strain identification. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1441–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1441-1446.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., van Loosdrecht M. C., Klaassen H. E., Lugtenberg B. Mutational changes in physiochemical cell surface properties of plant-growth-stimulating Pseudomonas spp. do not influence the attachment properties of the cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2756–2761. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2756-2761.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]