Abstract
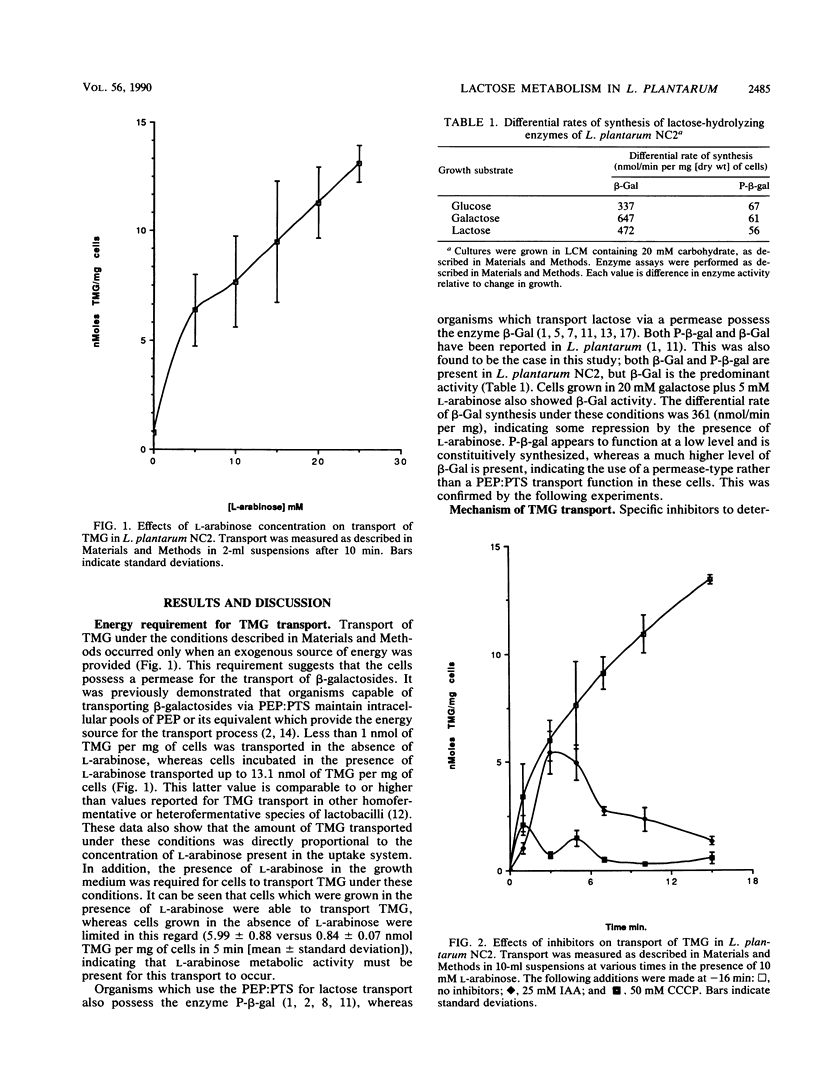
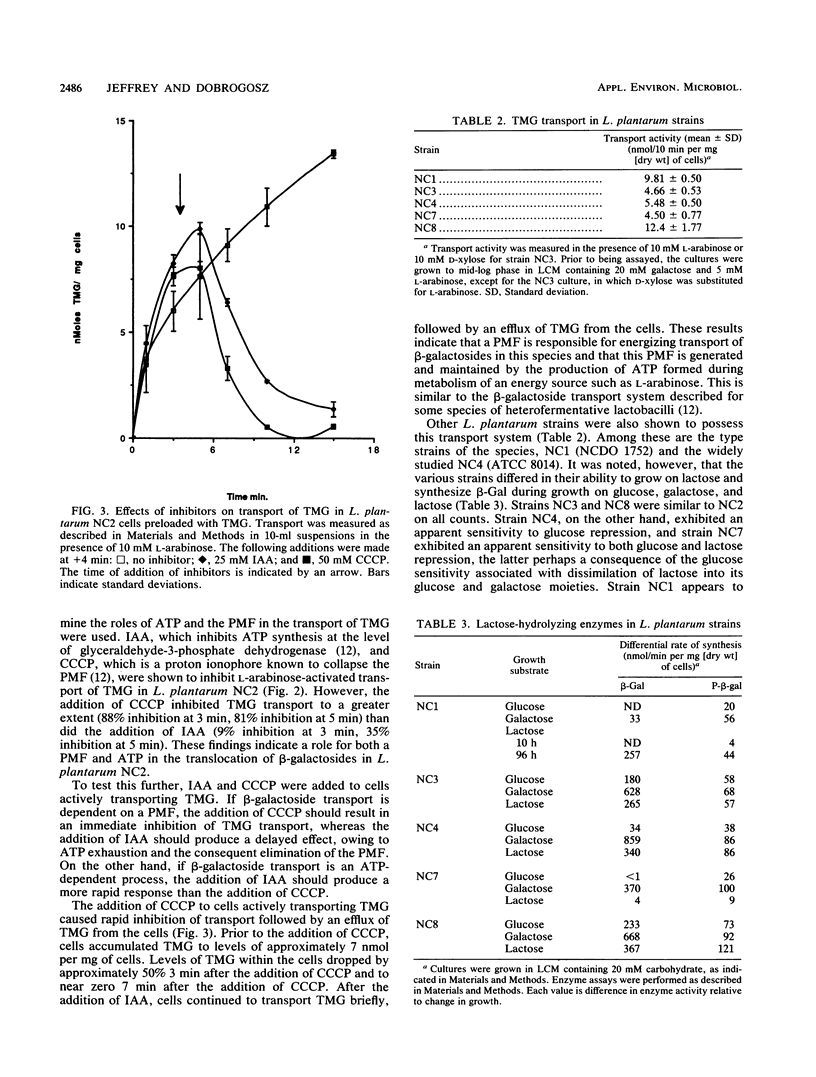
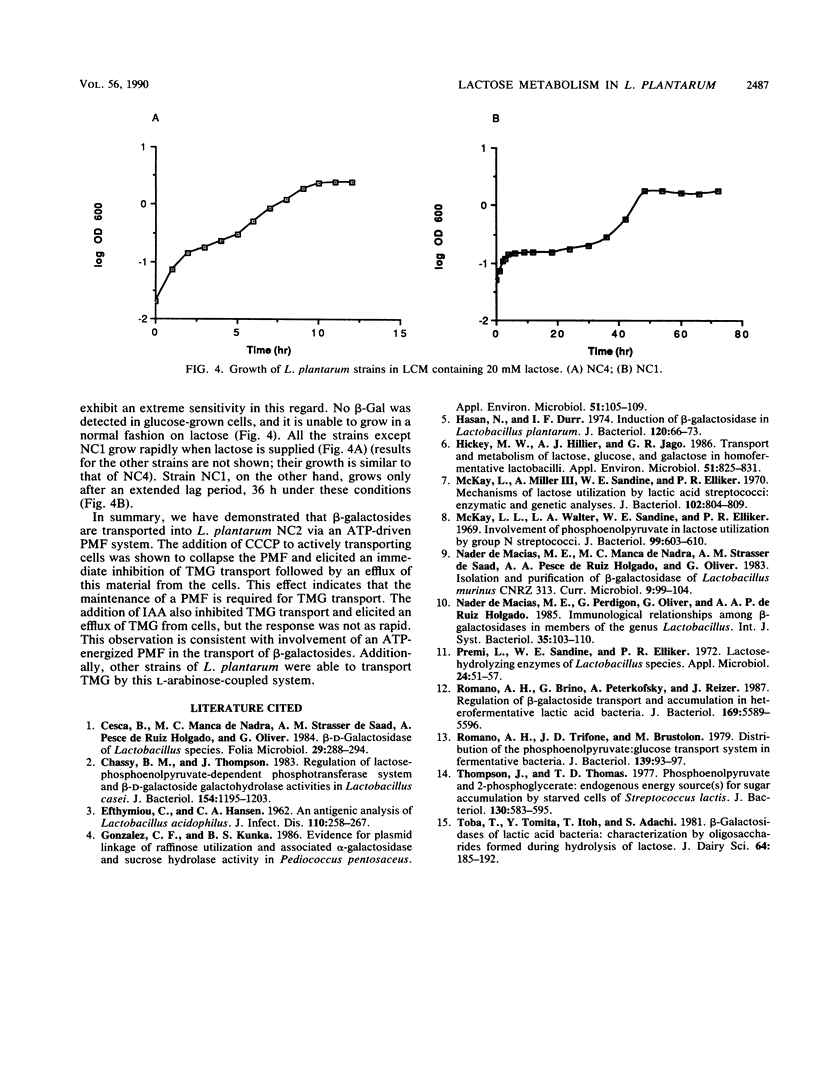
The ability of Lactobacillus plantarum NC2 to transport thiomethyl-β-d-galactoside in the presence or absence of various inhibitors was investigated to determine the mechanism of β-galactoside transport in this bacterium. A novel system employing l-arabinose as an energy-generating compound is described, and evidence that this transport is energized by an ATP-driven proton motive force is presented.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cesca B., Manca de Nadra M. C., Strasser de Saad A. M., Pesce de Ruiz Holgado A., Oliver G. beta-D-galactosidase of Lactobacillus species. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1984;29(4):288–294. doi: 10.1007/BF02875959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Thompson J. Regulation of lactose-phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system and beta-D-phosphogalactoside galactohydrolase activities in Lactobacillus casei. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1195–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1195-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EFTHYMIOU C., HANSEN P. A. An antigenic analysis of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Infect Dis. 1962 May-Jun;110:258–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Evidence for Plasmid Linkage of Raffinose Utilization and Associated alpha-Galactosidase and Sucrose Hydrolase Activity in Pediococcus pentosaceus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):105–109. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.105-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan N., Durr I. F. Induction of beta-galactosidase in Lactobacillus plantarum. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):66–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.66-73.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey M. W., Hillier A. J., Jago G. R. Transport and metabolism of lactose, glucose, and galactose in homofermentative lactobacilli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):825–831. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.825-831.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Walter L. A., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.603-610.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L., Miller A., 3rd, Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Mechanisms of lactose utilization by lactic acid streptococci: enzymatic and genetic analyses. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):804–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.804-809.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premi L., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Lactose-hydrolyzing enzymes of Lactobacillus species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.51-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Brino G., Peterkofsky A., Reizer J. Regulation of beta-galactoside transport and accumulation in heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5589–5596. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5589-5596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Trifone J. D., Brustolon M. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate:glucose phosphotransferase system in fermentative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):93–97. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.93-97.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Thomas T. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate and 2-phosphoglycerate: endogenous energy source(s) for sugar accumulation by starved cells of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.583-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



