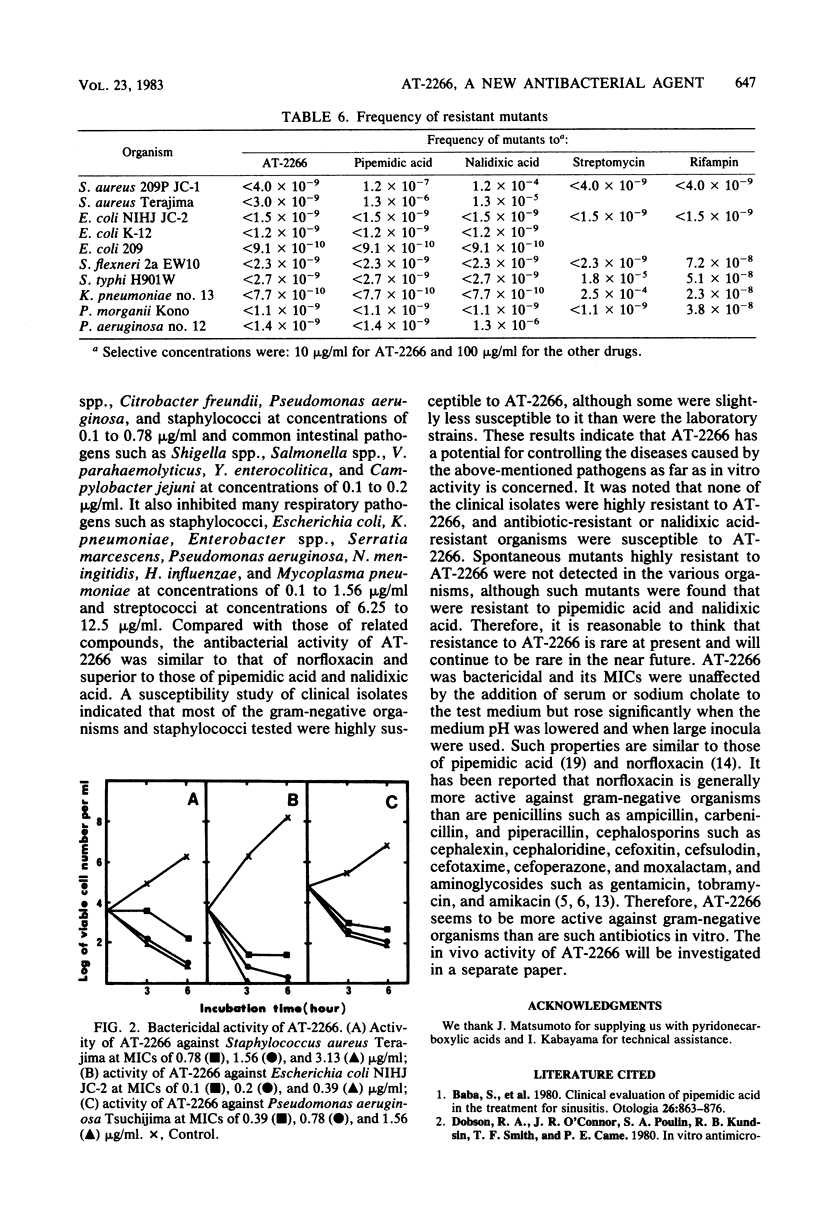
Abstract
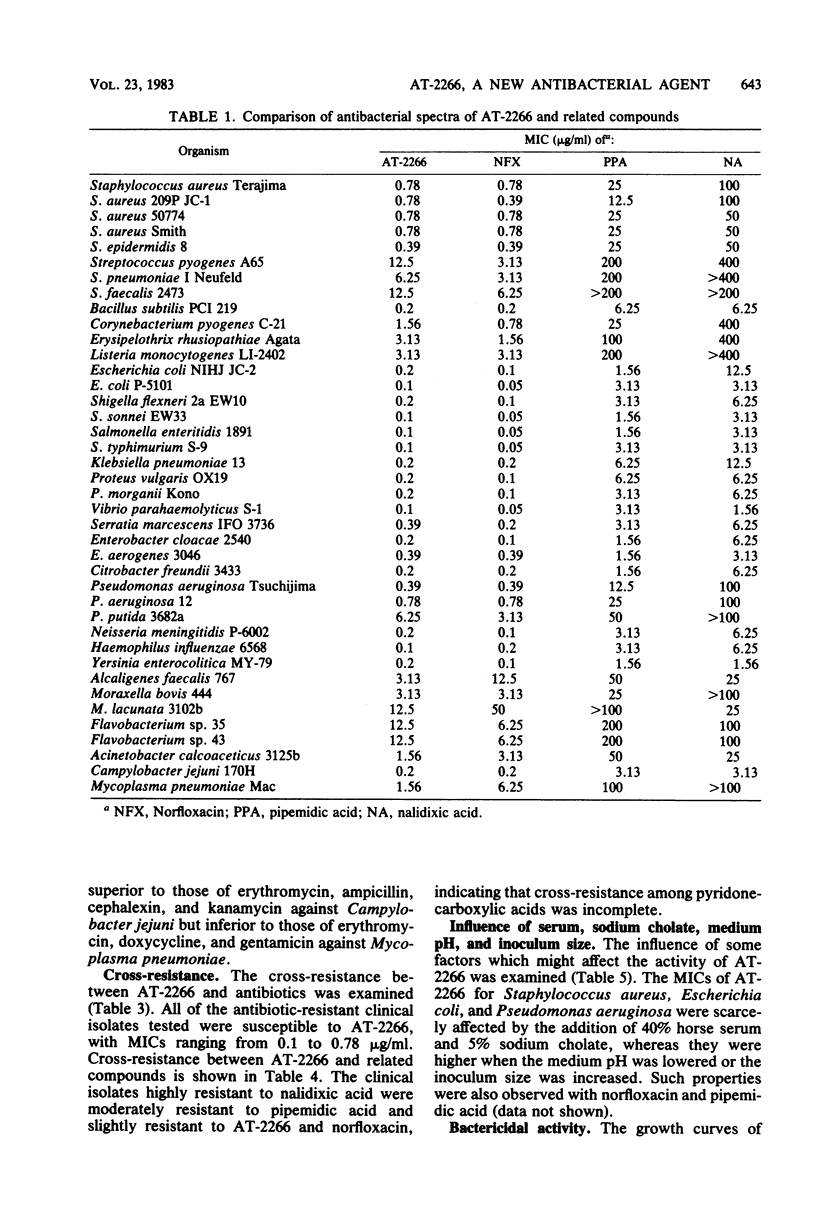
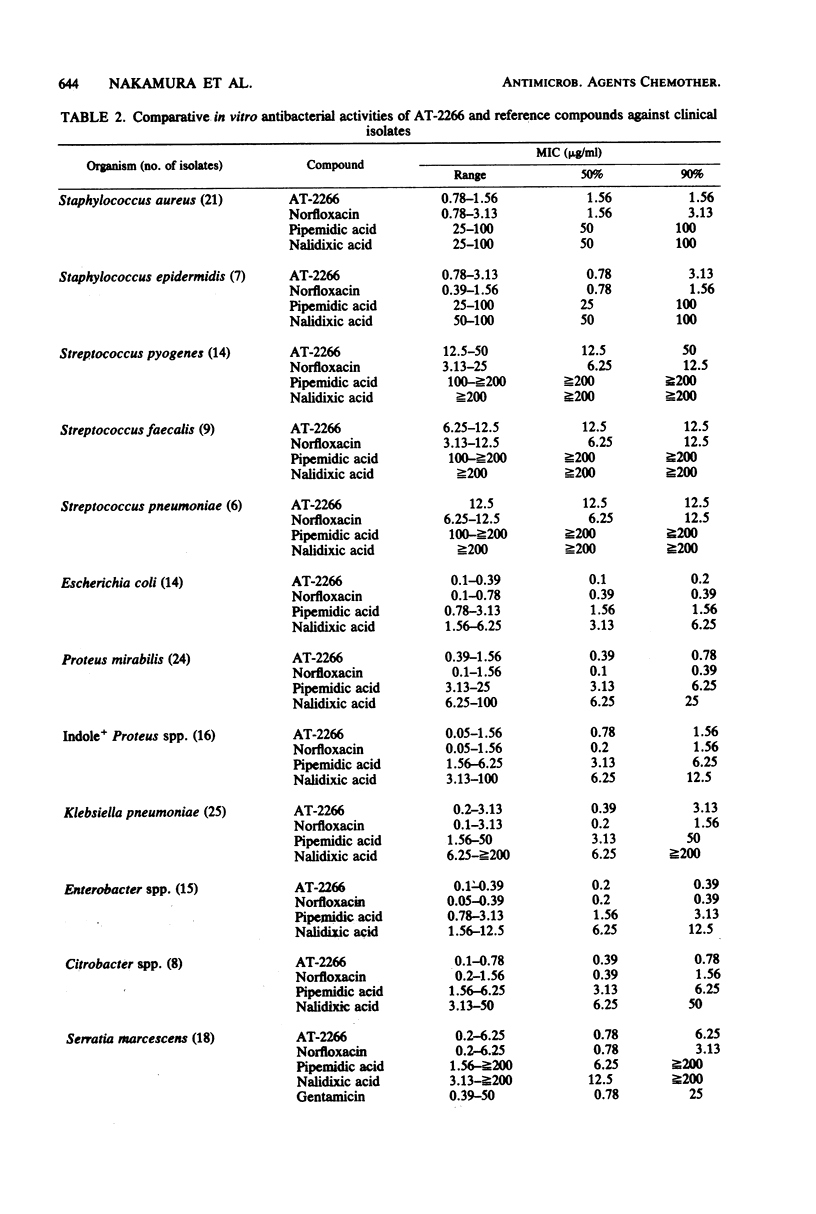
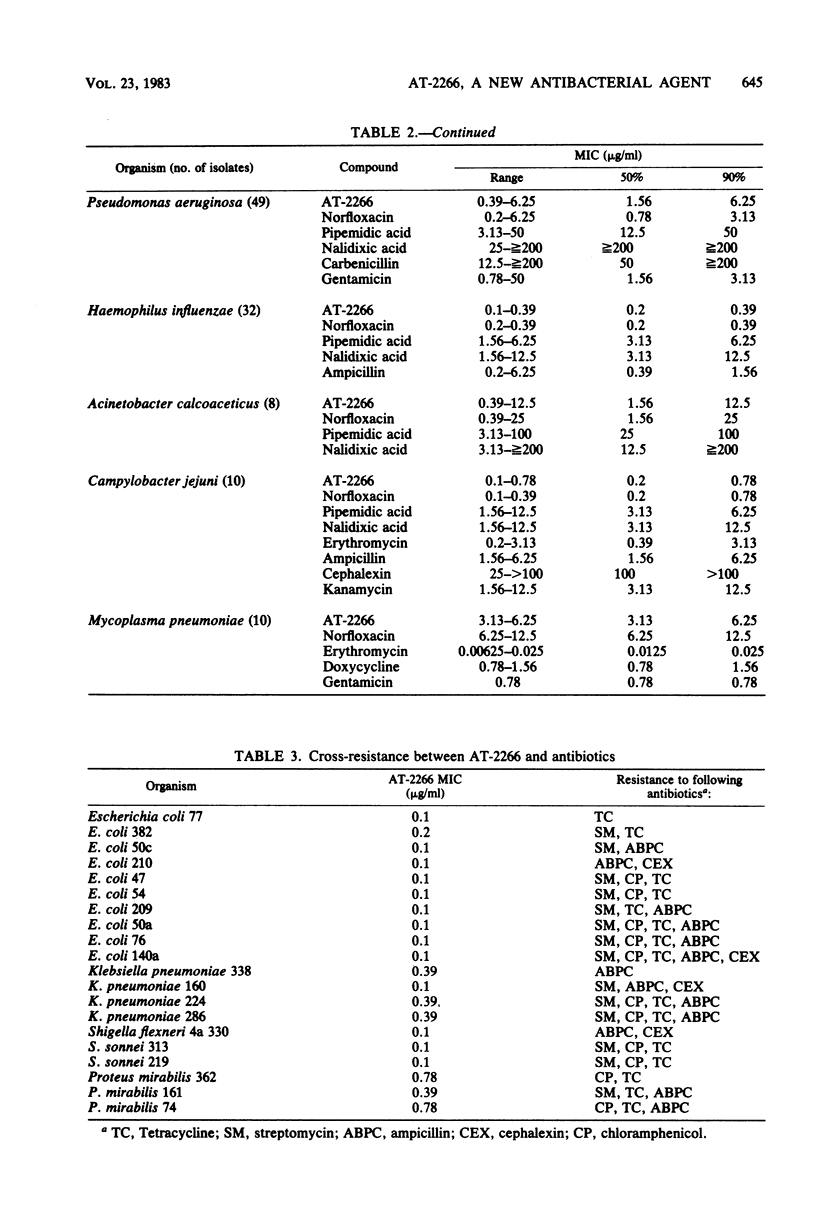
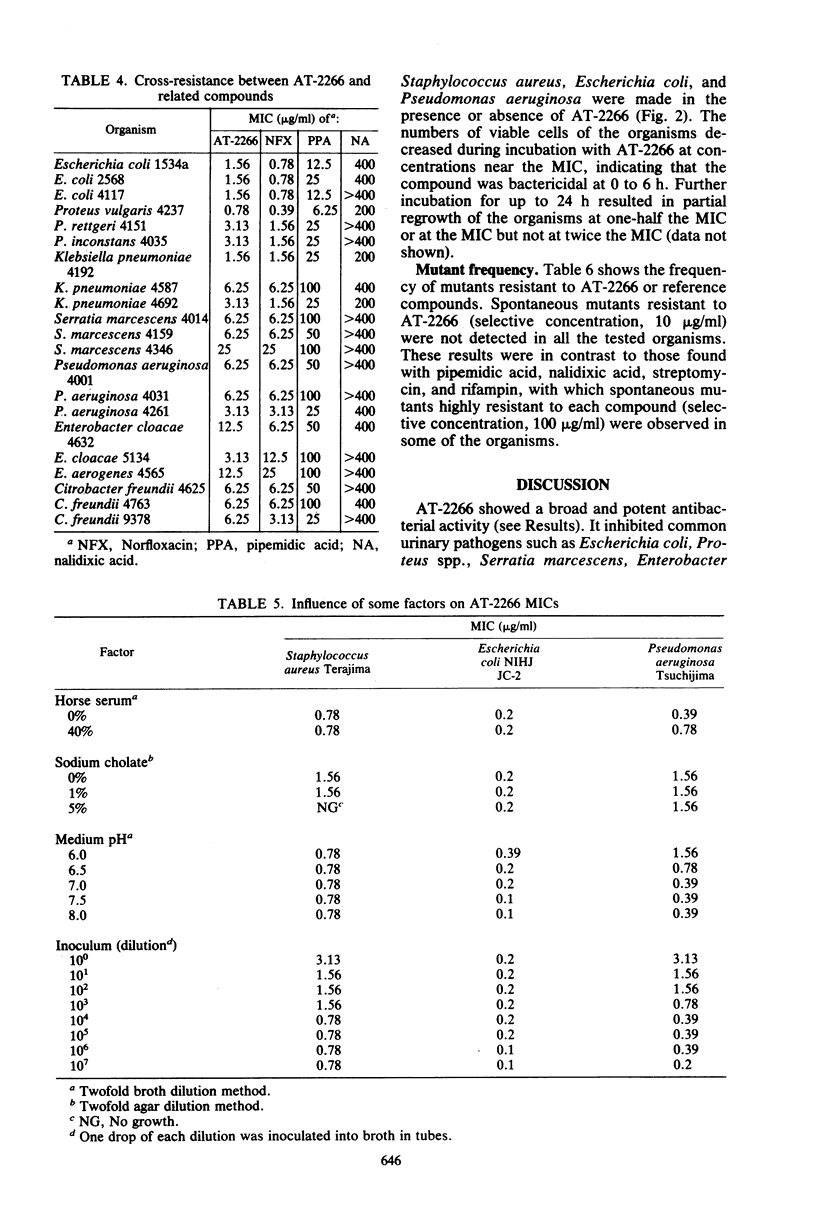
AT-2266, 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,8-naphthyridine-3 -carboxylic acid, is a new pyridonecarboxylic acid derivative with broad and potent antibacterial activity. It inhibited some gram-positive bacteria, such as staphylococci and Bacillus subtilis, and most gram-negative bacteria, including Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, and Campylobacter jejuni, at concentrations of 0.1 to 0.78 microgram/ml, and most gram-positive bacteria, glucose-nonfermenters, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae at concentrations of 1.56 to 12.5 micrograms/ml. Most of the clinical isolates tested were as susceptible to AT-2266 as were laboratory strains. The antibacterial potency of AT-2266 was higher than those of pipemidic acid and nalidixic acid and similar to that of norfloxacin. AT-2266 was not cross-resistant with antibiotics and inhibited most highly nalidixic acid-resistant bacteria at concentrations of 1.56 to 3.13 micrograms/ml. Its activity was barely affected by the addition of horse serum or sodium cholate but weakened by lowering the medium pH or increasing the inoculum size. AT-2266 was bactericidal at concentrations near its minimal inhibitory concentrations. Frequencies of mutants resistant to 10 micrograms of AT-2266 per ml were lower than 4.0 x 10(-9).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ito A., Hirai K., Inoue M., Koga H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of AM-715, a new nalidixic acid analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–108. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. Y., Gruninger R. P., Nelson S. M., Klicker R. E. Comparative in vitro activity of norfloxacin (MK-0366) and ten other oral antimicrobial agents against urinary bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):848–851. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Warren C., Shannon K., Phillips I. In vitro antibacterial activity of norfloxacin (MK-0366). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):604–607. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H., Itoh A., Murayama S., Suzue S., Irikura T. Structure-activity relationships of antibacterial 6,7- and 7,8-disubstituted 1-alkyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem. 1980 Dec;23(12):1358–1363. doi: 10.1021/jm00186a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESHER G. Y., FROELICH E. J., GRUETT M. D., BAILEY J. H., BRUNDAGE R. P. 1,8-NAPHTHYRIDINE DERIVATIVES. A NEW CLASS OF CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 Sep;91:1063–1065. doi: 10.1021/jm01240a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Takase Y., Nakamura S., Katae H., Minami A. Pipemidic acid, a new antibacterial agent active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: in vitro properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):132–138. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stilwell G., Holmes K., Turck M. In vitro evaluation of a new quinolone antibacterial. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):483–485. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick W. E., Preston D. A., White W. A., Gordee R. S. Compound 64716, a new synthetic antibacterial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):415–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



