Abstract
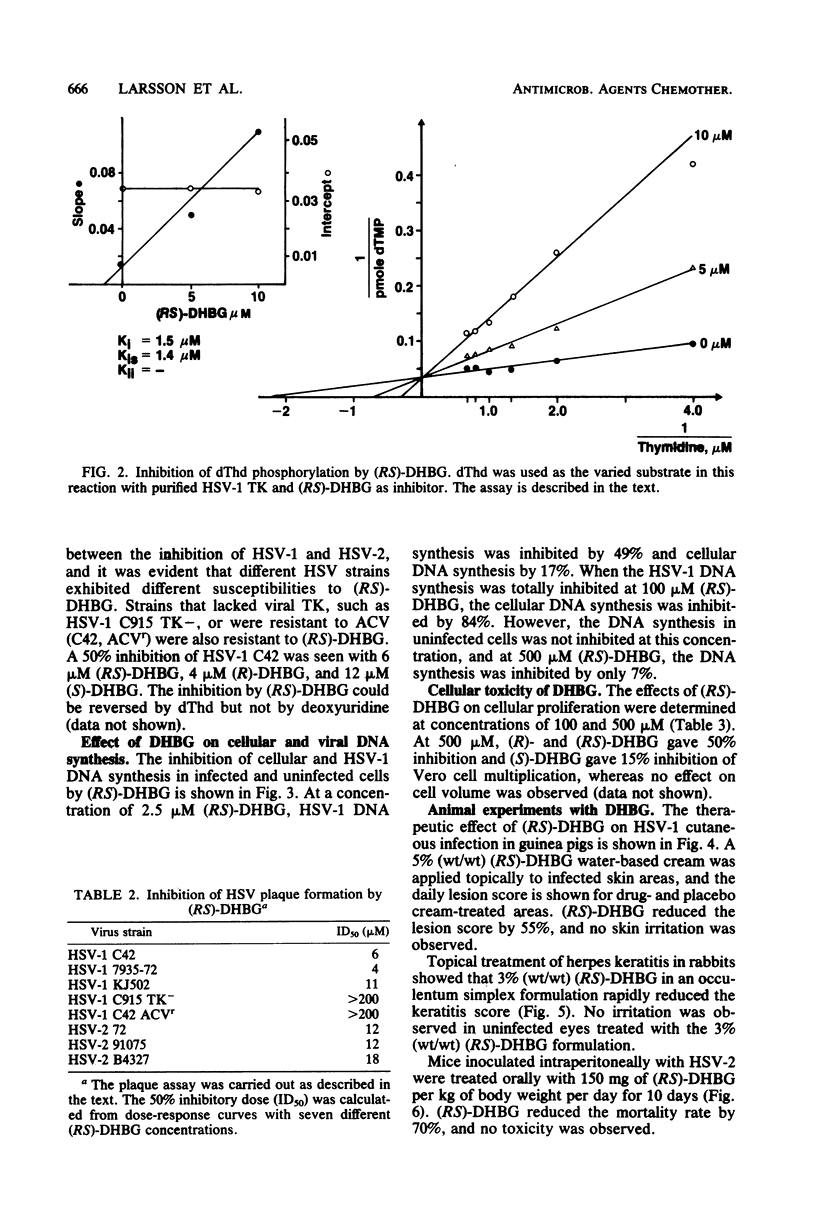
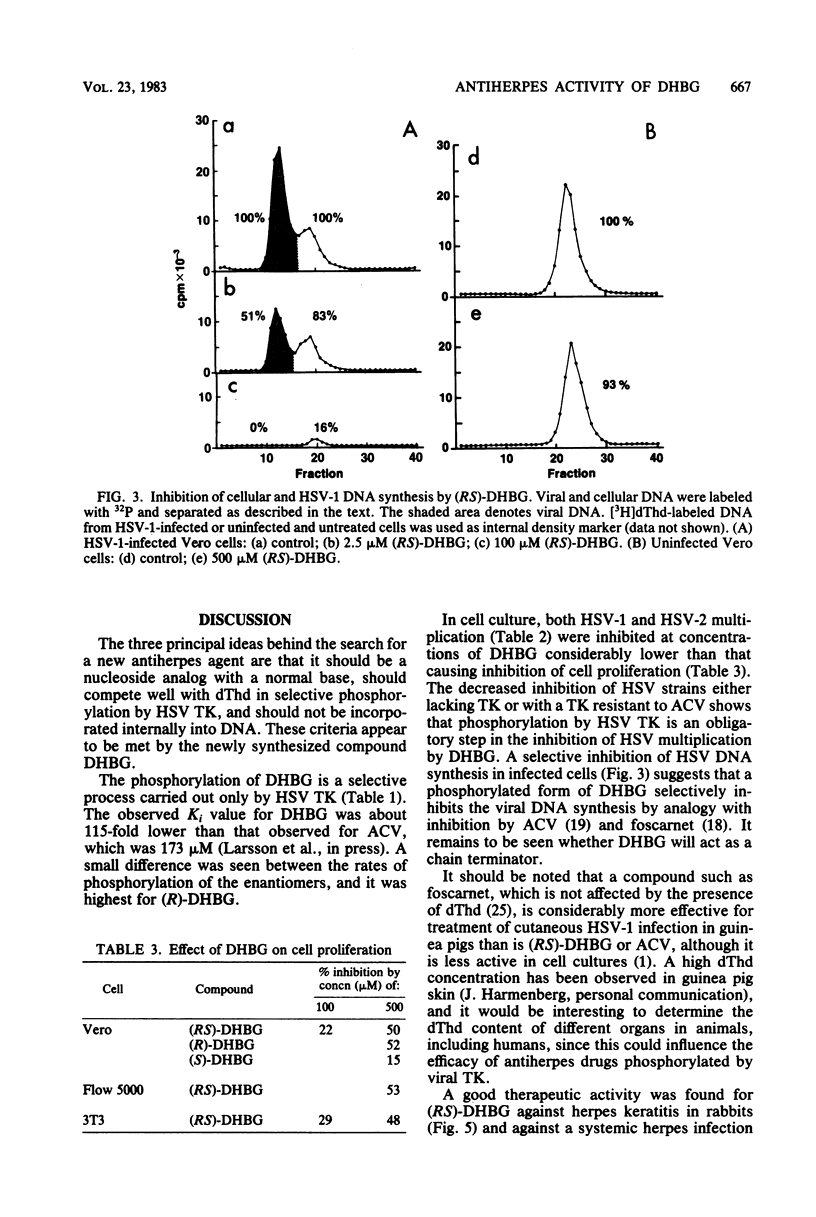
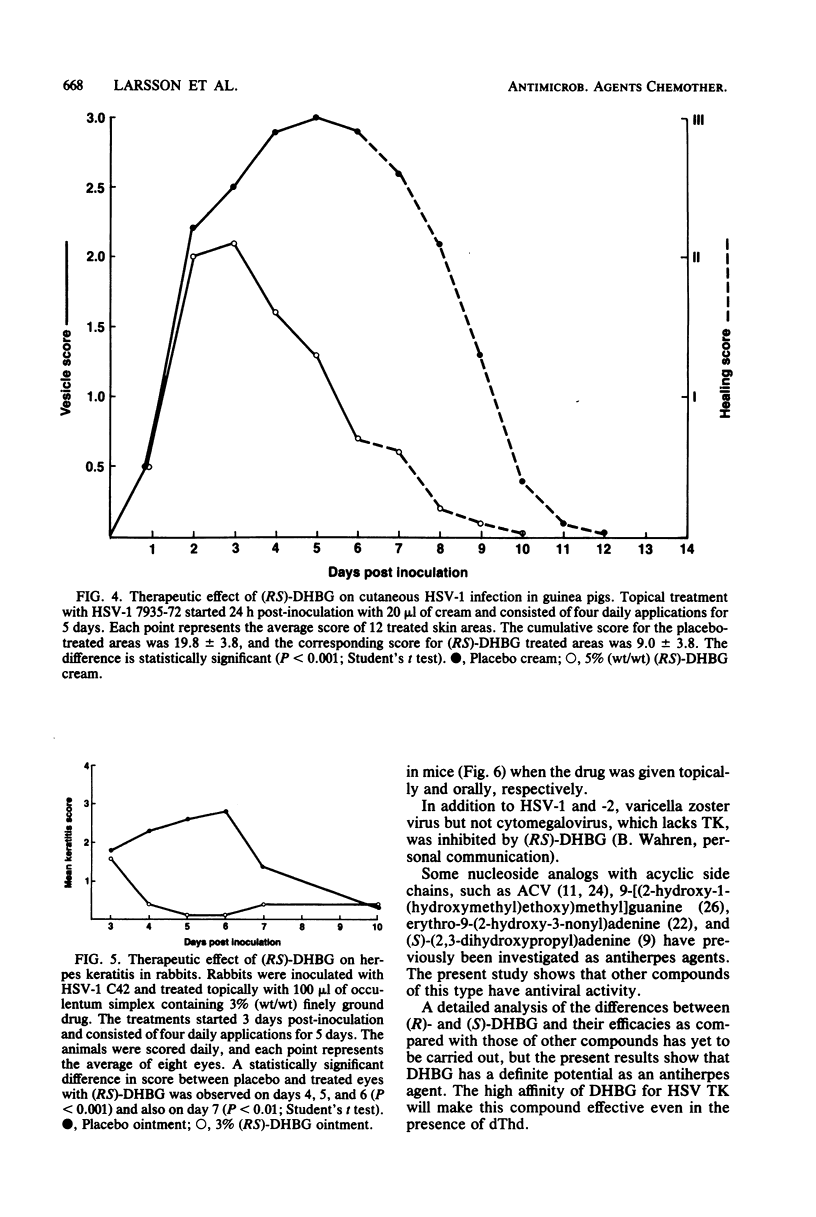
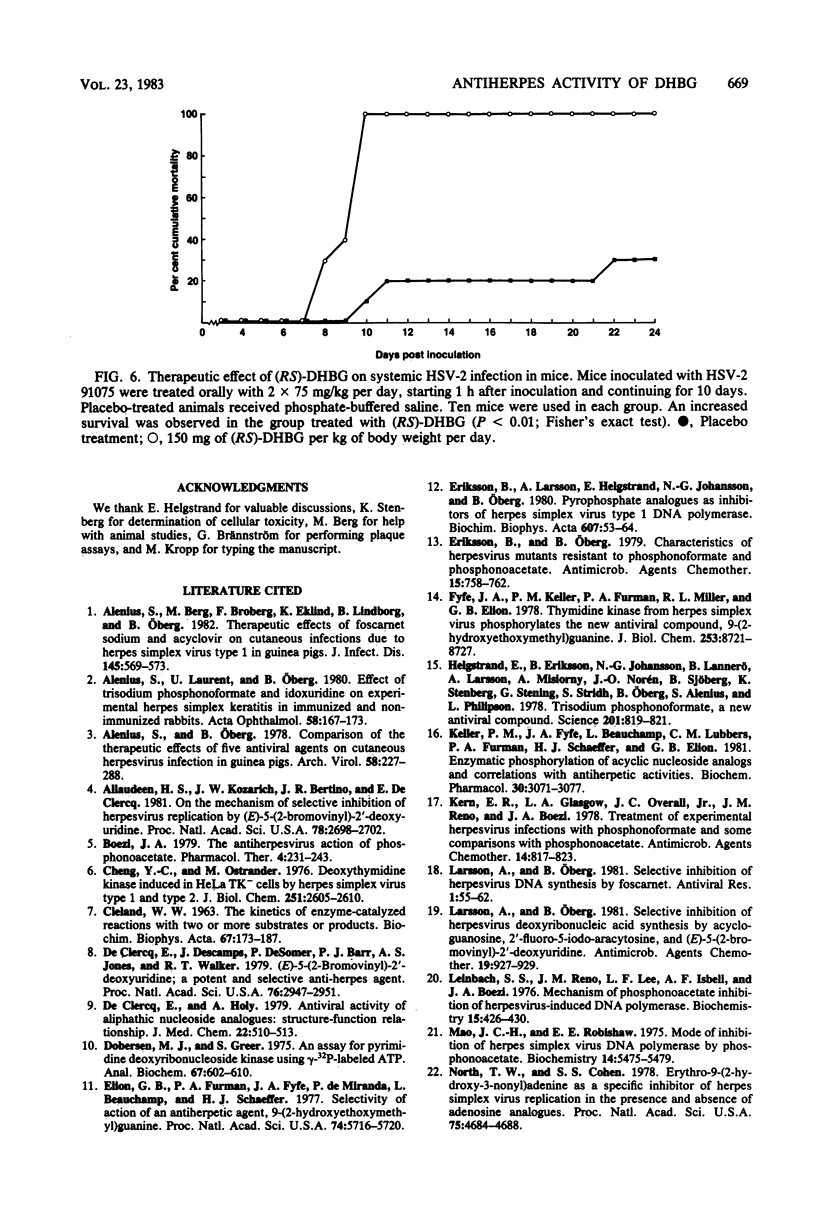
A new compound, 9-(3,4-dihydroxybutyl)guanine, has been synthesized and its antiherpes activity determined. 9-(3,4-Dihydroxybutyl)guanine was selectively phosphorylated by herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase and had a high affinity for this enzyme, with an inhibition constant of 1.5 microM. In cell culture, replication of different strains of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 was inhibited to the extent of 50% by 4 to 18 microM (RS)-9-(3,4-dihydroxybutyl)guanine. The (R)-enantiomer of this compound was more inhibitory than the (S)-enantiomer. Herpesvirus DNA synthesis was selectively inhibited by (RS)-9-(3,4-dihydroxybutyl)guanine in infected cells, and a low cellular toxicity was observed. (RS)-9-(3,4-Dihydroxybutyl)guanine had a therapeutic effect when applied topically to guinea pigs with cutaneous herpes simplex type 1 infections and to rabbits with herpes keratitis. Oral treatment of a generalized herpes simplex type 2 infection in mice had a therapeutic effect.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alenius S., Berg M., Broberg F., Eklind K., Lindborg B., Oberg B. Therapeutic effects of foscarnet sodium and acyclovir on cutaneous infections due to herpes simplex virus type 1 in guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):569–573. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alenius S., Laurent U., Oberg B. Effect of trisodium phosphonoformate and idoxuridine on experimental herpes simplex keratitis in immunized and non-immunized rabbits. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1980 Apr;58(2):167–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1980.tb05705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alenius S., Oberg B. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of five antiviral agents on cutaneous herpesvirus infection in guinea pigs. Arch Virol. 1978;58(4):277–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01317820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaudeen H. S., Kozarich J. W., Bertino J. R., De Clercq E. On the mechanism of selective inhibition of herpesvirus replication by (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2698–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boezi J. A. The antiherpesvirus action of phosphonoacetate. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;4(1):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. II. Inhibition: nomenclature and theory. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Ostrander M. Deoxythymidine kinase induced in HeLa TK- cells by herpes simplex virus type I and type II. II. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2605–2610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., De Somer P., Barr P. J., Jones A. S., Walker R. T. (E)-5-(2-Bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine: a potent and selective anti-herpes agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2947–2951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Holy A. Antiviral activity of aliphatic nucleoside analogues: structure-function relationship. J Med Chem. 1979 May;22(5):510–513. doi: 10.1021/jm00191a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobersen M. J., Greer S. An assay for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleoside kinase using gamma-32P-labeled ATP. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):602–610. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Larsson A., Helgstrand E., Johansson N. G., Oberg B. Pyrophosphate analogues as inhibitors of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 28;607(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Oberg B. Characteristics of herpesvirus mutants resistant to phosphonoformate and phosphonoacetate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):758–762. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Furman P. A., Miller R. L., Elion G. B. Thymidine kinase from herpes simplex virus phosphorylates the new antiviral compound, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgstrand E., Eriksson B., Johansson N. G., Lannerö B., Larsson A., Misiorny A., Norén J. O., Sjöberg B., Stenberg K., Stening G. Trisodium phosphonoformate, a new antiviral compound. Science. 1978 Sep 1;201(4358):819–821. doi: 10.1126/science.210500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Fyfe J. A., Beauchamp L., Lubbers C. M., Furman P. A., Schaeffer H. J., Elion G. B. Enzymatic phosphorylation of acyclic nucleoside analogs and correlations with antiherpetic activities. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Nov 15;30(22):3071–3077. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Glasgow L. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Reno J. M., Boezi J. A. Treatment of experimental herpesvirus infections with phosphonoformate and some comparisons with phosphonoacetate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):817–823. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Oberg B. Selective inhibition of herpesvirus deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by acycloguanosine, 2'-fluoro-5-iodo-aracytosine, and (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):927–929. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Mode of inhibition of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase by phosphonoacetate. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5475–5479. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North T. W., Cohen S. S. Erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine as a specific inhibitor of herpes simplex virus replication in the presence and absence of adenosine analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Boezi J. A. Inhibition of herpesvirus replication and herpesvirus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase by phosphonoformate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):188–192. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Beauchamp L., de Miranda P., Elion G. B., Bauer D. J., Collins P. 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):583–585. doi: 10.1038/272583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnürer J., Oberg B. Inhibitory effects of foscarnet on herpesvirus multiplication in cell culture. Arch Virol. 1981;68(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01314573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg K. Cellular toxicity of pyrophosphate analogues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 May 1;30(9):1005–1008. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stening G., Gotthammar B., Larsson A., Alenius S., Johansson N. G., Oberg B. Antiherpes activity of [E]-5-(1-propenyl)-2'-deoxyuridine and 5-(1-propenyl)-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyluracil. Antiviral Res. 1981 Nov;1(4):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(81)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



