Abstract
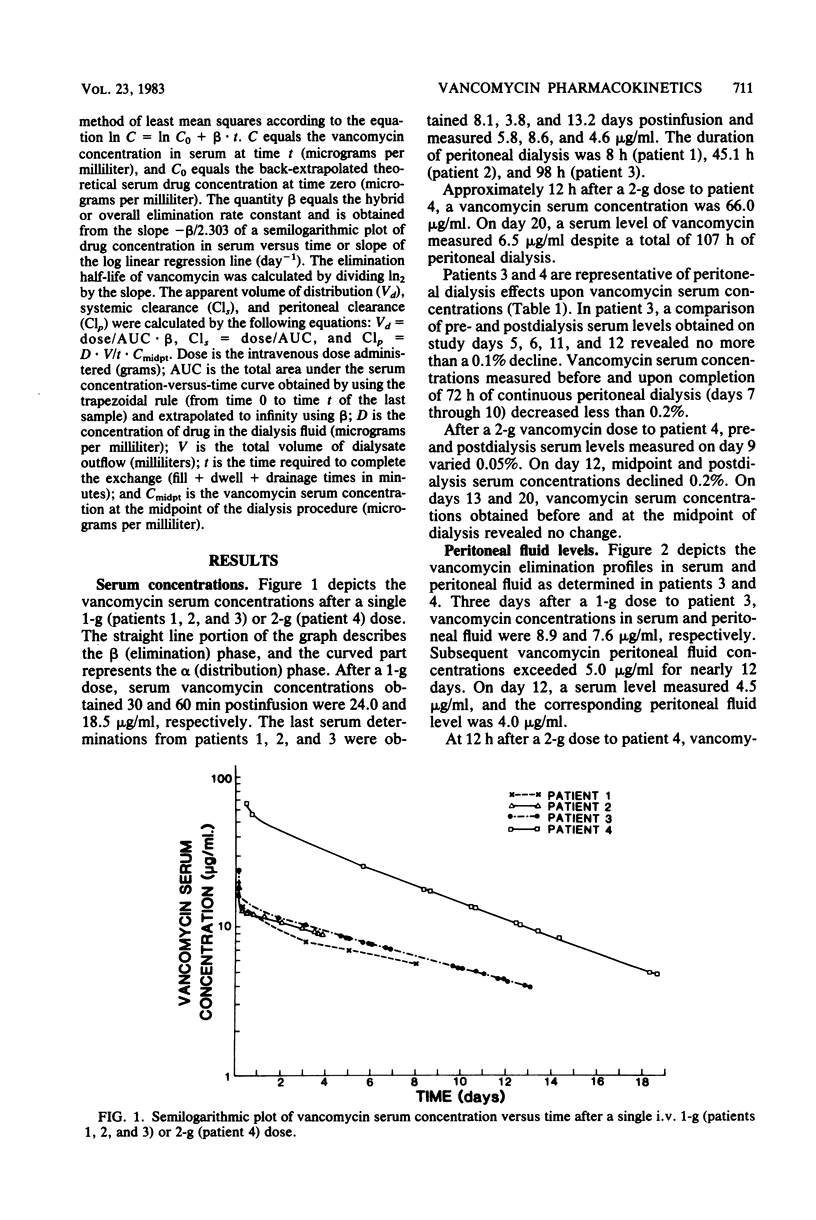
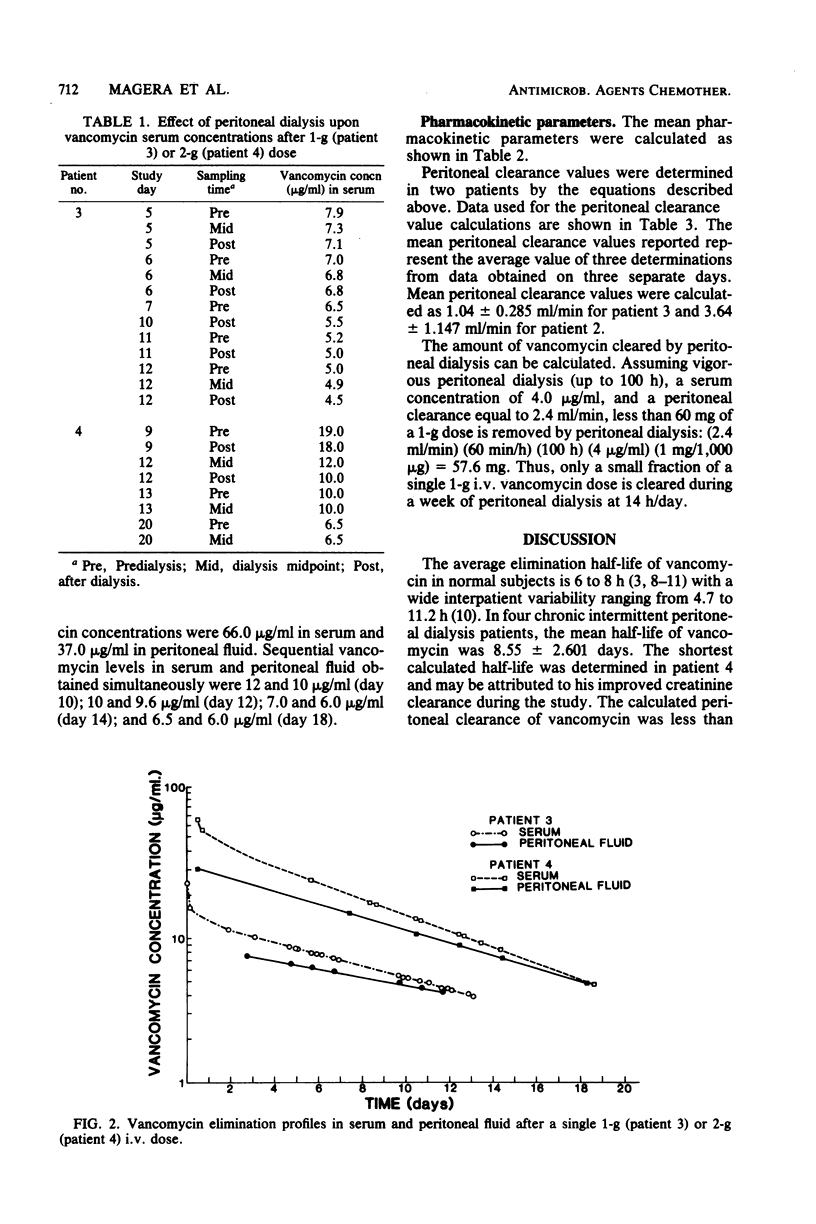
Vancomycin pharmacokinetics were studied in four patients with peritonitis undergoing chronic intermittent peritoneal dialysis. Serum levels exceeding 4.0 micrograms/ml were maintained for 8 and 13 days after a single 1-g intravenous dose. Vancomycin serum concentrations measured before, during, and upon completion of dialysis revealed no appreciable decline. Peritoneal fluid concentrations in two patients exceeded 4.0 micrograms/ml for more than 12 days.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayus J. C., Eneas J. F., Tong T. G., Benowitz N. L., Schoenfeld P. Y., Hadley K. L., Becker C. E., Humphreys M. H. Peritoneal clearance and total body elimination of vancomycin during chronic intermittent peritoneal dialysis. Clin Nephrol. 1979 Mar;11(3):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook F. V., Farrar W. E., Jr Vancomycin revisited. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jun;88(6):813–818. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-6-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Phillips I., Evans J. Vancomycin for staphylococcal shunt site infections in patients on regular haemodialysis. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 11;3(5714):80–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5714.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Casey J. I., Ruch P. A., Stumpf L. L., Finland M. Rapid microassay of gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, streptomycin, and vancomycin in serum or plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


