Abstract
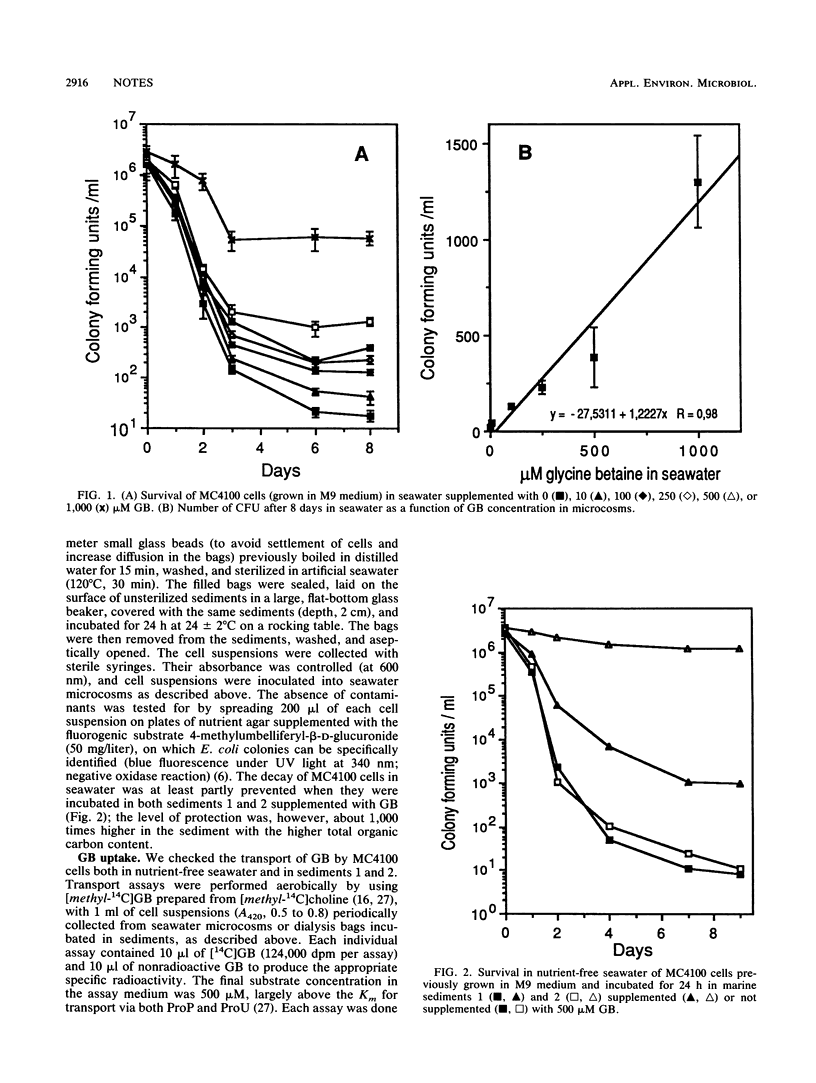
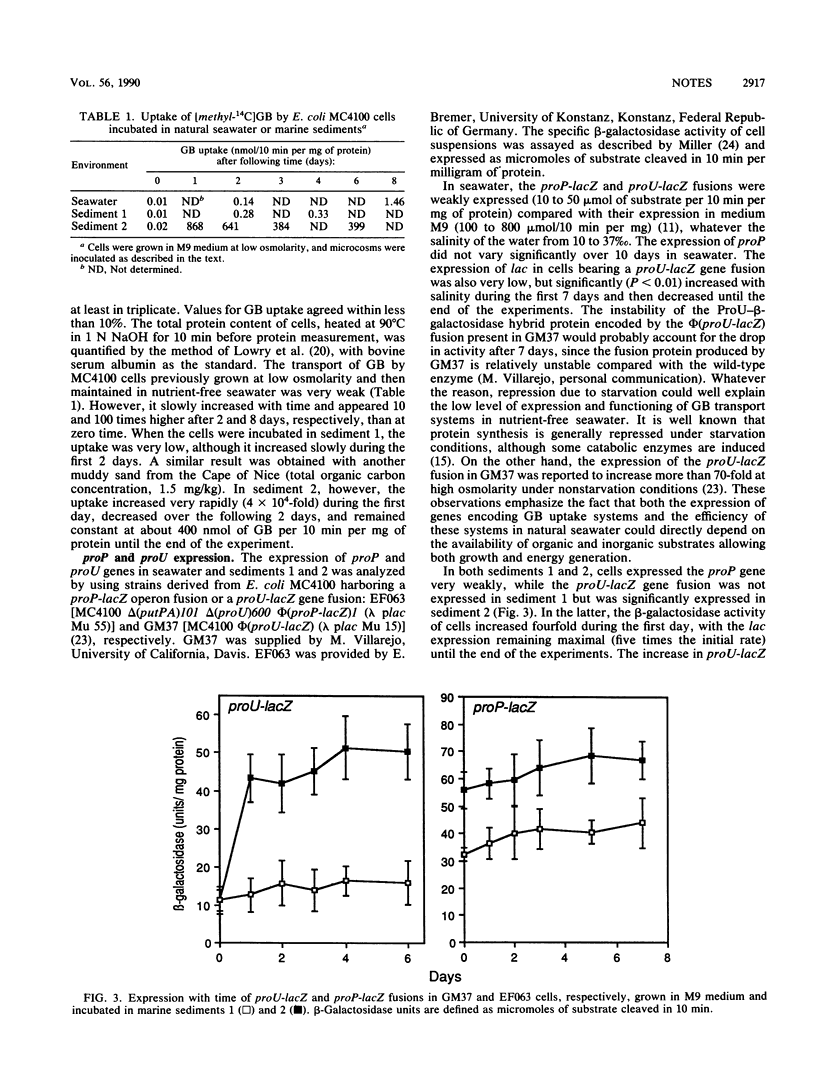
Considering both the protective effect of glycine betaine (GB) on enteric bacteria grown at high osmolarity and the possible presence of GB in marine sediments, we have analyzed the survival, in nutrient-free seawater, of Escherichia coli cells incubated in sediments supplemented with GB or not supplemented and measured the efficiency of GB uptake systems and the expression of proP and proU genes in both seawater and sediments. We did this by using strains harboring proP-lacZ and proU-lacZ operon or gene fusions. We found that the uptake of GB and the expression of both proP and proU were very weak in seawater. The survival ability of cells in seawater supplemented with GB was a linear function of GB concentration, although the overall protection by the osmolyte was low. In sediments, proP expression was weak and GB uptake and proU expression were variable, possibly depending on the availability of organic nutrients. In a sediment with a high total organic carbon content, GB uptake was very high and proU expression was enhanced; cells previously incubated in this sediment showed a higher resistance to decay in seawater. GB might therefore play a significant role in the long-term maintenance of enteric bacterial cells in some marine sediments.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth I. R., Cairney J., Sutherland L., Higgin C. F. Enteric bacteria and osmotic stress: an integrated homeostatic system. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1988;17:35S–49S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairney J., Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Osmoregulation of gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium: proU encodes an osmotically induced betaine transport system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1224–1232. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1224-1232.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):121–147. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.121-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattananda C. S., Gowrishankar J. Osmoregulation in Escherichia coli: complementation analysis and gene-protein relationships in the proU locus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1915–1922. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1915-1922.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng P. C., Hartman P. A. Fluorogenic assays for immediate confirmation of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1320–1329. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1320-1329.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoul M., Bernard T., Cormier M. Evidence that Escherichia coli accumulates glycine betaine from marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):551–554. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.551-554.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M. Metabolism of trimethylamine, choline, and glycine betaine by sulfate-reducing and methanogenic bacteria in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):719–725. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.719-725.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landfald B., Strøm A. R. Choline-glycine betaine pathway confers a high level of osmotic tolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):849–855. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.849-855.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Bouillard L. Glycine betaine, an osmotic effector in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):152–159. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.152-159.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Strom A. R., Dandekar A. M., Smith L. T., Valentine R. C. Molecular biology of osmoregulation. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1064–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4653.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Faatz E., Villarejo M., Bremer E. Binding protein dependent transport of glycine betaine and its osmotic regulation in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00430432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro P. M., Gauthier M. J., Breittmayer V. A., Bongiovanni J. Influence of osmoregulation processes on starvation survival of Escherichia coli in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):2017–2024. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.2017-2024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perroud B., Le Rudulier D. Glycine betaine transport in Escherichia coli: osmotic modulation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):393–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.393-401.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



