Abstract
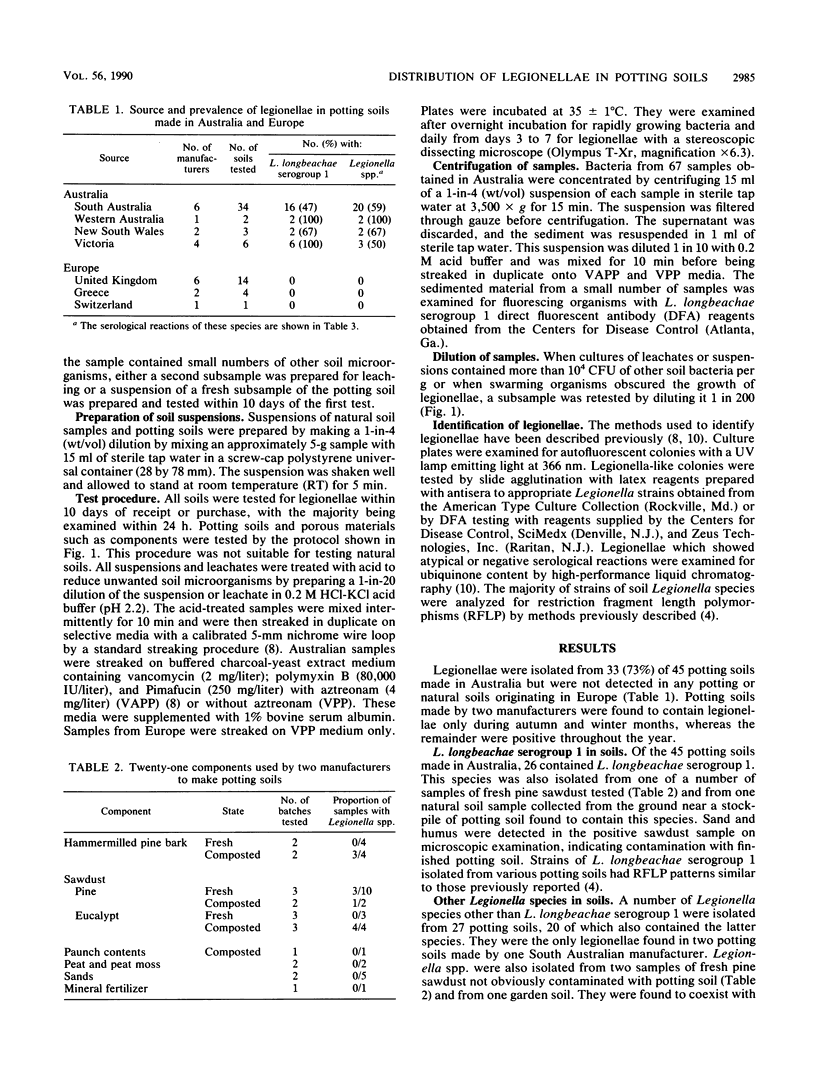
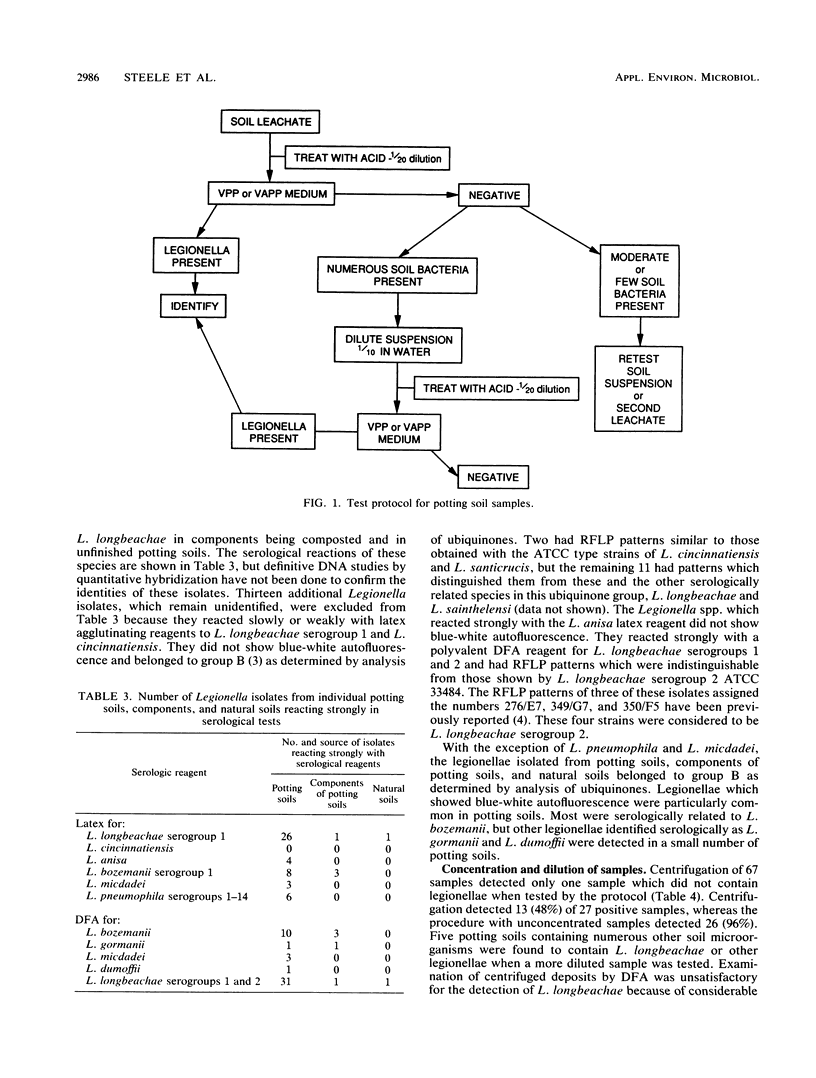
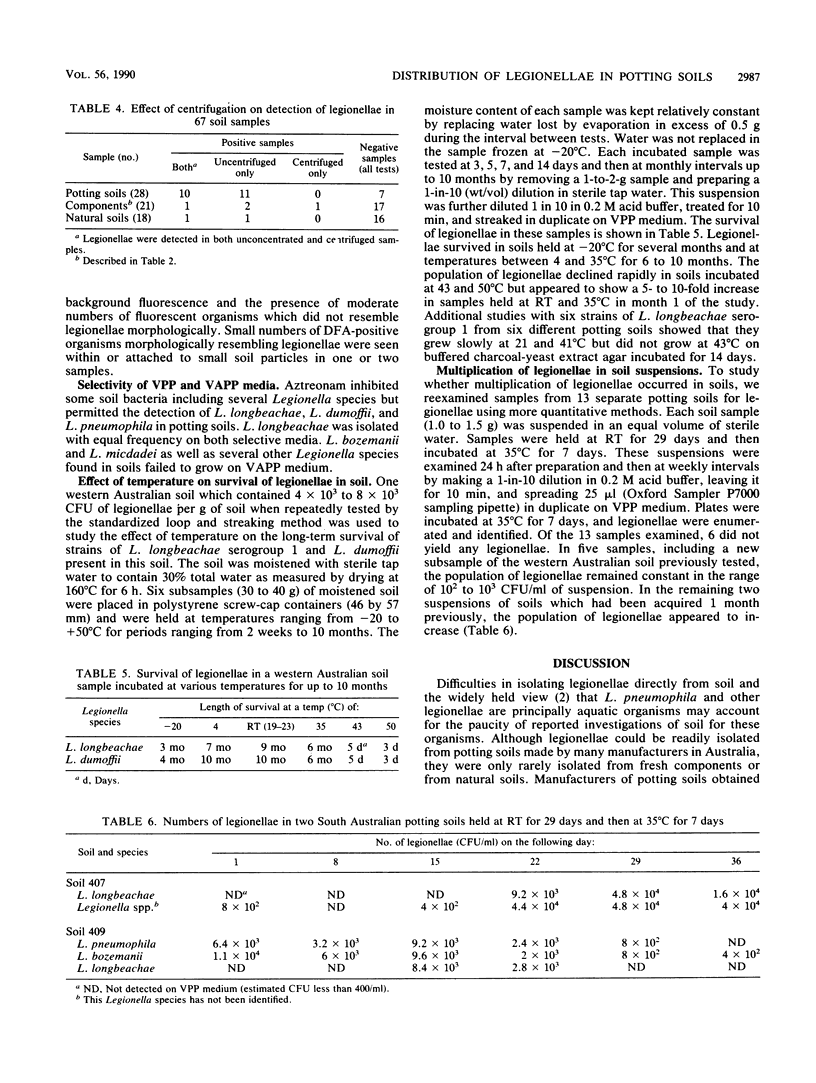
Legionella longbeachae serogroup 1 and other Legionella spp. were isolated from 73% of 45 potting soils made in Australia by 13 manufacturers but were not detected in 19 potting soils made in Greece, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom examined between March 1989 and May 1990. Several Legionella species were isolated from a small number of samples of uncomposted pine sawdusts, but it is not known whether sawdust was the source of some of the legionellae found in potting soils. Legionella spp. persisted for periods ranging from 3 to 10 months in a potting soil held at temperatures between -20 and 35 degrees C. Isolates of L. longbeachae serogroup 1 from soil did not grow at 43 degrees C, a temperature which was also lethal for this species in soil. Most Legionella spp. isolated from potting and natural soils belonged to one distinct group according to analysis of ubiquinones and were serologically related to several known species in this group. A small number of potting soils contained L. pneumophila and L. micdadei.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Cellular fatty acid compositions and isoprenoid quinone contents of 23 Legionella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):465–473. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.465-473.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser J. A., Adams M., Doyle R., Sangster N., Steele T. W. Genetic relatedness of Legionella longbeachae isolates from human and environmental sources in Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2784–2790. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2784-2790.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Patton C. M., Feeley J. C., Johnson S. E., Gorman G., Martin W. T., Skaliy P., Mallison G. F., Politi B. D., Mackel D. C. Isolation of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium from environmental samples. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):664–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A., Feeley J. C., Wong E. S., Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella gormanii sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.718-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry M. F., Stampleman L., Hutchinson J. H., Folta D., Steinberg M. G., Krasnogor L. J. Waterborne Legionella bozemanii and nosocomial pneumonia in immunosuppressed patients. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):205–210. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. W., Lanser J., Sangster N. Isolation of Legionella longbeachae serogroup 1 from potting mixes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.49-53.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker S. B., Bennett J. V., Tsai T. F., Fraser D. W., McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Williams K. H., Jr, Stuart W. H., Dull H. B., Eickhoff T. C. An outbreak in 1965 of severe respiratory illness caused by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):512–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson I. J., Sangster N., Ratcliff R. M., Mugg P. A., Davos D. E., Lanser J. A. Problems associated with identification of Legionella species from the environment and isolation of six possible new species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):796–802. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.796-802.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



