Abstract
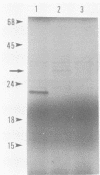
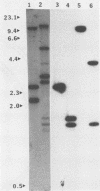
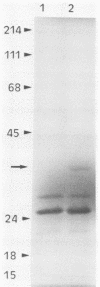
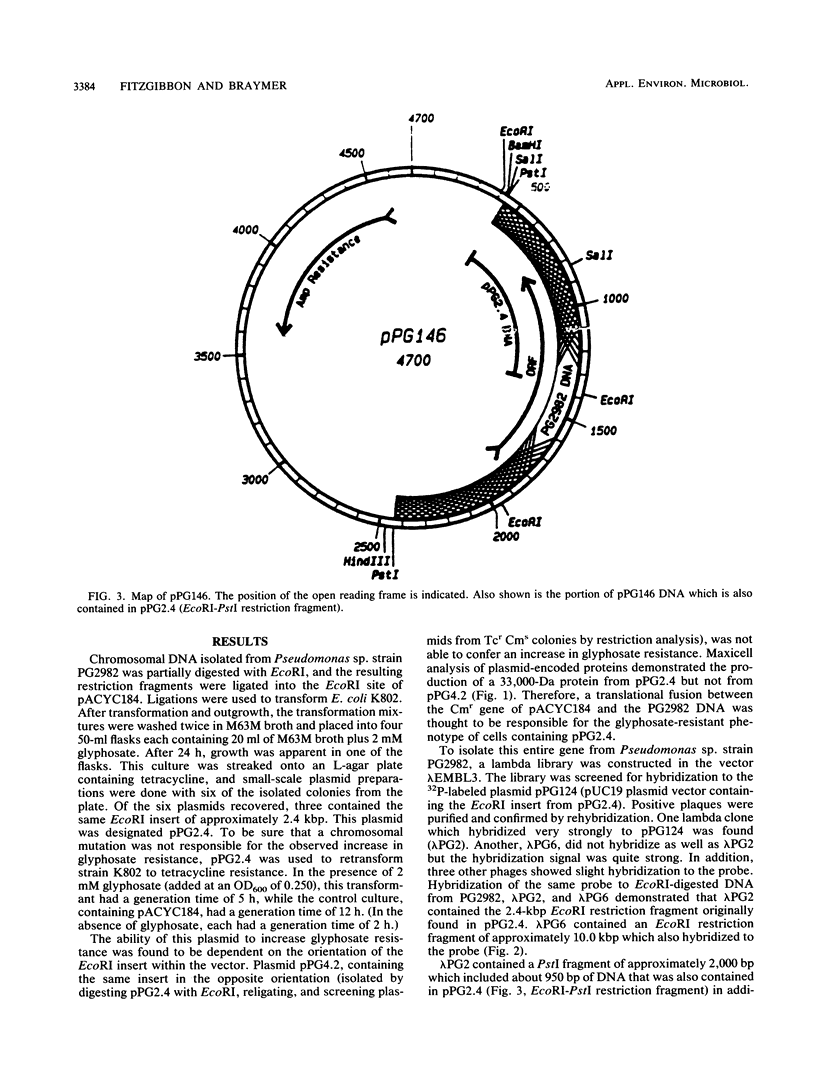
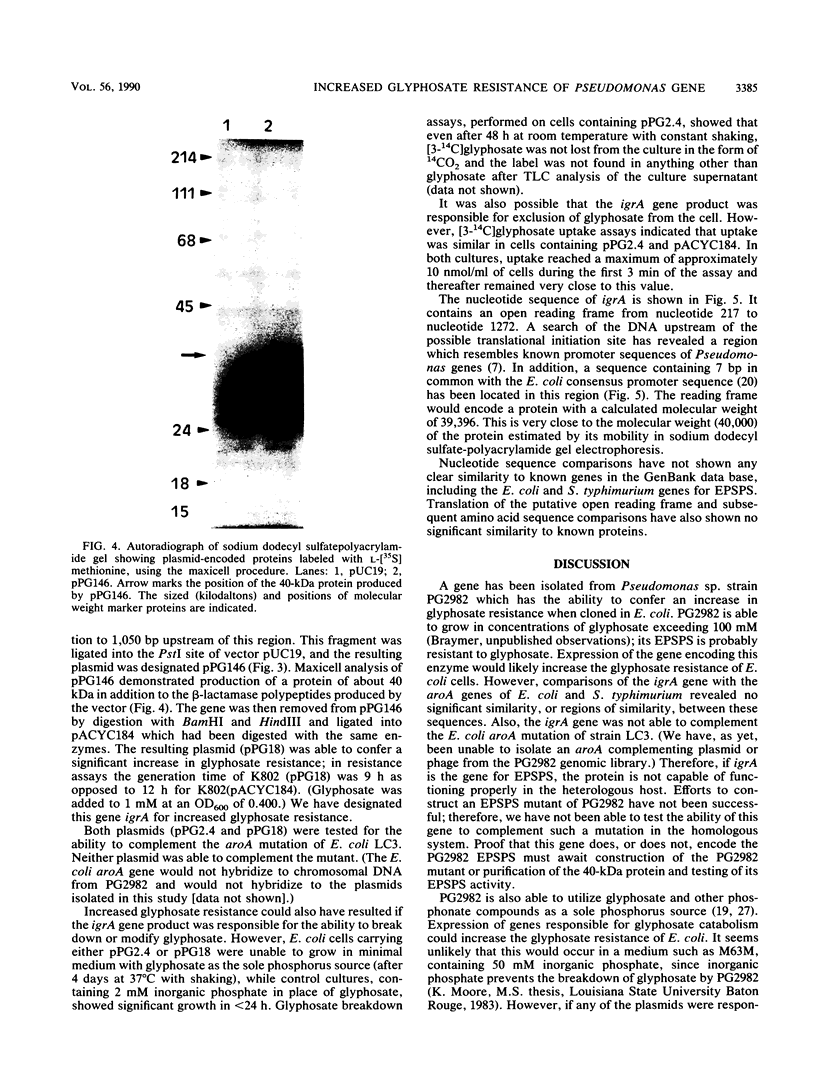
A plasmid carrying a 2.4-kilobase-pair fragment of DNA from Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982 has been isolated which was able to increase the glyphosate resistance of Escherichia coli cells. The increase in resistance was dependent on the presence of a plasmid-encoded protein with a molecular weight of approximately 33,000, the product of a translational fusion between a gene on the vector, pACYC184, and the insert DNA. An overlapping region of the PG2982 chromosome carrying the entire gene (designated igrA) was cloned, and a plasmid (pPG18) carrying the gene was also able to increase glyphosate resistance in E. coli. A protein with a molecular weight of approximately 40,000 was encoded by the PG2982 DNA contained in pPG18. This plasmid was not able to complement a mutation in the gene for 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (aroA) in E. coli, and modification of glyphosate by E. coli cells containing the plasmid could not be demonstrated. The nucleotide sequence of the PG2982 DNA contained an open reading frame able to encode a protein with a calculated molecular weight of 39,396.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Sen L. C., Stalker D. M. An Altered aroA Gene Product Confers Resistance to the Herbicide Glyphosate. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):370–371. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4608.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbon J., Braymer H. D. Phosphate starvation induces uptake of glyphosate by Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1886–1888. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1886-1888.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Pittard J. Pathways of biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids and vitamins and their control in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):465–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. Which Utilizes the Phosphonate Herbicide Glyphosate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):316–320. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.316-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Horsch R. B., Klee H. J., Kishore G. M., Winter J. A., Tumer N. E., Hironaka C. M., Sanders P. R., Gasser C. S., Aykent S., Siegel N. R., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T. Engineering herbicide tolerance in transgenic plants. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):478–481. doi: 10.1126/science.233.4762.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D. L., Braymer H. D. Glyphosate catabolism by Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.702-707.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D. L., Schmitt E. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Phosphonate Utilization by the Glyphosate-Degrading Pseudomonas sp. Strain PG2982. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):1049–1050. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.1049-1050.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart C. C., Johänning D., Müller G., Amrhein N. Selective overproduction of 5-enol-pyruvylshikimic acid 3-phosphate synthase in a plant cell culture which tolerates high doses of the herbicide glyphosate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16338–16346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinrücken H. C., Amrhein N. The herbicide glyphosate is a potent inhibitor of 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1207–1212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90547-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]