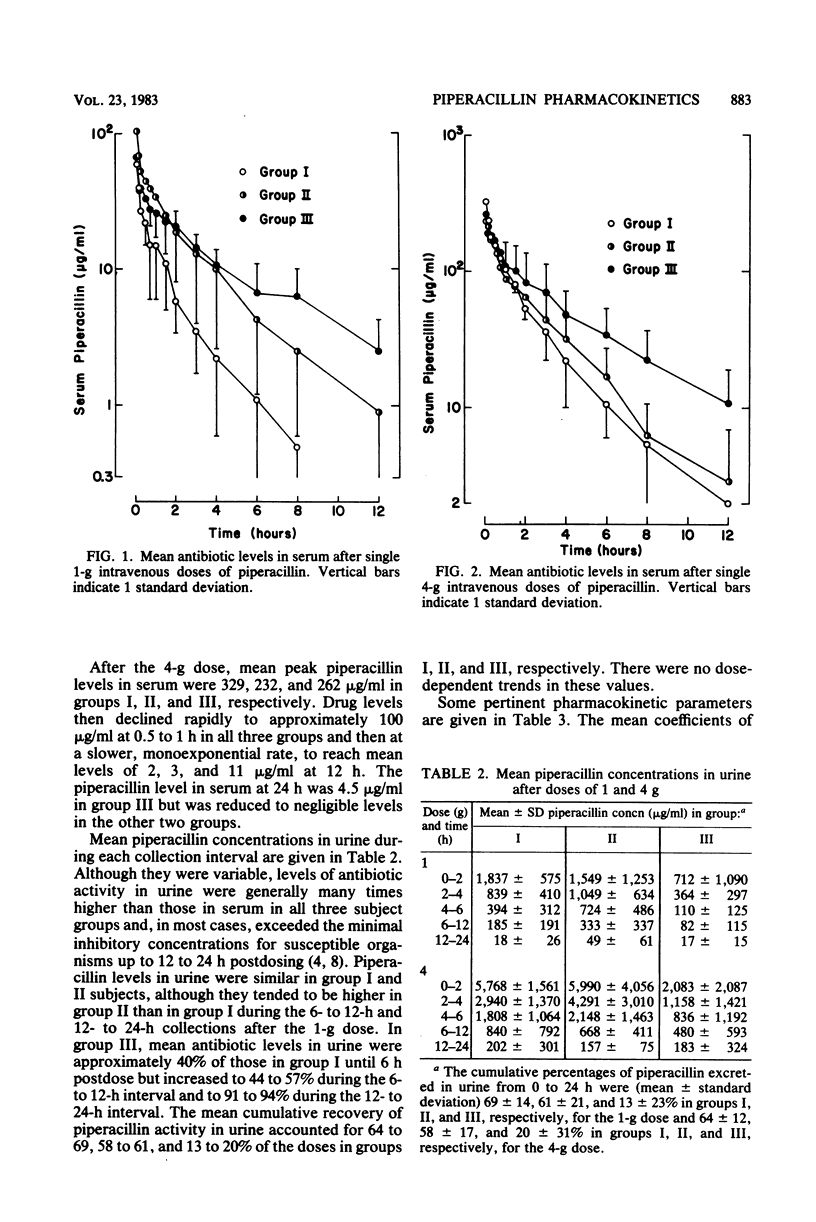
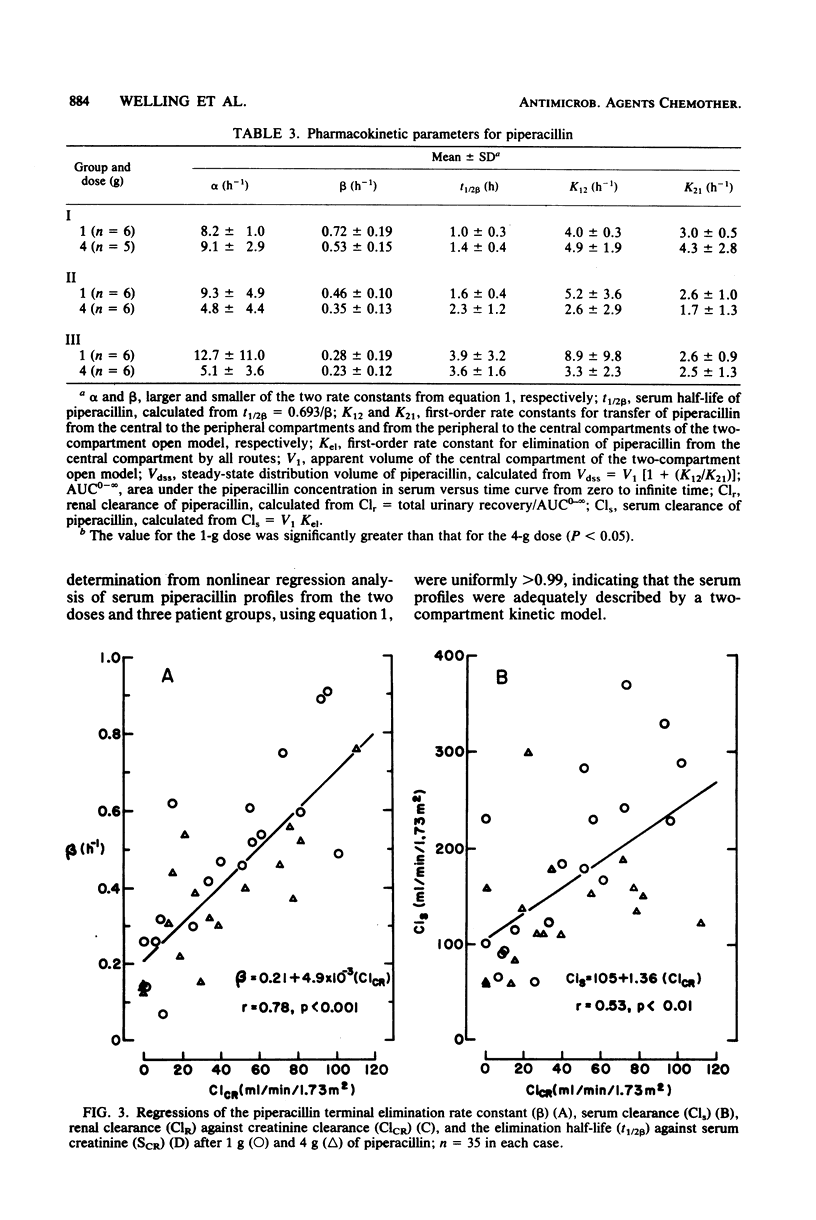
Abstract
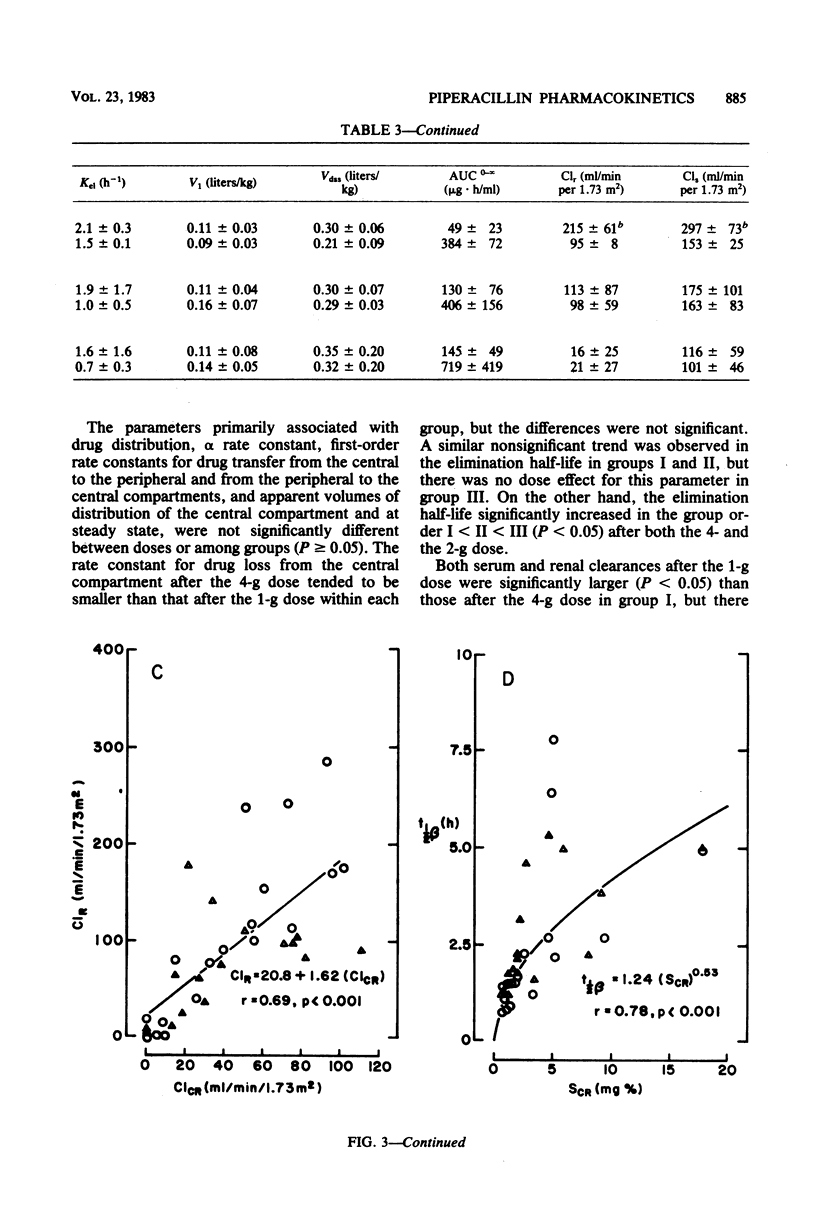
The pharmacokinetics of piperacillin were examined after single intravenous doses to three groups of male patients with creatinine clearances of greater than or equal to 60 (group I), greater than or equal to 20 but less than 60 (group II), and less than 20 (group III) ml/min per 1.73 m2. Each of 32 patients received either 1 or 4 g of piperacillin as a bolus injection. Three patients received both doses. After a rapid 0.5- to 1-h distribution phase, antibiotic levels in serum declined monoexponentially. After the 1-g dose, mean peak piperacillin levels in serum were 60, 103, and 67 micrograms/ml and the beta phase elimination half-lives were 1.0, 1.6, and 3.9 h in groups I, II, and III, respectively. After the 4-g dose, the respective mean peak piperacillin levels in serum were 329, 232, and 262 micrograms/ml and beta phase half-lives were 1.4, 2.3, and 2.6 h in the three groups. There was no clear evidence of significant dose-dependent effects on any pharmacokinetic parameters in any of the groups. Piperacillin levels in urine were far higher than those in serum, generally exceeding the minimal inhibitory concentrations for susceptible organisms during the 24 h after both the 1- and the 4-g dose. Piperacillin dosage modification is required only in patients with severe renal impairment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batra V. K., Morrison J. A., Lasseter K. C., Joy V. A. Piperacillin kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Jul;26(1):41–53. doi: 10.1002/cpt197926141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke E. L., Appel G. B., Neu H. C. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous piperacillin in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):788–791. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frimodt-Möller N., Maigaard S., Toothaker R. D., Bundtzen R. W., Brodey M. V., Craig W. A., Welling P. G., Madsen P. O. Mezlocillin pharmacokinetics after single intravenous doses to patients with varying degrees of renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):599–607. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Piperacillin, a new penicillin active against many bacteria resistant to other penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):358–367. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giron J. A., Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Biliary concentrations of piperacillin in patients undergoing cholecystectomy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):309–311. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne S. E., Waterworth P. M. Piperacillin, a new penicillin with high anti-pseudomonal activity. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):247–254. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Gibaldi M. Serum creatinine and drug half-lives in renal failure. JAMA. 1972 Aug 21;221(8):918–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo J., Jr, Thompson M. I., Russo M. E., Saxon B. A., Matsen J. M., Moody F. G., Rikkers L. F. Piperacillin distribution into bile, gallbladder wall, abdominal skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue in surgical patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):488–492. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander S., Bergan T., Fossberg E. Piperacillin in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Chemotherapy. 1980;26(2):141–144. doi: 10.1159/000237896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. I., Russo M. E., Matsen J. M., Atkin-Thor E. Piperacillin pharmacokinetics in subjects with chronic renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):450–453. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjandramaga T. B., Mullie A., Verbesselt R., De Schepper P. J., Verbist L. Piperacillin: human pharmacokinetics after intravenous and intramuscular administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):829–837. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



