Abstract
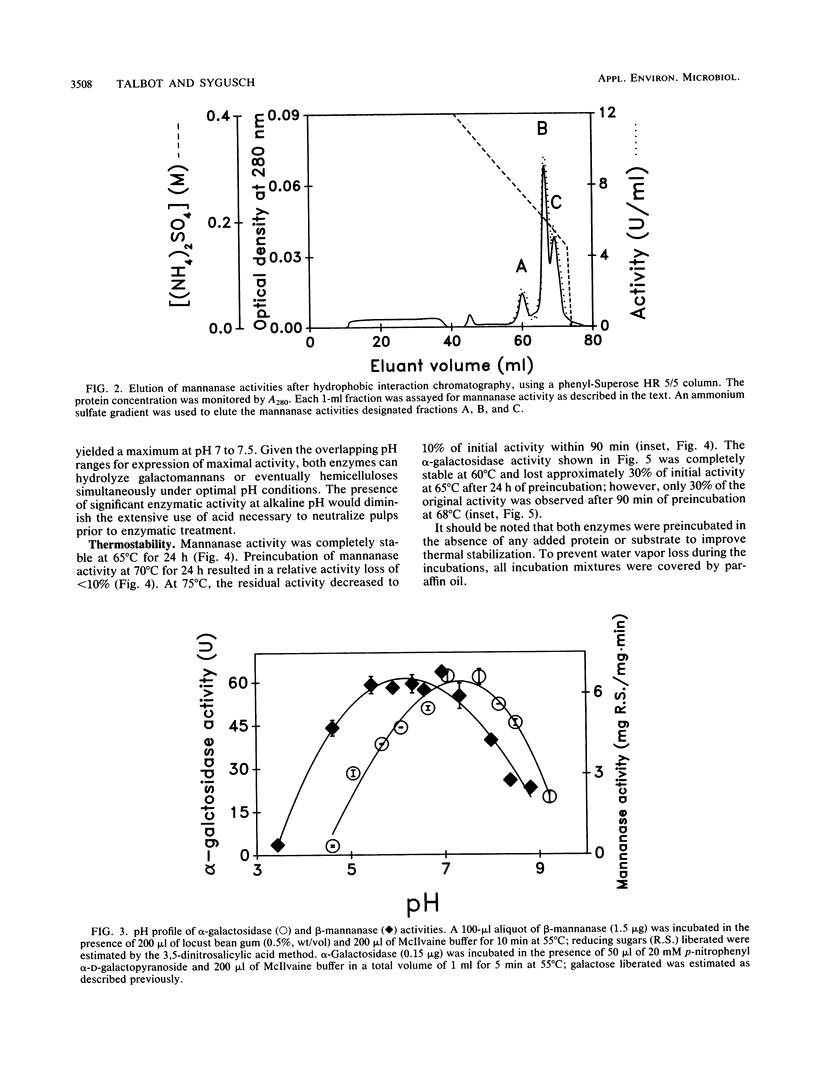
Bacillus stearothermophilus secretes beta-mannanase and alpha-galactosidase enzymatic activities capable of hydrolyzing galactomannan substrates. Expression of the hemicellulase activities in the presence of locust bean gum was sequential, with mannanase activity preceding expression of alpha-galactosidase activity. The hemicellulase activities were purified to homogeneity by a combination of ammonium sulfate fractionation, gel filtration, hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and ion-exchange and chromatofocusing techniques. The purified beta-D-mannanase is a dimeric enzyme (162 kilodaltons) composed of subunits having identical molecular weight (73,000). Maximal activity did not vary between pH 5.5 and 7.5. The beta-D-mannanase activity exhibited thermostability, retaining nearly full activity after incubation for 24 h at 70 degrees C and pH 6.5. The enzyme displayed high specificity for galactomannan substrates, with no-secondary xylanase or cellulase activity detected. Hydrolysis of locust bean gum yielded short oligosaccharides compatible with an endo mode of substrate depolymerization. Initial rate velocities of the mannanase activity displayed substrate inhibition and yielded estimates for Vmax and Km of 455 +/- 60 U/mg and 1.5 +/- 0.3 mg/ml, respectively, at 70 degrees C and pH 6.5. The alpha-galactosidase activity corresponded to a trimeric enzyme (247 kilodaltons) having subunits of identical molecular weight (82,000). The alpha-galactosidase had maximal activity at pH 7 to 7.5 and retained full activity after 24 h of incubation at 60 degrees C. The enzyme had only limited activity on galactomannan substrates as compared with hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl alpha-D-galactose. Kinetics of p-nitrophenyl alpha-D-galactose hydrolysis yielded linear reciprocal plots corresponding to Vmax and Km of 195 +/- 10 U/mg and 0.25 +/- 0.02 mM, respectively, at 60 degrees C and pH 7. The characterization of the mannanase activity is consistent with its potential use in enzymatic bleaching of softwood pulps.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gherardini F. C., Salyers A. A. Purification and characterization of a cell-associated, soluble mannanase from Bacteroides ovatus. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2038–2043. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2038-2043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. M., Goodman R. E. Isozymes of alpha-galactosidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Aug;26(8):978–984. doi: 10.1139/m80-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier A., Sygusch J. Purification and Characterization of Three Chitosanase Activities from Bacillus megaterium P1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):844–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.844-848.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. J., Goldberg I. D., Amelunxen R. E. Development of defined and minimal media for the growth of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.279-284.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]