Abstract
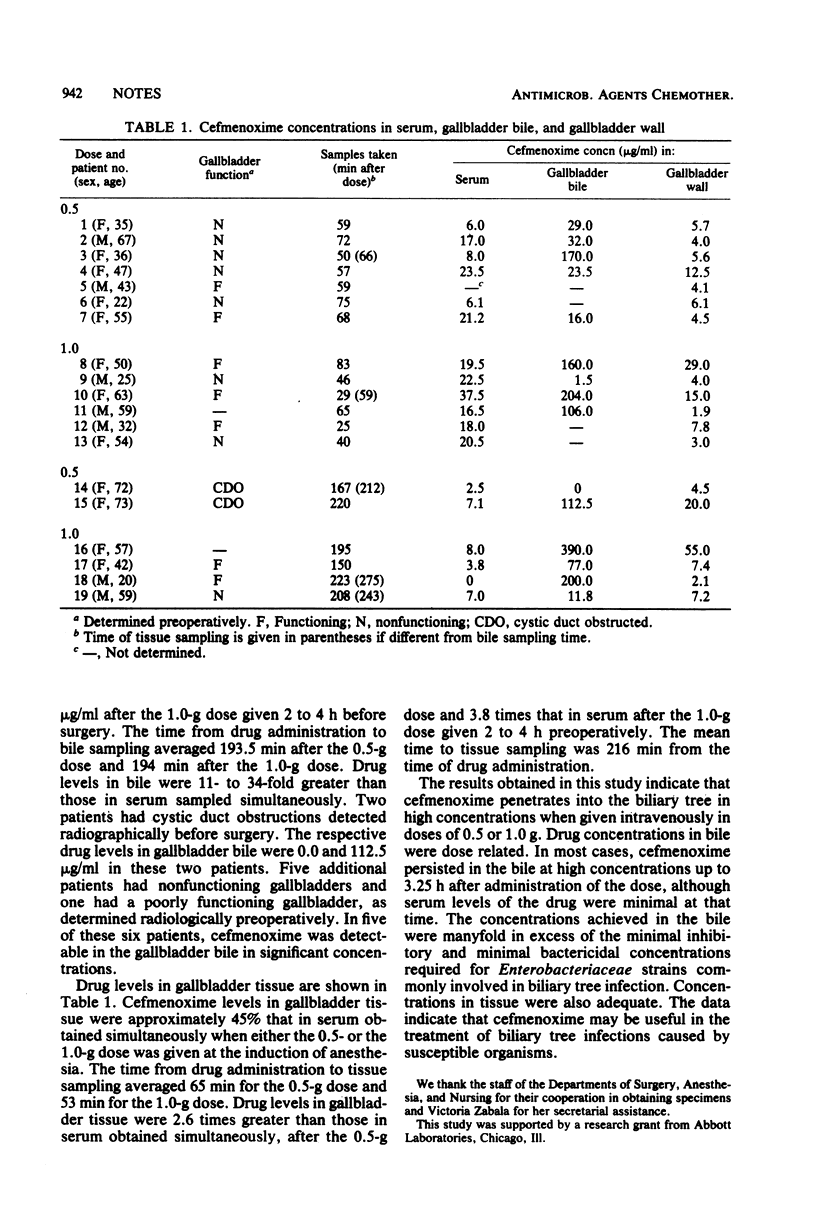
Cefmenoxime concentrations in gallbladder bile and tissue were assessed in patients undergoing cholecystectomy. A 0.5-g intravenous dose produced mean concentrations in bile of 54.1 micrograms/ml at 62.9 min and 56.3 micrograms/ml at 194 min after the dose was given. A 1.0-g intravenous dose produced concentrations in bile of 117.9 micrograms/ml at 53 min and 169.7 micrograms/ml of 194 min after the dose was given. Mean concentrations in tissue ranged from 6.1 to 17.9 micrograms/g. Biliary tree penetration was dose and time dependent. Therapeutic concentrations were achieved.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaitin H. Bacteriology of calculous cholecystitis. Int Surg. 1973 Mar;58(3):169–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetlin S. H., Elliott D. W. Biliary bacteremia. Arch Surg. 1971 Apr;102(4):303–307. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1971.01350040065012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crombez E., Van der Weken G., Van den Bossche W., De Moerloose P. Determination of cefatrizine in serum and urine by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1979 May 11;173(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80456-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. C., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a new cephalosporin: in vitro activity, comparison with other antimicrobial agents, beta-lactamase stability, and disk diffusion testing with tentative interpretive criteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):747–759. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga F. H. Gallbladder bacteriology, histology, and gallstones. Study of unselected cholecystectomy specimens in Honolulu. Arch Surg. 1973 Feb;106(2):169–171. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1973.01350140033011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswitz J. T. Bacteria and biliary tract disease. Am J Surg. 1974 Nov;128(5):644–646. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(74)80019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Drysdale R. B., Quoraishi A. H., Burdon D. W., Alexander-Williams J. Antibiotic treatment of biliary sepsis. Surg Clin North Am. 1975 Dec;55(6):1379–1390. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)40797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddocks A. C., Hilson G. R., Taylor R. The bacteriology of the obstructed biliary tree. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1973 May;52(5):316–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G. R. Bacteriology and antibiotic selection in biliary tract surgery. Arch Surg. 1968 Oct;97(4):533–537. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01340040029002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. In vitro activity and beta-lactamase stability of cefmenoxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):316–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M. L., Justesen T. Anaerobic and aerobic bacteriological studies in biliary tract disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(5):437–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm J. M., Girolami R. L., Shipkowitz N. L., Bower R. R. Antimicrobial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):454–460. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



