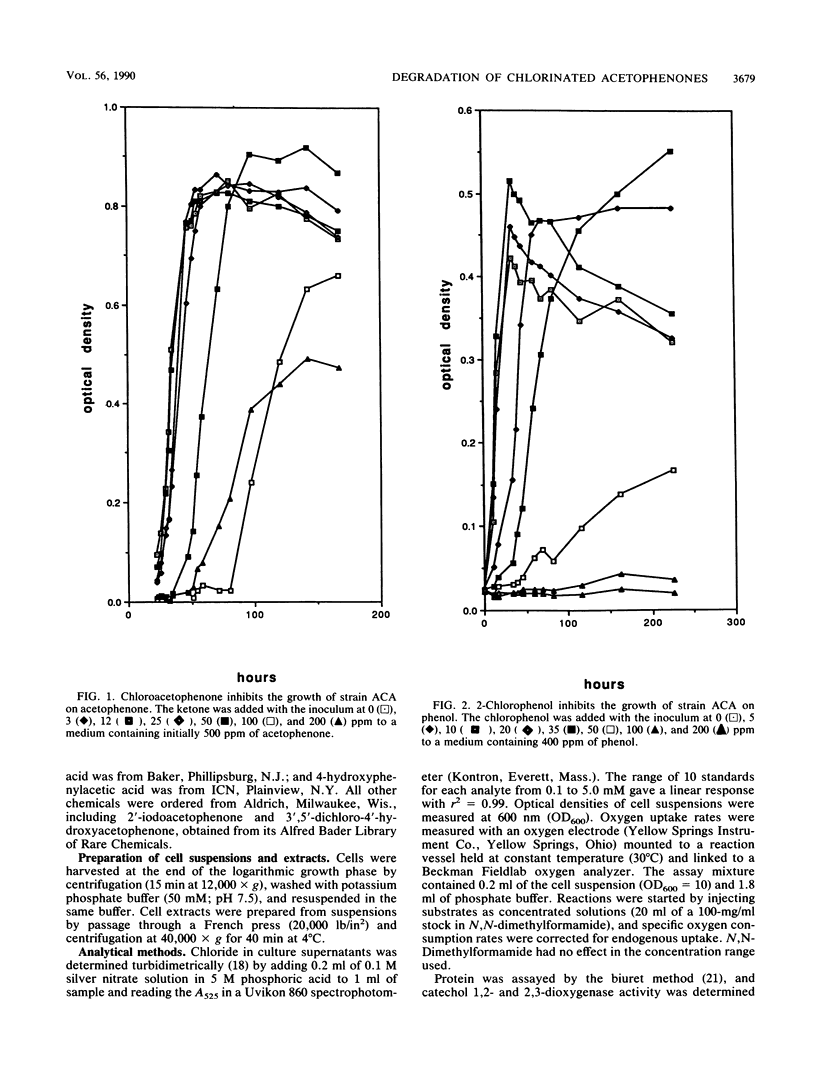
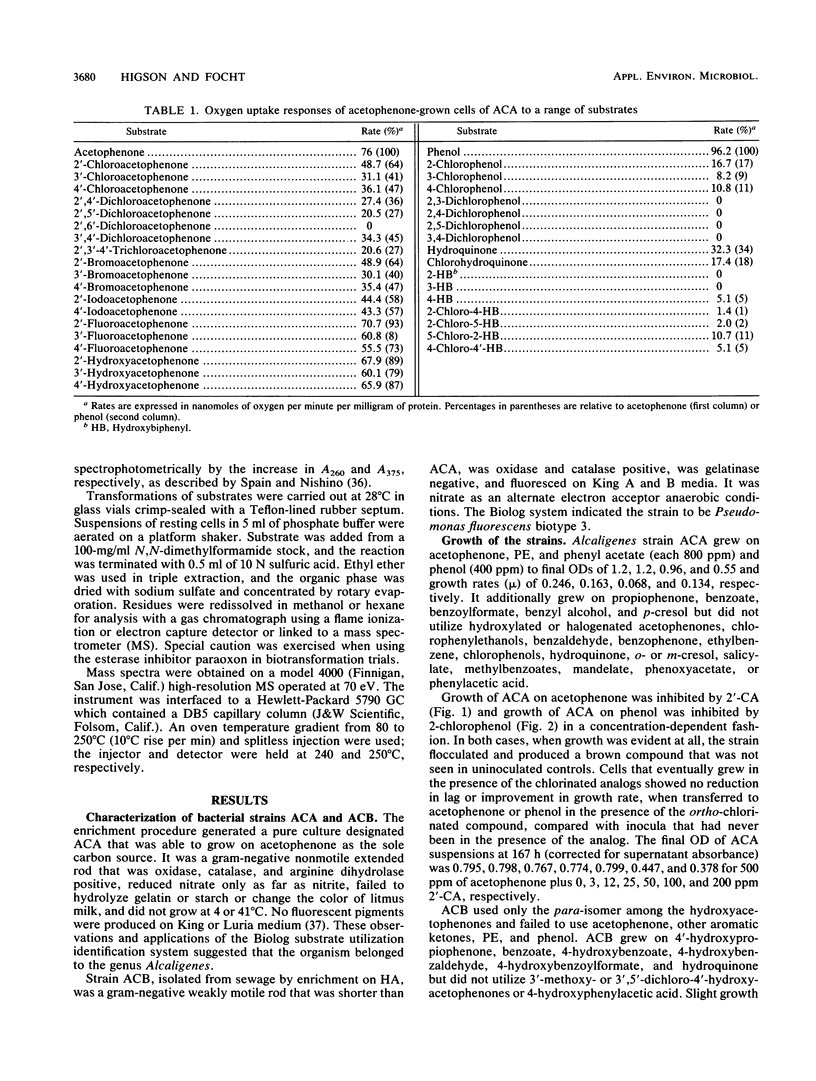
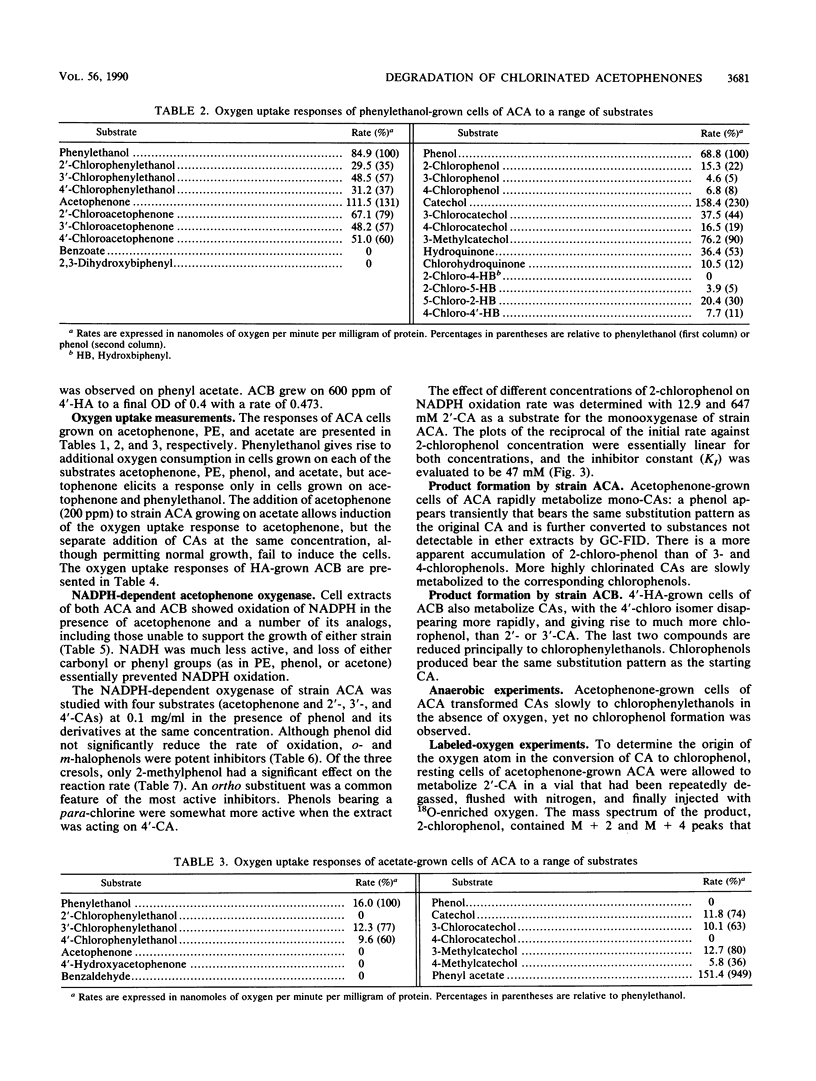
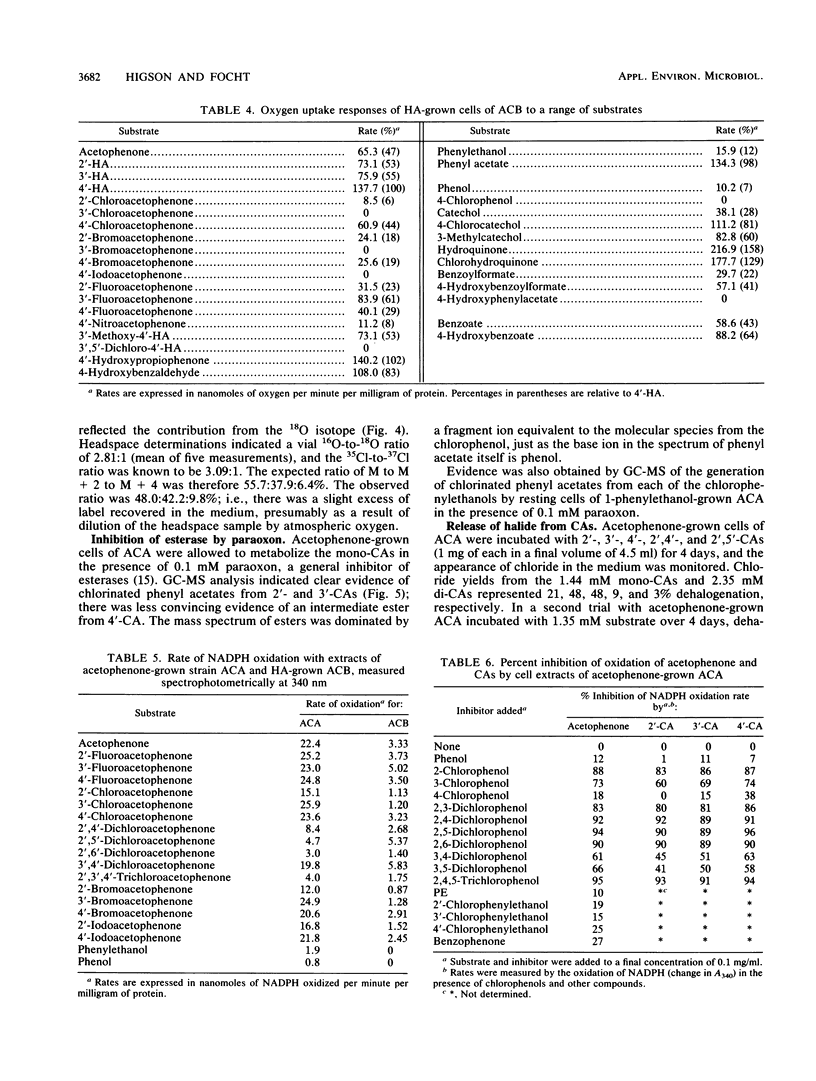
Abstract
Two strains, Alcaligenes sp. strain ACA and Pseudomonas fluorescens ACB, isolated from acetophenone and 4′-hydroxyacetophenone enrichments, respectively, cometabolize a range of chlorinated acetophenones (CAs). A biological Baeyer-Villiger reaction converts the CA to chlorophenyl acetate. This is evident only in the presence of an esterase inhibitor, since the CA is normally rapidly hydrolyzed to a chlorophenol which has the same substitution pattern as the original ketone. The oxygenase that attacks the ketone uses NADPH in the incorporation of one atom of 18O2 and is strongly inhibited by phenols that bear an ortho or meta chlorine or bromine, but much less by cresols or phenol itself. A feedback phenomenon may thus account for the inability of strain ACA to grow on CAs, which also fail to induce the cells for their own metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton M. R., Crawford R. L. Novel biotransformations of 4-chlorobiphenyl by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):594–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.594-595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard D. L., Haberl M. L., May R. J., Brennan M. J. Evidence for novel mechanisms of polychlorinated biphenyl metabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus H850. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1103-1112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon K. I., Hutson D. H., Wright A. N. The metabolism and degradation of vinyl phosphate insecticides. Residue Rev. 1973;47:55–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8488-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon K. I., Wright A. N. The breakdown of 14-C-chlorfenvinphos in soils and in crops grown in the soils. J Sci Food Agric. 1967 Apr;18(4):143–150. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740180403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton L. N., Brand J. M., Markovetz A. J. Source of oxygen in the conversion of 2-tridecanone to undecyl acetate by Pseudomonas cepacia and Nocardia sp. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 16;369(1):45–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONRAD H. E., DUBUS R., NAMTVEDT M. J., GUNSALUS I. C. MIXED FUNCTION OXIDATION. II. SEPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYMES CATALYZING CAMPHOR LACTONIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:495–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps R. E. The microbial metabolism of acetophenone. Metabolism of acetophenone and some chloroacetophenones by an Arthrobacter species. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;152(2):233–241. doi: 10.1042/bj1520233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps R. E., Trudgill P. W., Whateley J. G. The metabolism of 1-phenylethanol and acetophenone by Nocardia T5 and an Arthrobacter species. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):175–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue N. A., Trudgill P. W. The metabolism of cyclohexanol by Acinetobacter NCIB 9871. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. Aerobic cometabolism of DDT analogues by Hydrogenomonas sp. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):20–22. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Gschwendt B., Yeh W. K., Kobal V. M. Initial reactions in the oxidation of ethylbenzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1520–1528. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M., Trudgill P. W. The metabolism of cyclopentanol by Pseudomonas N.C.I.B. 9872. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):595–603. doi: 10.1042/bj1290595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauge J., Andreoni A. Quarterly report on hospital financial status. Hospitals. 1978 Jan 16;52(2):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higson F. K., Focht D. D. Bacterial metabolism of hydroxylated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):946–952. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.946-952.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröckel L., Focht D. D. Construction of chlorobenzene-utilizing recombinants by progenitive manifestation of a rare event. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2470-2475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamikawa T., Jayasankar N. P., Bohm B. A., Taylor I. E., Towers G. H. An inducible hydrolase from Aspergillus niger, acting on carbon-carbon bonds, for phlorrhizin and other C-acylated phenols. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):889–897. doi: 10.1042/bj1160889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris D. B., Trudgill P. W. The metabolism of cyclohexanol by Nocardia globerula CL1. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1210363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRAIRIE R. L., TALALAY P. Enzymatic formation of testololactone. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:203–208. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shum A. C., Markovetz A. J. Purification and properties of undecyl acetate esterase from Pseudomonas cepacia grown on 2-tridecanone. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):880–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.880-889.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



