Abstract
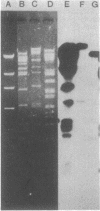
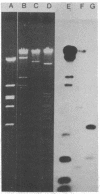
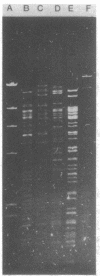
Plasmids belonging to the three HI plasmid incompatibility subgroups were characterized by the use of restriction enzymes and Southern transfer hybridization. A diversity of restriction enzyme patterns was noted among the HI subgroups, and a small amount of DNA homology was observed by probing these digests with a nick-translated HI1 plasmid. Within a single subgroup (HI1 and HI2), similar restriction enzyme patterns were noted. Plasmids of all three HI subgroups and the HII group had a guanine plus cytosine content of 49 to 50 mol%. The IncHII plasmid pHH1508a also showed some homology with the HI1 probe. The DNA homology observed is probably responsible for common phenotypic properties encoded by these plasmids.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A. The molecular relatedness of R factors in enterobacteria of human and animal origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):376–382. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Hughes V. M., Richards H., Datta N. R plasmids of a new incompatibility group determine constitutive production of H pili. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Morphological and serological relationships of conjugative pili. Plasmid. 1980 Sep;4(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Molecular studies of R factor compatibility groups. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):387–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.387-398.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. C., Kado C. I. Studies on Agrobacterium tumefaciens. VIII. Avirulence induced by temperature and ethidium bromide. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Nov;23(11):1554–1561. doi: 10.1139/m77-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero E., Perduca M. Compatibility groups of R-factors for trimethoprim resistance isolated in Italy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Nov;3 (Suppl 100):35–38. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_c.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel A. F., Chabbert Y. A. Taxonomy and epidemiology of gram-negative bacterial plasmids studied by DNA-DNA filter hybridization in formamide. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer H. E., Sederoff R. R. Improved estimation of DNA fragment lengths from Agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Interactions of group H resistance factors with the F factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.623-628.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z., Green P. Thermosensitive antibiotic resistance plasmids in enterobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):37–47. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Grant R. B. Incompatibility and bacteriophage inhibition properties of N-1, a plasmid belonging to the H2 incompatibility group. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 May 20;153(1):5–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01035990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Grant R. B. Incompatibility and surface exclusion properties of H1 and H2 plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):174–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.174-178.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Levine J. G. Studies of temperature-sensitive transfer and maintenance of H incompatibility group plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):475–484. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]