Abstract
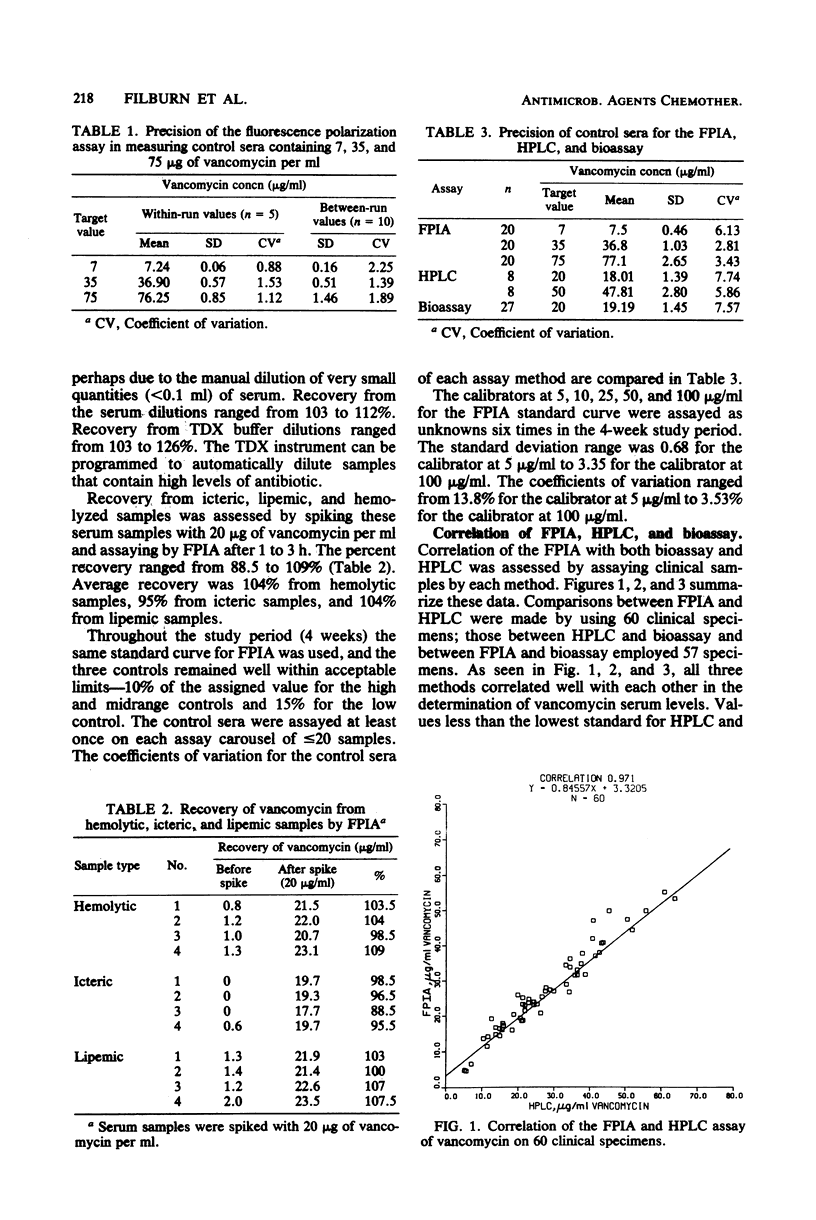
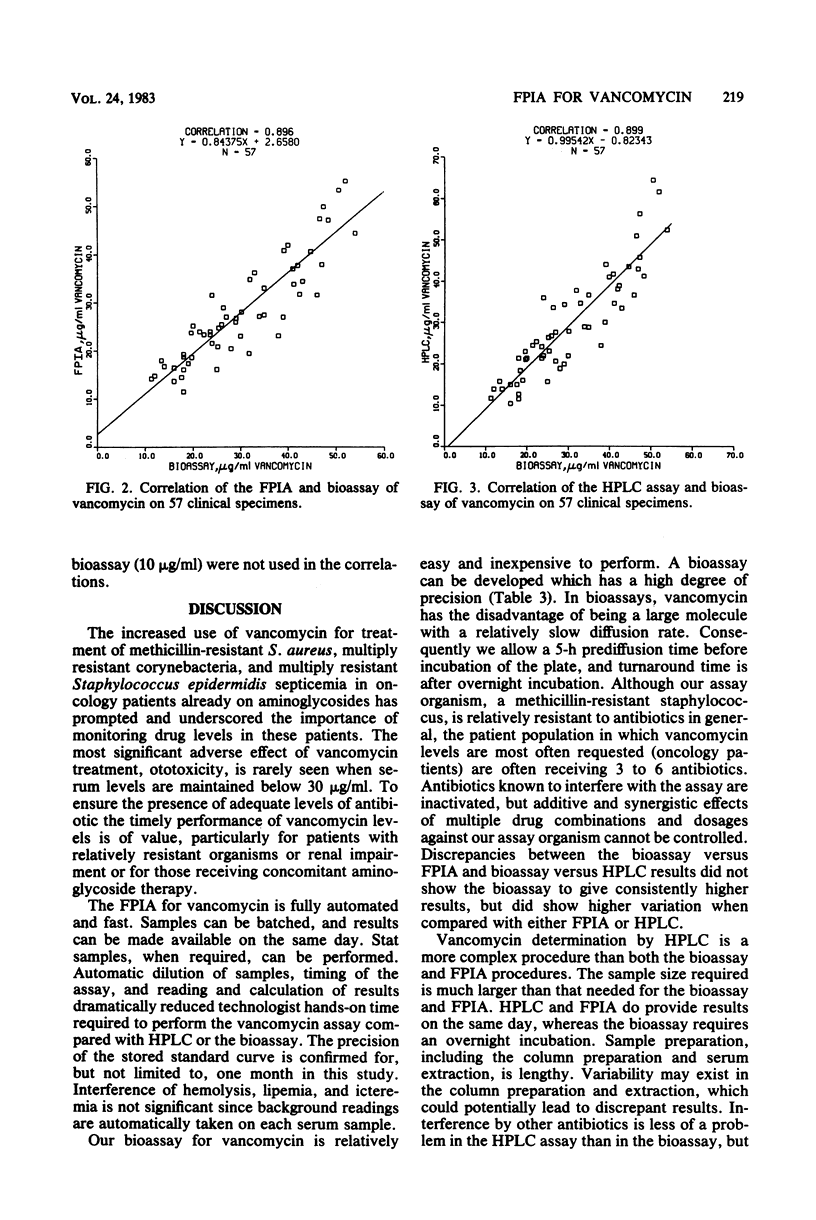
An automated fluorescence polarization immunoassay for the determination of vancomycin levels in serum was evaluated. The vancomycin assay is a homogeneous competitive inhibition immunoassay based on changes in fluorescence polarization that occur with antibody binding. This assay was compared with a liquid chromatographic assay and an agar well diffusion bioassay method by using clinical serum specimens and controls. Linear regression analysis of the data obtained on clinical specimens by the three methods resulted in correlation coefficients of 0.97 for the fluorescence polarization immunoassay versus the liquid chromatographic assay (n = 60), 0.90 for the fluorescence polarization immunoassay versus the bioassay (n = 57), and 0.90 for the liquid chromatographic assay versus the bioassay (n = 57). Repetitive analysis of control sera containing 7, 35, and 75 micrograms of vancomycin per ml by the fluorescence polarization immunoassay yielded coefficients of variation of 3.0, 1.7, and 2.3, respectively. No interference was demonstrated in spiked hemolytic, lipemic, or icteric sera, and the assay was free of matrix effects. The automated fluorescence polarization immunoassay system offers a rapid, efficient, and accurate method for monitoring vancomycin serum levels for both toxicity and efficacy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook F. V., Farrar W. E., Jr Vancomycin revisited. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jun;88(6):813–818. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-6-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Phillips I., Evans J. Vancomycin for staphylococcal shunt site infections in patients on regular haemodialysis. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 11;3(5714):80–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5714.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong K. L., Ho D. H., Bogerd L., Pan T., Brown N. S., Gentry L., Bodey G. P., Sr Sensitive radioimmunoassay for vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):139–143. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci J. E. Vancomycin. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Oct;52(10):631–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Benner E. J., Kayser F. H. Susceptibility of "methicillin"-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to 12 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E. Fluorescence polarization immunoassay for the determination of therapeutic drug levels in human plasma. J Anal Toxicol. 1981 Sep-Oct;5(5):236–240. doi: 10.1093/jat/5.5.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E., Stroupe S. D., Schwenzer K. S., Wang C. J., Lu-Steffes M., Hill H. D., Popelka S. R., Holen J. T., Kelso D. M. Fluorescence polarization immunoassay. iii. an automated system for therapeutic drug determination. Clin Chem. 1981 Sep;27(9):1575–1579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY W. M., PERRY D. M., BAUER A. W. Treatment of staphylococcal septicemia with vancomycin: report of thirty-three cases. N Engl J Med. 1960 Jan 14;262:49–55. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196001142620201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D. D., Murray J. S. Persistence of vancomycin in the blood during renal failure and its treatment by hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 12;274(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605122741902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S. Simple method for elimination of aminoglycosides from serum to permit bioassay of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):286–287. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. A., Kopp B. Sensitive bioassay for vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):30–33. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Bakie C. Synergism of vancomycin-gentamicin and vancomycin-streptomycin against enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Aug;4(2):120–124. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.2.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



