Abstract
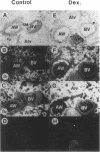
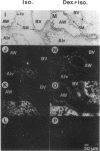
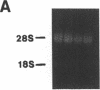
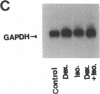
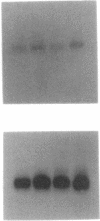
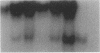
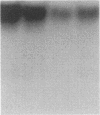
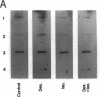
We investigated the in vivo effects of a glucocorticoid on beta-agonist-induced downregulation of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors (determined by [125I]iodocyanopindolol binding), mRNA expression (assessed by Northern blotting), and gene transcription (using nuclear run-on assays) in rat lung. Dexamethasone (Dex) (0.2 mg/kg/d, days 1-8) increased beta 1- and beta 2-receptor numbers by 70 and 69% above control, respectively, but did not change their mRNA expression. Isoproterenol (Iso) (0.96 mg/kg/d, days 2-8) decreased beta 1- and beta 2-receptor numbers by 48 and 51%, respectively, and also reduced mRNA expression by 69 and 57%, respectively. The combination of Dex and Iso resulted in no net change in beta 2-receptor number and its mRNA expression, although there was a significant reduction in beta 1-receptor number and mRNA expression. The mapping of beta 1- and beta 2-receptors by receptor autoradiography confirmed these findings over alveoli, epithelium, endothelium, and airway and vascular smooth muscle. We also measured the activation of the transcription factor, cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) using an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. CREB-like DNA-binding activity was decreased after Iso treatment but this decrease was prevented after treatment with Dex. Nuclear run-on assays revealed that the transcription rate of the beta 1-receptor gene did not alter after Dex treatment, but was reduced after Iso treatment. The transcription rate of the beta 2-receptor gene was increased after Dex treatment by approximately twofold, but there was no change after Iso treatment. We conclude that glucocorticoids can prevent homologous downregulation of beta 2-receptor number and mRNA expression at the transcriptional level without affecting beta 1-receptors and that the transcription factor CREB may be involved in this phenomenon. Such an effect may have clinical implications for preventing the development of tolerance to beta 2-agonists in asthmatic patients treated with beta-agonist bronchodilators.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Beta-adrenoceptors on smooth muscle, nerves and inflammatory cells. Life Sci. 1993;52(26):2101–2109. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90725-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstairs J. R., Nimmo A. J., Barnes P. J. Autoradiographic visualization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in human lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):541–547. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., McParland C. P., Britto S. A., Swystun V. A., Rutherford B. C. Regular inhaled salbutamol and airway responsiveness to allergen. Lancet. 1993 Oct 2;342(8875):833–837. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92695-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Altschmied J., Herbsman O., Caron M. G., Mellon P. L., Lefkowitz R. J. A cAMP response element in the beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene confers transcriptional autoregulation by cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19330–19335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors in hamster smooth muscle cells are transcriptionally regulated by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9067–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. From ligand binding to gene expression: new insights into the regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Ostrowski J., Lefkowitz R. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor 5'-flanking promoter region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Feb 20;1172(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90287-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. O., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-promoted high affinity state of the beta-adrenergic receptor in human neutrophils: modulation by corticosteroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Oct;53(4):703–708. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-4-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. O., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by steroid hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:119–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Collins S., Daniel K. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7920–7924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Briend-Sutren M. M., Lasnier F., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Differential regulation of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor protein and mRNA levels by glucocorticoids during 3T3-F442A adipose differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16343–16349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galant S. P., Duriseti L., Underwood S., Insel P. A. Decreased beta-adrenergic receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes after adrenergic therapy. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 26;299(17):933–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810262991707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocayne J., Robinson D. A., FitzGerald M. G., Chung F. Z., Kerlavage A. R., Lentes K. U., Lai J., Wang C. D., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Primary structure of rat cardiac beta-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors obtained by automated DNA sequence analysis: further evidence for a multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8296–8300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors: agonist-induced reduction in receptor mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by "permissive" hormones: glucocorticoids increase steady-state levels of receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8415–8419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Wang H. Y., Malbon C. C. Agonist-induced destabilization of beta-adrenergic receptor mRNA. Attenuation of glucocorticoid-induced up-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19928–19933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamid Q. A., Mak J. C., Sheppard M. N., Corrin B., Venter J. C., Barnes P. J. Localization of beta 2-adrenoceptor messenger RNA in human and rat lung using in situ hybridization: correlation with receptor autoradiography. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb 25;206(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauck R. W., Böhm M., Gengenbach S., Sunder-Plassmann L., Fruhmann G., Erdmann E. Beta 2-adrenoceptors in human lung and peripheral mononuclear leukocytes of untreated and terbutaline-treated patients. Chest. 1990 Aug;98(2):376–381. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak J. C., Nishikawa M., Barnes P. J. Glucocorticosteroids increase beta 2-adrenergic receptor transcription in human lung. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jan;268(1 Pt 1):L41–L46. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1995.268.1.L41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Hadcock J. R. Evidence that glucocorticoid response elements in the 5'-noncoding region of the hamster beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene are obligate for glucocorticoid regulation of receptor mRNA levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):676–681. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mano K., Akbarzadeh A., Townley R. G. Effect of hydrocortisone on beta-adrenergic receptors in lung membranes. Life Sci. 1979 Nov 26;25(22):1925–1930. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada M. T., Haskell K. M., Ecker D. J., Stadel J. M., Crooke S. T. Genetic regulation of beta 2-adrenergic receptors in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2600053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Mak J. C., Shirasaki H., Barnes P. J. Differential down-regulation of pulmonary beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptor messenger RNA with prolonged in vivo infusion of isoprenaline. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 15;247(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Mak J. C., Shirasaki H., Harding S. E., Barnes P. J. Long-term exposure to norepinephrine results in down-regulation and reduced mRNA expression of pulmonary beta-adrenergic receptors in guinea pigs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 Jan;10(1):91–99. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.10.1.8292387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor B. J., Aikman S. L., Barnes P. J. Tolerance to the nonbronchodilator effects of inhaled beta 2-agonists in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992 Oct 22;327(17):1204–1208. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199210223271704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M. J., Adcock I. M., Brown C. R., Barnes P. J. Beta-adrenoceptor agonists interfere with glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding in rat lung. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr 28;289(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port J. D., Huang L. Y., Malbon C. C. Beta-adrenergic agonists that down-regulate receptor mRNA up-regulate a M(r) 35,000 protein(s) that selectively binds to beta-adrenergic receptor mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24103–24108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosewicz S., McDonald A. R., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D., Miesfeld R. L., Logsdon C. D. Mechanism of glucocorticoid receptor down-regulation by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2581–2584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpace P. J., Baresi L. A., Morley J. E. Glucocorticoids modulate beta-adrenoceptor subtypes and adenylate cyclase in brown fat. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):E153–E158. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.2.E153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Taylor D. R., Print C. G., Lake D. C., Li Q. Q., Flannery E. M., Yates D. M., Lucas M. K., Herbison G. P. Regular inhaled beta-agonist treatment in bronchial asthma. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1391–1396. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93098-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam M., Colvard D., Keeting P. E., Rasmussen K., Riggs B. L., Spelsberg T. C. Glucocorticoid regulation of alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, and proto-oncogenes in normal human osteoblast-like cells. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Dec;50(4):411–424. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersfield A. E., Barnes P. J. Beta 2-agonists and corticosteroids: new developments and controversies. Report of a meeting in November 1990. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Dec;146(6):1637–1641. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.6.1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. R., Sears M. R., Herbison G. P., Flannery E. M., Print C. G., Lake D. C., Yates D. M., Lucas M. K., Li Q. Regular inhaled beta agonist in asthma: effects on exacerbations and lung function. Thorax. 1993 Feb;48(2):134–138. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]