Abstract
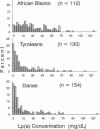
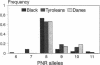
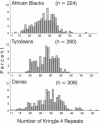
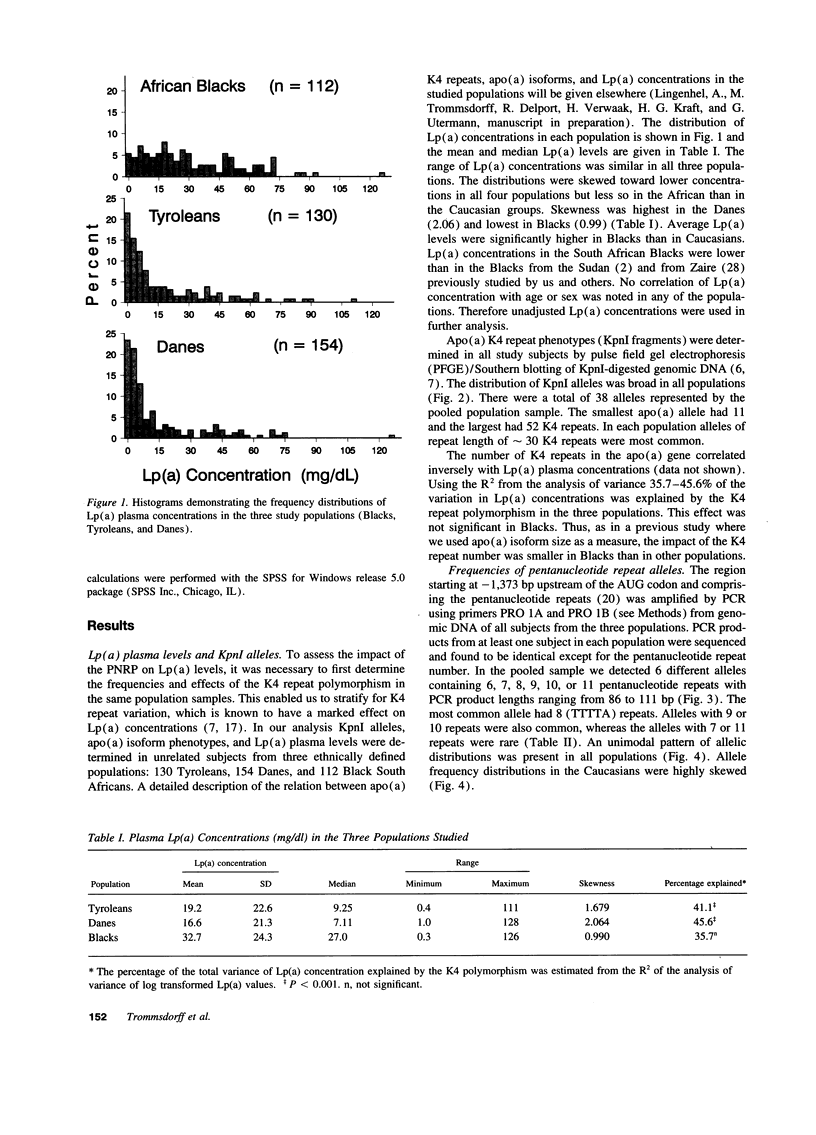
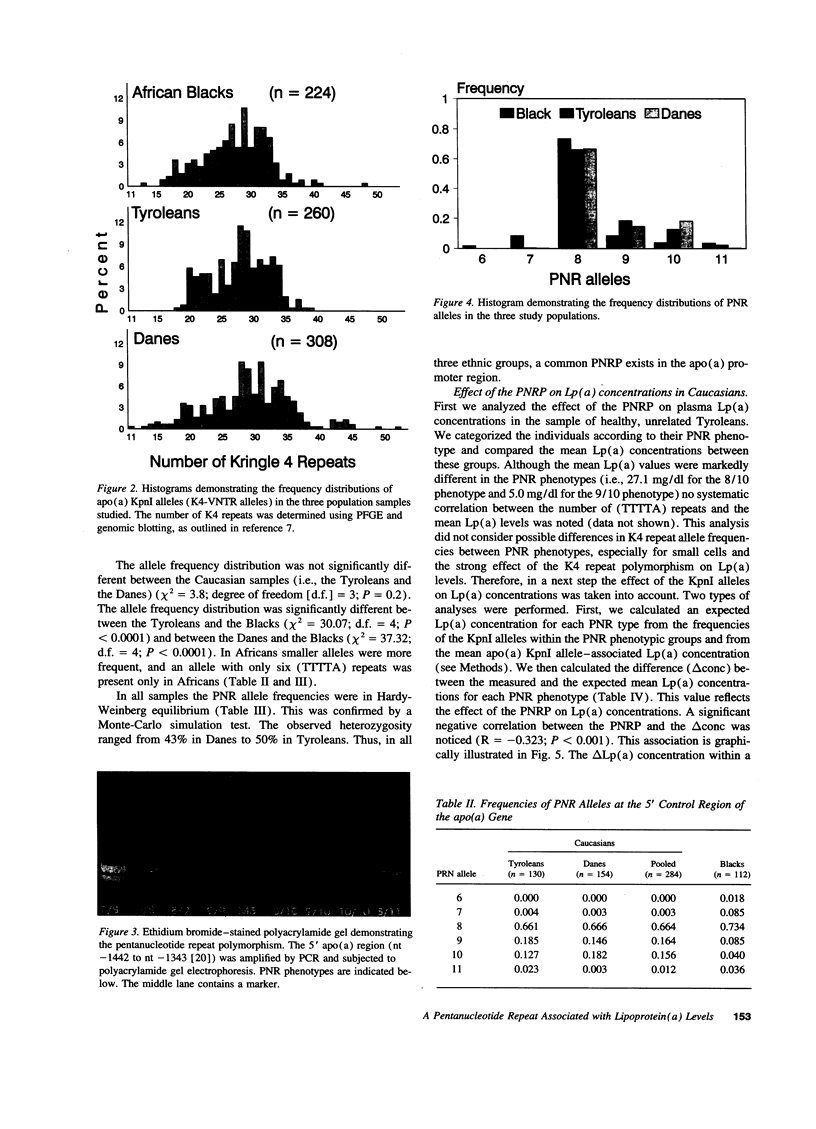
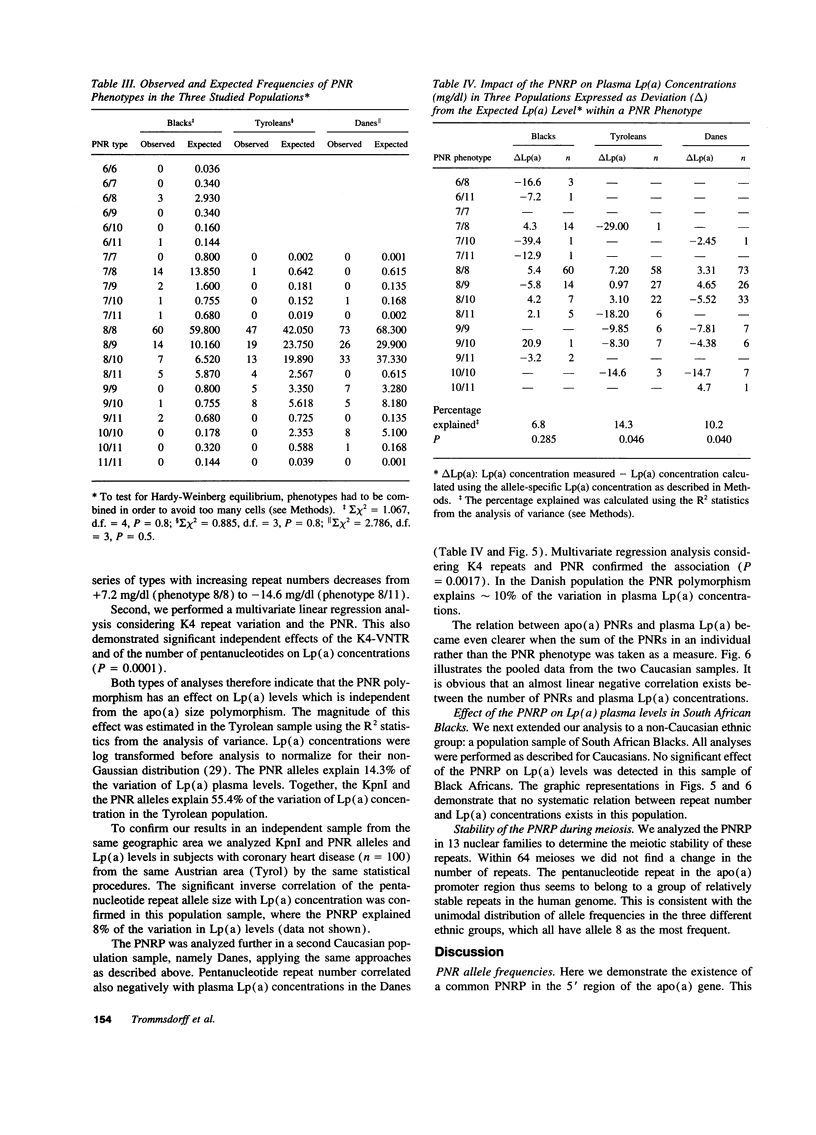
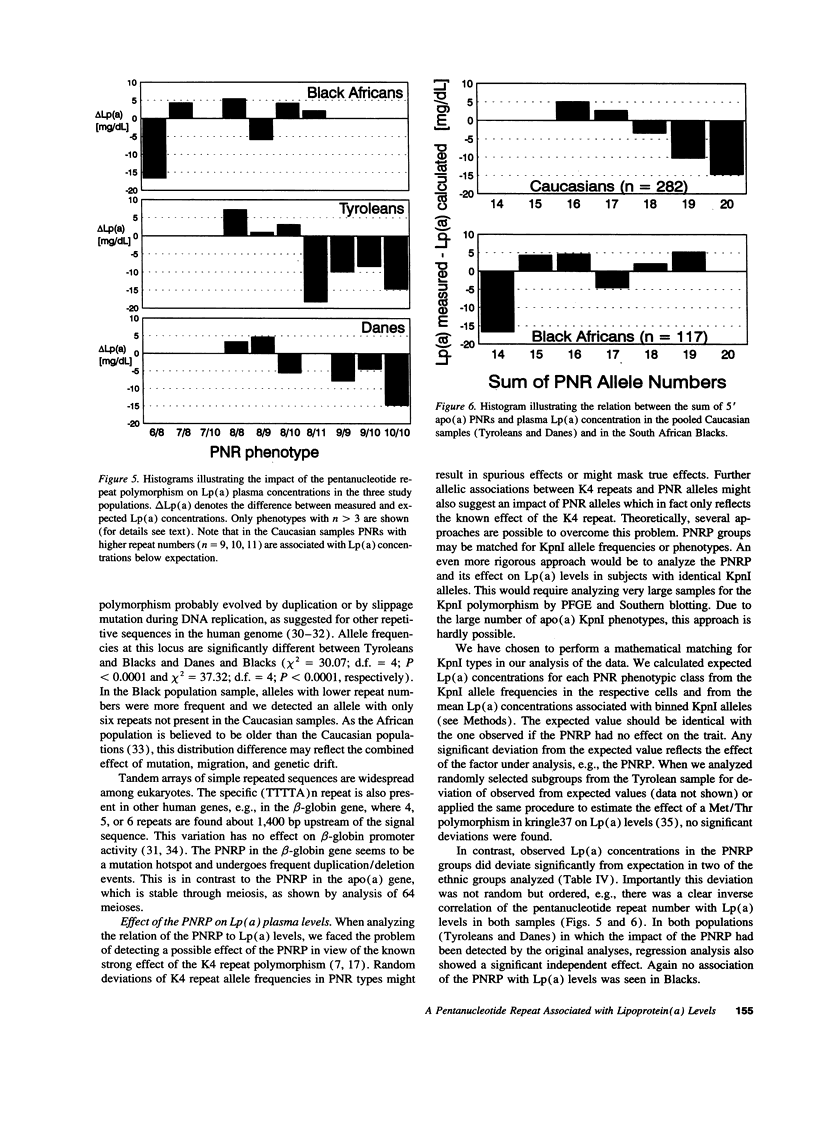
The enormous interindividual variation in the plasma concentrations of the atherogenic lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is almost entirely controlled by the apo(a) locus on chromosome 6q26-q27. A variable number of transcribed kringle4 repeats (K4-VNTR) in the gene explains a large fraction of this variation, whereas the rest is presently unexplained. We here have analyzed the effect of the K4-VNTR and of a pentanucleotide repeat polymorphism (TTTTA)n (n = 6-11) in the 5' control region of the apo(a) gene on plasma Lp(a) levels in unrelated healthy Tyroleans (n = 130), Danes (n = 154), and Black South Africans (n = 112). The K4-VNTR had a significant effect on plasma Lp(a) levels in Caucasians and explained 41 and 45% of the variation in Lp(a) plasma concentration in Tyroleans and Danes, respectively. Both, the pentanucleotide repeat (PNR) allele frequencies and their effects on Lp(a) concentrations were heterogeneous among populations. A significant negative correlation between the number of pentanucleotide repeats and the plasma Lp(a) concentration was observed in Tyroleans and Danes. The effect of the 5' PNRP on plasma Lp(a) concentrations was independent from the K4-VNTR and explained from 10 to 14% of the variation in Lp(a) concentrations in Caucasians. No significant effect of the PNRP was present in Black Africans. This suggests allelic association between PNR alleles and sequences affecting Lp(a) levels in Caucasians. Thus, in Caucasians but not in Blacks, concentrations of the atherogenic Lp(a) particle are strongly associated with two repeat polymorphisms in the apo(a) gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boerwinkle E., Leffert C. C., Lin J., Lackner C., Chiesa G., Hobbs H. H. Apolipoprotein(a) gene accounts for greater than 90% of the variation in plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):52–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI115855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budowle B., Giusti A. M., Waye J. S., Baechtel F. S., Fourney R. M., Adams D. E., Presley L. A., Deadman H. A., Monson K. L. Fixed-bin analysis for statistical evaluation of continuous distributions of allelic data from VNTR loci, for use in forensic comparisons. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):841–855. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Kalaitsidaki M., Warren A. C., Avramopoulos D., Antonarakis S. E. A novel zinc finger cDNA with a polymorphic pentanucleotide repeat (ATTTT)n maps on human chromosome 19p. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):621–625. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaw A., Boerwinkle E., Cohen J. C., Hobbs H. H. Comparative analysis of the apo(a) gene, apo(a) glycoprotein, and plasma concentrations of Lp(a) in three ethnic groups. Evidence for no common "null" allele at the apo(a) locus. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2526–2534. doi: 10.1172/JCI117263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger D. J., Kemp P. R., Liu A. C., Lawn R. M., Metcalfe J. C. Activation of transforming growth factor-beta is inhibited in transgenic apolipoprotein(a) mice. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):460–462. doi: 10.1038/370460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger D. J., Kirschenlohr H. L., Metcalfe J. C., Weissberg P. L., Wade D. P., Lawn R. M. Proliferation of human smooth muscle cells promoted by lipoprotein(a). Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1655–1658. doi: 10.1126/science.8503012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Gordon B. R., Parker T. S. Plasmin catalyzes binding of lipoprotein (a) to immobilized fibrinogen and fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3847–3851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamboh M. I., Ferrell R. E., Kottke B. A. Expressed hypervariable polymorphism of apolipoprotein (a). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):1063–1074. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K. Associations of disease with genetic markers: déjà vu all over again. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jul 15;48(2):71–73. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320480202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koschinsky M. L., Beisiegel U., Henne-Bruns D., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M. Apolipoprotein(a) size heterogeneity is related to variable number of repeat sequences in its mRNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):640–644. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Haibach C., Lingenhel A., Brunner C., Trommsdorff M., Kronenberg F., Müller H. J., Utermann G. Sequence polymorphism in kringle IV 37 in linkage disequilibrium with the apolipoprotein (a) size polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;95(3):275–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00225193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Köchl S., Menzel H. J., Sandholzer C., Utermann G. The apolipoprotein (a) gene: a transcribed hypervariable locus controlling plasma lipoprotein (a) concentration. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):220–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00220066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Malgaretti N., Köchl S., Acquati F., Utermann G., Taramelli R. Demonstration of physical linkage between the promoter region and the polymorphic kringle IV domain in the Apo(a) gene by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):260–262. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner C., Cohen J. C., Hobbs H. H. Molecular definition of the extreme size polymorphism in apolipoprotein(a). Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):933–940. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J. Lipoprotein(a). A unique risk factor for atherothrombotic disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Sep-Oct;10(5):672–679. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.5.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaretti N., Acquati F., Magnaghi P., Bruno L., Pontoglio M., Rocchi M., Saccone S., Della Valle G., D'Urso M., LePaslier D. Characterization by yeast artificial chromosome cloning of the linked apolipoprotein(a) and plasminogen genes and identification of the apolipoprotein(a) 5' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11584–11588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Dieplinger H., Lackner C., Hoppichler F., Lloyd J. K., Muller D. R., Labeur C., Talmud P. J., Utermann G. Abetalipoproteinemia with an ApoB-100-lipoprotein(a) glycoprotein complex in plasma. Indication for an assembly defect. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra H. J., Arveiler D., Evans A. E., Cambou J. P., Amouyel P., Bingham A., McMaster D., Schaffer P., Douste-Blazy P., Luc G. A case-control study of lipoprotein particles in two populations at contrasting risk for coronary heart disease. The ECTIM Study. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Jun;12(6):701–707. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.6.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra H. J., Luyéyé I., Bouramoué C., Demarquilly C., Fruchart J. C. Black-white differences in serum Lp(a) lipoprotein levels. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Sep 15;168(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti M., Zhang F. P., Fu Y. H., Warren S. T., Oostra B. A., Caskey C. T., Nelson D. L. Absence of expression of the FMR-1 gene in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90125-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Kidd K. K. HLA and disease susceptibility: a primer. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 10;297(19):1060–1062. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711102971909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholzer C., Hallman D. M., Saha N., Sigurdsson G., Lackner C., Császár A., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):607–614. doi: 10.1007/BF00201550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholzer C., Saha N., Kark J. D., Rees A., Jaross W., Dieplinger H., Hoppichler F., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Apo(a) isoforms predict risk for coronary heart disease. A study in six populations. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Oct;12(10):1214–1226. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.10.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlötterer C., Tautz D. Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):211–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A. Duplication/deletion polymorphism 5' - to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5037–5047. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Hiyama K., Kodaira M., Satoh C. The length polymorphism in the 5' flanking region of the human beta-globin gene with denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in a Japanese population. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):219–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00204187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):904–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2530631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij C., Bakker C. E., de Graaff E., Keulemans J., Willemsen R., Verkerk A. J., Galjaard H., Reuser A. J., Hoogeveen A. T., Oostra B. A. Characterization and localization of the FMR-1 gene product associated with fragile X syndrome. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):722–724. doi: 10.1038/363722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigilant L., Stoneking M., Harpending H., Hawkes K., Wilson A. C. African populations and the evolution of human mitochondrial DNA. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1503–1507. doi: 10.1126/science.1840702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade D. P., Clarke J. G., Lindahl G. E., Liu A. C., Zysow B. R., Meer K., Schwartz K., Lawn R. M. Genetic influences on lipoprotein(a) concentration. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):499–502. doi: 10.1042/bst0210499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. L., Hixson J. E., Rainwater D. L., Lanford R. E. Molecular basis for "null" lipoprotein(a) phenotypes and the influence of apolipoprotein(a) size on plasma lipoprotein(a) level in the baboon. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9060–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. L., Lanford R. E. Cell surface assembly of lipoprotein(a) in primary cultures of baboon hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28716–28723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zysow B. R., Lindahl G. E., Wade D. P., Knight B. L., Lawn R. M. C/T polymorphism in the 5' untranslated region of the apolipoprotein(a) gene introduces an upstream ATG and reduces in vitro translation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):58–64. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]