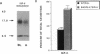Abstract
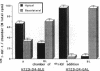
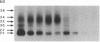
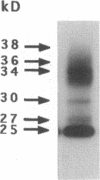
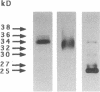
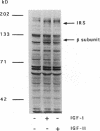
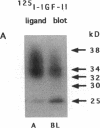
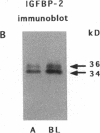
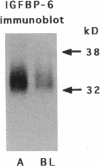
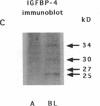
In this study, we have used enterocyte-like differentiated HT29-D4 human colonic carcinoma cells cultured in a glucose-free medium (HT29-D4-GAL cells) on semi-permeable supports in order to investigate the polarity of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system. We report that these cells secrete endogenous IGF-II predominantly (66%) from the basolateral cell surface where type I IGF receptors are almost all (> 96%) localized. HT29-D4-GAL cells also secrete IGF-binding protein (IGFBP) -2, -4, and -6 as evidenced by Western ligand and immunoblot analyses of conditioned medium. IGFBP-2 and IGFBP-4 are secreted primarily into the basolateral side (71 and 87%, respectively), whereas IGFBP-6 is targeted to the apical surface (76%) as a possible consequence of an active sorting. Finally, HT29-D4-GAL cells are found to display responses to IGF-II added to the basolateral but not the apical membrane side in terms of intracellular tyrosine phosphorylation and long-term stimulation of amino acid uptake. This study indicates (a) that IGF-II is potentially capable of autocrine regulation on the basolateral side of HT29-D4-GAL cell, and (b) that IGFBP-6 has a unique pattern of secretory polarity. It supports the concept that a differential sorting of the various forms of IGFBPs might play a modulatory role in the maintenance of a functional polarity in the differentiated HT29-D4-GAL cells.
Full text
PDF


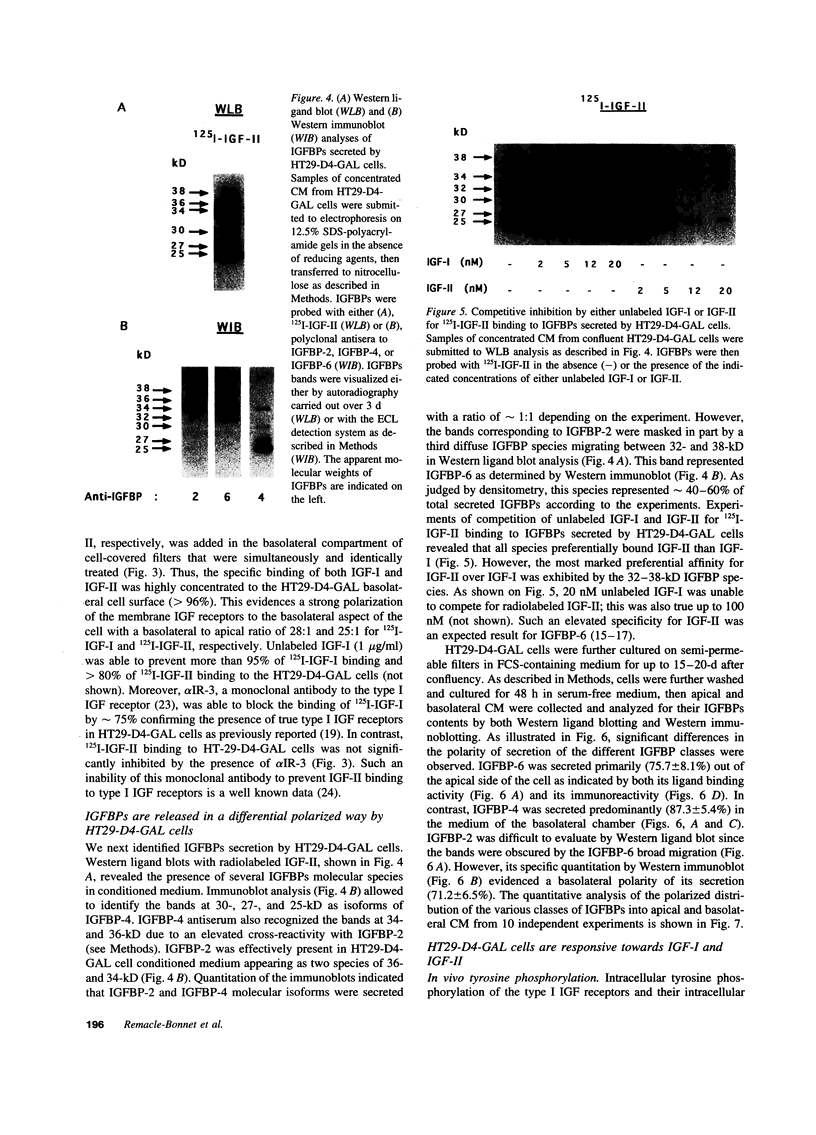
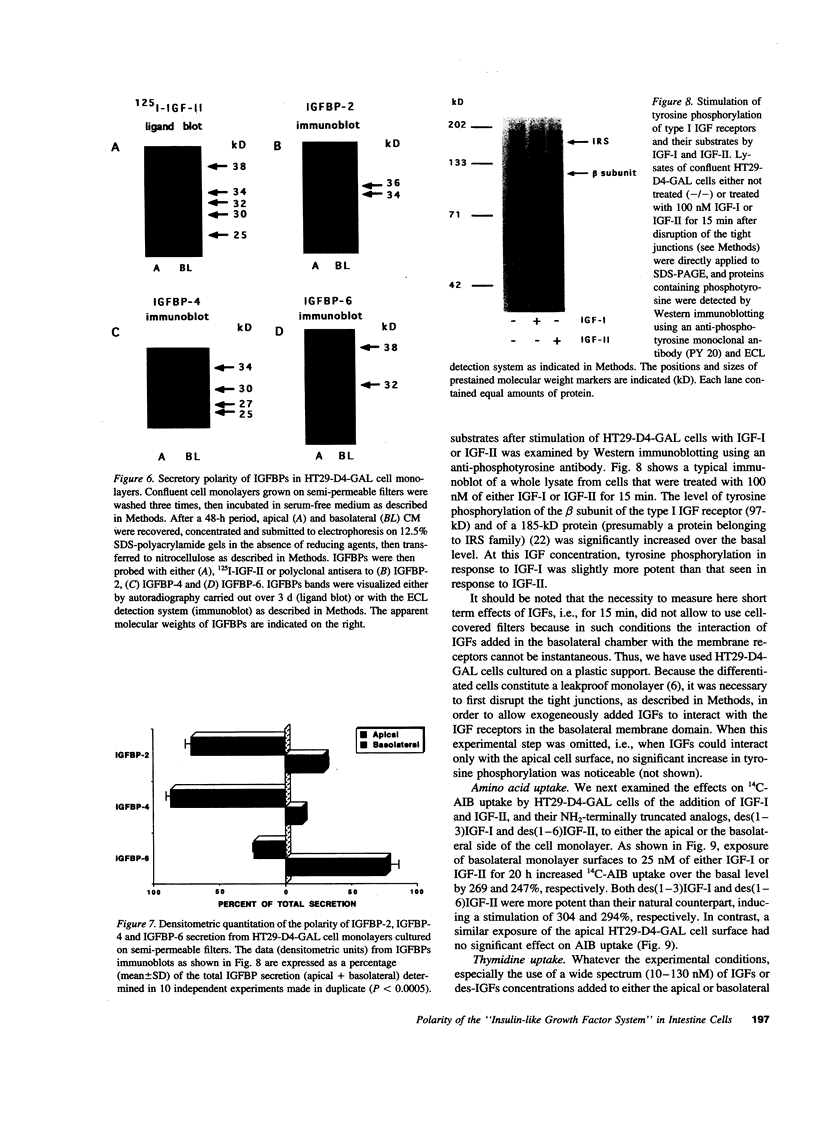
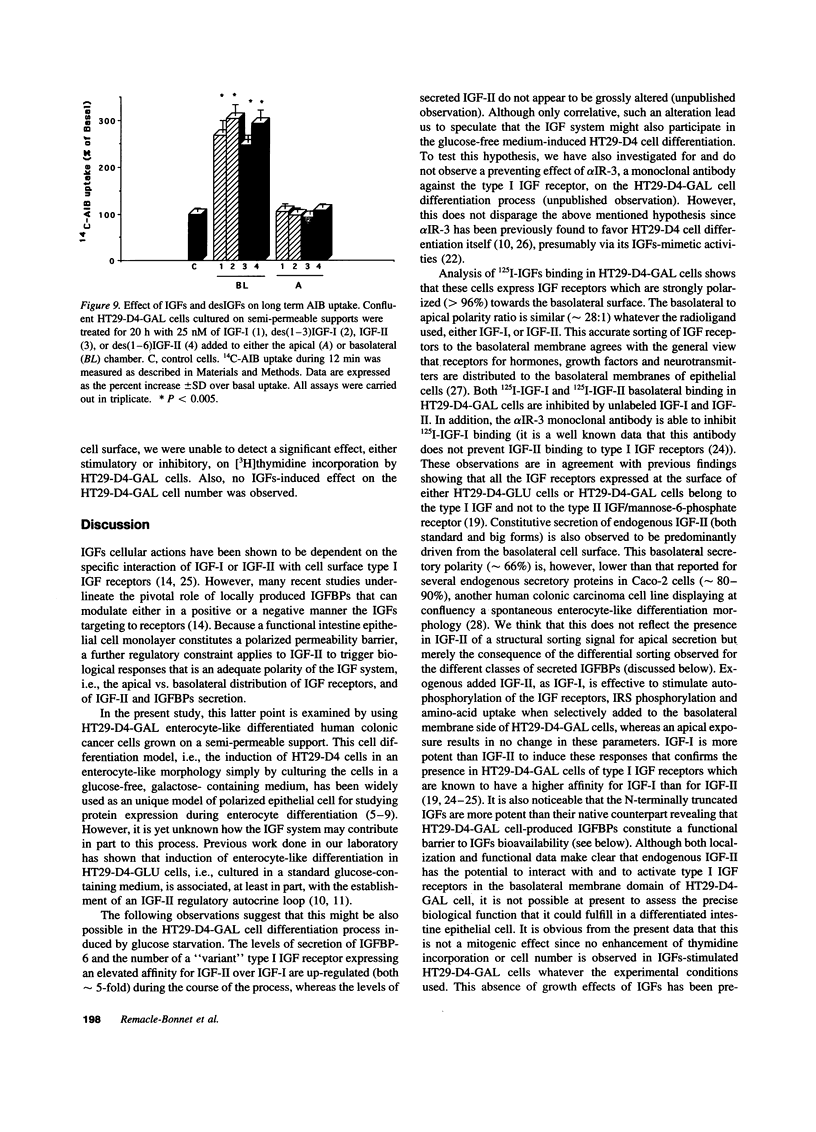


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach L. A., Hsieh S., Brown A. L., Rechler M. M. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-6 inhibits IGF-II-induced differentiation of L6A1 myoblasts. Endocrinology. 1994 Nov;135(5):2168–2176. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.5.7525263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach L. A., Hsieh S., Sakano K., Fujiwara H., Perdue J. F., Rechler M. M. Binding of mutants of human insulin-like growth factor II to insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1-6. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9246–9254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach L. A., Thotakura N. R., Rechler M. M. Human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 is O-glycosylated. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):301–307. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80807-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baghdiguian S., Verrier B., Gerard C., Fantini J. Insulin like growth factor I is an autocrine regulator of human colon cancer cell differentiation and growth. Cancer Lett. 1992 Feb 14;62(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90194-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Hart I. K., Coles H. S., Burne J. F., Voyvodic J. T., Richardson W. D., Raff M. C. Cell death and control of cell survival in the oligodendrocyte lineage. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90531-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Bar R. S., Boes M., Dake B. L., Bayne M., Cascieri M. Intrinsic bioactivity of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins from vascular endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):2630–2638. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-2630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Lamson G., Okajima T., Rosenfeld R. G. Transfection of the human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 gene into Balb/c fibroblasts inhibits cellular growth. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Mar;7(3):380–386. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.3.7683373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohick W. S., Clemmons D. R. The insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:131–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Insulin-like growth factor II binding and action in human fetal fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Dec;133(3):560–566. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Dexter T. M. Growth factors in development, transformation, and tumorigenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90638-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culouscou J. M., Remacle-Bonnet M., Garrouste F., Fantini J., Marvaldi J., Pommier G. Production of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) and different forms of IGF-binding proteins by HT-29 human colon carcinoma cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jun;143(3):405–415. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantini J., Abadie B., Tirard A., Remy L., Ripert J. P., el Battari A., Marvaldi J. Spontaneous and induced dome formation by two clonal cell populations derived from a human adenocarcinoma cell line, HT29. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jul;83:235–249. doi: 10.1242/jcs.83.1.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantini J., Martin J. M., Luis J., Rémy L., Tirard A., Marvaldi J., Pichon J. Restricted localization of functional vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptors in in vitro differentiated human colonic adenocarcinoma cells (HT29-D4). Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;46(3):458–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantini J., Rognoni J. B., Verrier B., Lehmann M., Roccabianca M., Mauchamp J., Marvaldi J. Suramin-treated HT29-D4 cells grown in the presence of glucose in permeable culture chambers form electrically active epithelial monolayers. A comparative study with HT29-D4 cells grown in the absence of glucose. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;51(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantini J., Verrier B., Marvaldi J., Mauchamp J. In vitro differentiated HT 29-D4 clonal cell line generates leakproof and electrically active monolayers when cultured in porous-bottom culture dishes. Biol Cell. 1989;65(2):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain-Lee E. L., Janicot M., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Casella S. J. Expression of a type I insulin-like growth factor receptor with low affinity for insulin-like growth factor II. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):413–417. doi: 10.1042/bj2810413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I. Intestinal epithelial differentiation: new insights from chimeric and transgenic mice. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1187–1194. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. I., Gockerman A., Busby W. H., Jr, Wright G., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 stimulates cell migration and binds to the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin by means of its Arg-Gly-Asp sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10553–10557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Faria T. N., Stannard B., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Role of tyrosine kinase activity in signal transduction by the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor. Characterization of kinase-deficient IGF-I receptors and the action of an IGF-I-mimetic antibody (alpha IR-3). J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2655–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Seguchi T., Ono M. Glycosylation mutations of serine/threonine-linked oligosaccharides in low-density lipoprotein receptor: indispensable roles of O-glycosylation. J Cell Sci. 1991 Feb;98(Pt 2):131–134. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Coverley J. A., Baxter R. C. Regulation of immunoreactive insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 in normal and transformed human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11470–11477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Willetts K. E., Baxter R. C. Purification and properties of a novel insulin-like growth factor-II binding protein from transformed human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4124–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris B. A., Nelson W. J. Alterations in the establishment and maintenance of epithelial cell polarity as a basis for disease processes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):3–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI114427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K., Apodaca G., Aroeti B., Okamoto C. Plasma membrane protein sorting in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):577–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Müller H. L., Lamson G., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent action of IGF-binding protein-3 in Hs578T human breast cancer cells. Cell surface binding and growth inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14964–14971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Müller H. L., Neely E. K., Lamson G., Rosenfeld R. G. New concepts in insulin-like growth factor receptor physiology. Growth Regul. 1993 Jun;3(2):113–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. H., McCusker R. H., Vanderhoof J. A., Mohammadpour H., Harty R. F., MacDonald R. G. Secretion of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) and IGF-binding protein-2 by intestinal epithelial (IEC-6) cells: implications for autocrine growth regulation. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1359–1368. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1380441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier G. J., Garrouste F. L., el Atiq F., Roccabianca M., Marvaldi J. L., Remacle-Bonnet M. M. Potential autocrine role of insulin-like growth factor II during suramin-induced differentiation of HT29-D4 human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 1;52(11):3182–3188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier G., Garrouste F., el Atiq F., Marvaldi J., Remacle-Bonnet M. Potential role of IGFBPS in the regulation of the differentiation state of human colonic carcinoma cells. Growth Regul. 1993 Mar;3(1):80–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacle-Bonnet M. M., Culouscou J. M., Garrouste F. L., Rabenandrasana C., Marvaldi J. L., Pommier G. J. Expression of type I, but not type II insulin-like growth factor receptor on both undifferentiated and differentiated HT29 human colon carcinoma cell line. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Aug;75(2):609–616. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.2.1322432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacle-Bonnet M., Garrouste F., el Atiq F., Roccabianca M., Marvaldi J., Pommier G. des-(1-3)-IGF-I, an insulin-like growth factor analog used to mimic a potential IGF-II autocrine loop, promotes the differentiation of human colon-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1992 Dec 2;52(6):910–917. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Traber M. G. A specific sorting signal is not required for the polarized secretion of newly synthesized proteins from cultured intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):471–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roghani M., Lassarre C., Zapf J., Povoa G., Binoux M. Two insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins are responsible for the selective affinity for IGF-II of cerebrospinal fluid binding proteins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Sep;73(3):658–666. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-3-658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. S., Shao Z. M., Hussain A., Clemmons D. R., Chen J. C., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Fontana J. A. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding-protein-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6: synthesis, secretion, and gene expression in estrogen receptor-negative human breast carcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Jun;155(3):556–567. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041550314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimasaki S., Gao L., Shimonaka M., Ling N. Isolation and molecular cloning of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-6. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):938–948. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimasaki S., Ling N. Identification and molecular characterization of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP-1, -2, -3, -4, -5 and -6). Prog Growth Factor Res. 1991;3(4):243–266. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(91)90003-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Dai B., Dhruva B., Widen S. G. Episomal expression of sense and antisense insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-4 complementary DNA alters the mitogenic response of a human colon cancer cell line (HT-29) by mechanisms that are independent of and dependent upon IGF-I. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6563–6570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]