Abstract
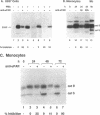
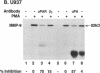
Binding of urokinase to the glycolipid-anchored urokinase receptor (uPAR) has been implicated in macrophage differentiation. However, no biochemical markers of differentiation have yet been directly linked to uPAR occupancy. As extensive changes in proteolytic profile characterize monocytic differentiation, we have examined the role of uPAR occupancy on protease expression by differentiating phagocytes. Antibodies to either urokinase or to uPAR that prevent receptor binding inhibited induction of cathepsin B in cultured monocytes and both cathepsin B and 92-kD gelatinase mRNA and protein in phorbol diester-stimulated myeloid cells. Mannosamine, an inhibitor of glycolipid anchor assembly, also blocked protease expression. Anti-catalytic urokinase antibodies, excess inactive urokinase, or aprotinin had no effect, indicating that receptor occupancy per se regulated protease expression. Antibodies to the integrins CD11a and CD29 or to the glycolipid-anchored proteins CD14 and CD55 also had no effect. Protease induction was independent of matrix attachment. Antibodies to urokinase or uPAR affected neither the decrease in cathepsin G nor the increase in tumor necrosis factor-alpha in phorbol ester-stimulated cells. These data establish that uPAR is a multifunctional receptor, not only promoting pericellular proteolysis and matrix attachment, but also effecting cysteine- and metallo-protease expression during macrophage differentiation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander C. M., Werb Z. Proteinases and extracellular matrix remodeling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;1(5):974–982. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D., Crocker J., Vaughan A. T. Synthesis of cathepsin B by cells derived from the HL60 promyelocytic leukaemia cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jun;115(3):249–254. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Masur S. K., Lazega D., Waxman S., Ossowski L. Induction of cell migration by pro-urokinase binding to its receptor: possible mechanism for signal transduction in human epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):259–270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Cury J. D., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Neutral proteinases of human mononuclear phagocytes. Cellular differentiation markedly alters cell phenotype for serine proteinases, metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Bertozzi P., Sailor L. Z., Nusrat A. R. Alveolar macrophage urokinase receptors localize enzyme activity to the cell surface. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):L432–L438. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.6.L432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Reilly J. J., Jr, Kobzik L. Role of plasminogen activator in degradation of extracellular matrix protein by live human alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):412–419. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I. Characterization of a functional thrombin receptor. Issues and opportunities. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):351–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI115592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damsky C. H., Werb Z. Signal transduction by integrin receptors for extracellular matrix: cooperative processing of extracellular information. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):772–781. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90100-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso M., Anichini E., Pedersen N., Blasi F., Fibbi G., Pucci M., Ruggiero M. Urokinase-urokinase receptor interaction: non-mitogenic signal transduction in human epidermal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jan 29;190(2):347–352. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eierman D. F., Johnson C. E., Haskill J. S. Human monocyte inflammatory mediator gene expression is selectively regulated by adherence substrates. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1970–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Scully M. F., Kakkar V. V. Plasminogen activation initiated by single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Potentiation by U937 monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Wohlwend A., Belin D., Schleuning W. D., Vassalli J. D. Characterization of the cellular binding site for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1180–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibbi G., Ziche M., Morbidelli L., Magnelli L., Del Rosso M. Interaction of urokinase with specific receptors stimulates mobilization of bovine adrenal capillary endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Dec;179(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Thut C. J., VandeBos T., Gimpel S. D., Delaney P. B., King J., Price V., Cosman D., Beckmann M. P. Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor is structurally related to the IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2839–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Soppet D. Sequence and expression of caveolin, a protein component of caveolae plasma membrane domains phosphorylated on tyrosine in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10517–10521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr Tyrosine phosphorylation of a 22-kDa protein is correlated with transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20163–20166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross T. J., Sitrin R. G. The THP-1 cell line is a urokinase-secreting mononuclear phagocyte with a novel defect in the production of plasminogen activator inhibitor-2. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1873–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinec N., Dalet-Fumeron V., Pagano M. "In vitro" study of basement membrane degradation by the cysteine proteinases, cathepsins B, B-like and L. Digestion of collagen IV, laminin, fibronectin, and release of gelatinase activities from basement membrane fibronectin. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1993 Dec;374(12):1135–1146. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1993.374.7-12.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyetko M. R., Todd R. F., 3rd, Wilkinson C. C., Sitrin R. G. The urokinase receptor is required for human monocyte chemotaxis in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1380–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI117114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. D., Connolly N. L., Burnett D., Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., Ley T. J. Developmental regulation of the human cathepsin G gene in myelomonocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1524–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Johnson C., Eierman D., Becker S., Warren K. Adherence induces selective mRNA expression of monocyte mediators and proto-oncogenes. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1690–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass R. Retrodifferentiation--an alternative biological pathway in human leukemia cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;58(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C. J., Rebibou J. M., Peraldi M. N., Meulders Q., Rondeau E. Growth factor-like effect of urokinase type plasminogen activator in human renal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1408–1416. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90443-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Pöschl B., van Loon A. P. Tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta bind to the same two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors and maximally activate the transcription factor NF-kappa B at low receptor occupancy and within minutes after receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15183–15188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. L., Rozek M. M., Suenram C. A., Schwartz C. J. Activation of human blood monocytes by adherence to tissue culture plastic surfaces. Exp Mol Pathol. 1987 Jun;46(3):266–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(87)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Christ G., Binder B. R. Growth stimulation of human epidermal cells by urokinase is restricted to the intact active enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):103–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Moniwa N., Sugimura M., Shinohara H., Ohi H., Terao T. Effects of membrane-associated cathepsin B on the activation of receptor-bound prourokinase and subsequent invasion of reconstituted basement membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 28;1178(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Field M. C., Caras I. W., Menon A. K., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Mannosamine, a novel inhibitor of glycosylphosphatidylinositol incorporation into proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1969–1977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Rønne E., Roldan A. L., Behrendt N., Rømer J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase receptor mRNA level and gene transcription are strongly and rapidly increased by phorbol myristate acetate in human monocyte-like U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5177–5181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Wegenka U. M., Yuan J., Buschmann J., Schindler C., Ziemiecki A., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Yasukawa K., Taga T. Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8272872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. The matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):455–463. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Rothberg K. G., Maxfield F. R. Sequestration of GPI-anchored proteins in caveolae triggered by cross-linking. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1948–1951. doi: 10.1126/science.7516582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):161–195. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A. R., Chapman H. A., Jr An autocrine role for urokinase in phorbol ester-mediated differentiation of myeloid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI115070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Christensen E. I., Davidsen O., Gliemann J. Urokinase receptors in human monocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Møller B., Jensen P. H., Moestrup S. K., Holtet T. L., Etzerodt M., Thøgersen H. C., Munch M., Andreasen P. A. Purified alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/LDL receptor-related protein binds urokinase.plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex. Evidence that the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor mediates cellular degradation of urokinase receptor-bound complexes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14543–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. In vivo invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2437–2445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picone R., Kajtaniak E. L., Nielsen L. S., Behrendt N., Mastronicola M. R., Cubellis M. V., Stoppelli M. P., Pedersen S., Danø K., Blasi F. Regulation of urokinase receptors in monocytelike U937 cells by phorbol ester phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):693–702. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug M., Plesner T., Rønne E., Ellis V., Høyer-Hansen G., Hansen N. E., Danø K. The receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator is deficient on peripheral blood leukocytes in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1992 Mar 15;79(6):1447–1455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani S. A., Mazar A. P., Bernier S. M., Haq M., Bolivar I., Henkin J., Goltzman D. Structural requirements for the growth factor activity of the amino-terminal domain of urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14151–14156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønne E., Behrendt N., Ellis V., Ploug M., Danø K., Høyer-Hansen G. Cell-induced potentiation of the plasminogen activation system is abolished by a monoclonal antibody that recognizes the NH2-terminal domain of the urokinase receptor. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENSON R. P. A modification of receptor theory. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Dec;11(4):379–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarialho-Kere U. K., Welgus H. G., Parks W. C. Distinct mechanisms regulate interstitial collagenase and 92-kDa gelatinase expression in human monocytic-like cells exposed to bacterial endotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17354–17361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Hovi T., Vaheri A. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor secreted by cultured human monocyte-macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):125–132. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Sudol M., Tang Z., Lisanti M. P. Signal transducing molecules and glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked proteins form a caveolin-rich insoluble complex in MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):789–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi G. P., Munger J. S., Meara J. P., Rich D. H., Chapman H. A. Molecular cloning and expression of human alveolar macrophage cathepsin S, an elastinolytic cysteine protease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7258–7262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A. Thrombin-cellular interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;485:228–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitrin R. G., Todd R. F., 3rd, Mizukami I. F., Gross T. J., Shollenberger S. B., Gyetko M. R. Cytokine-specific regulation of urokinase receptor (CD87) expression by U937 mononuclear phagocytes. Blood. 1994 Aug 15;84(4):1268–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanová I., Horejsí V., Ansotegui I. J., Knapp W., Stockinger H. GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1016–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.1719635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M., Braulke T., von Figura K., Hasilik A. Effects of differentiation-inducing agents on synthesis, maturation and secretion of cathepsin D in U937 and HL-60 cells. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Apr;368(4):413–418. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. J., Walters J. A., Hudson J., Gimble J. M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA accumulation in human myelomonocytic cell lines. Role of transcriptional regulation by DNA sequence motifs and mRNA stabilization. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernet T., Khouri H. E., Laflamme P., Tessier D. C., Musil R., Gour-Salin B. J., Storer A. C., Thomas D. Y. Processing of the papain precursor. Purification of the zymogen and characterization of its mechanism of processing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21451–21457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz D. A., Chapman H. A. Reversible cellular adhesion to vitronectin linked to urokinase receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14746–14750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz D. A., Sailor L. Z., Chapman H. A. Cytokines induce urokinase-dependent adhesion of human myeloid cells. A regulatory role for plasminogen activator inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1541–1552. doi: 10.1172/JCI116360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Nakanishi I., Yamashita K., Hayakawa T., Okada Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (92 kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase) from U937 monoblastoid cells: correlation with cellular invasion. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):991–999. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways D. K., Dodd R. C., Bennett T. E., Gray T. K., Earp H. S. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances phorbol ester-stimulated differentiation and protein kinase C-dependent substrate phosphorylation activity in the U937 human monoblastoid cell. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1654–1661. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y., Waltz D. A., Rao N., Drummond R. J., Rosenberg S., Chapman H. A. Identification of the urokinase receptor as an adhesion receptor for vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32380–32388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Campbell E. J., Cury J. D., Eisen A. Z., Senior R. M., Wilhelm S. M., Goldberg G. I. Neutral metalloproteinases produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. Enzyme profile, regulation, and expression during cellular development. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1496–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI114867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Connolly N. L., Senior R. M. 12-o-Tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate-differentiated U937 cells express a macrophage-like profile of neutral proteinases. High levels of secreted collagenase and collagenase inhibitor accompany low levels of intracellular elastase and cathepsin G. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1675–1681. doi: 10.1172/JCI112485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Walsh B. J., Lund K. A. Global modulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor is triggered by occupancy of only a few receptors. Evidence for a binary regulatory system in normal human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18912–18920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm O., Weidle U., Höhl S., Rettenberger P., Schmitt M., Graeff H. Recombinant soluble urokinase receptor as a scavenger for urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). Inhibition of proliferation and invasion of human ovarian cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 10;337(2):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh E. T., Rosse W. F. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2305–2310. doi: 10.1172/JCI117234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou M. J., Brown E. J. CR3 (Mac-1, alpha M beta 2, CD11b/CD18) and Fc gamma RIII cooperate in generation of a neutrophil respiratory burst: requirement for Fc gamma RIII and tyrosine phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1407–1416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]