Abstract
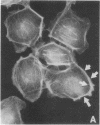
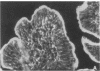
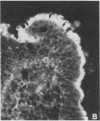
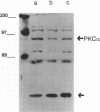
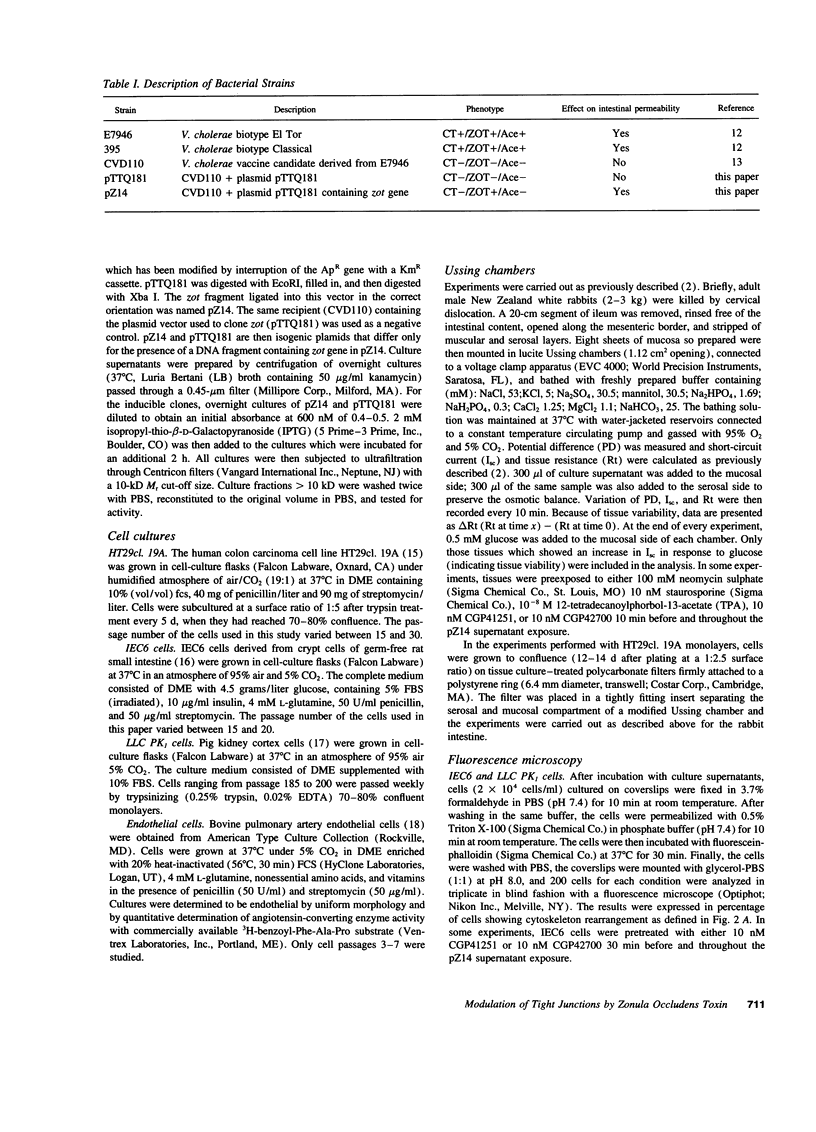
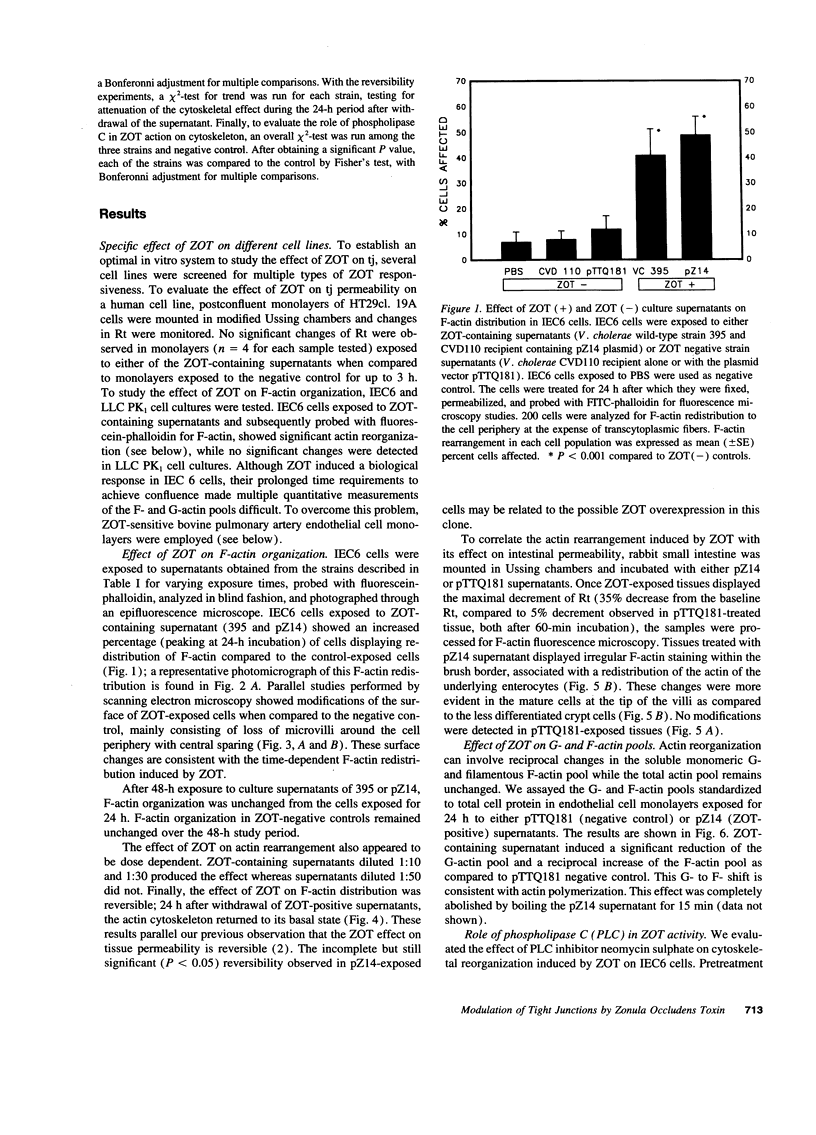
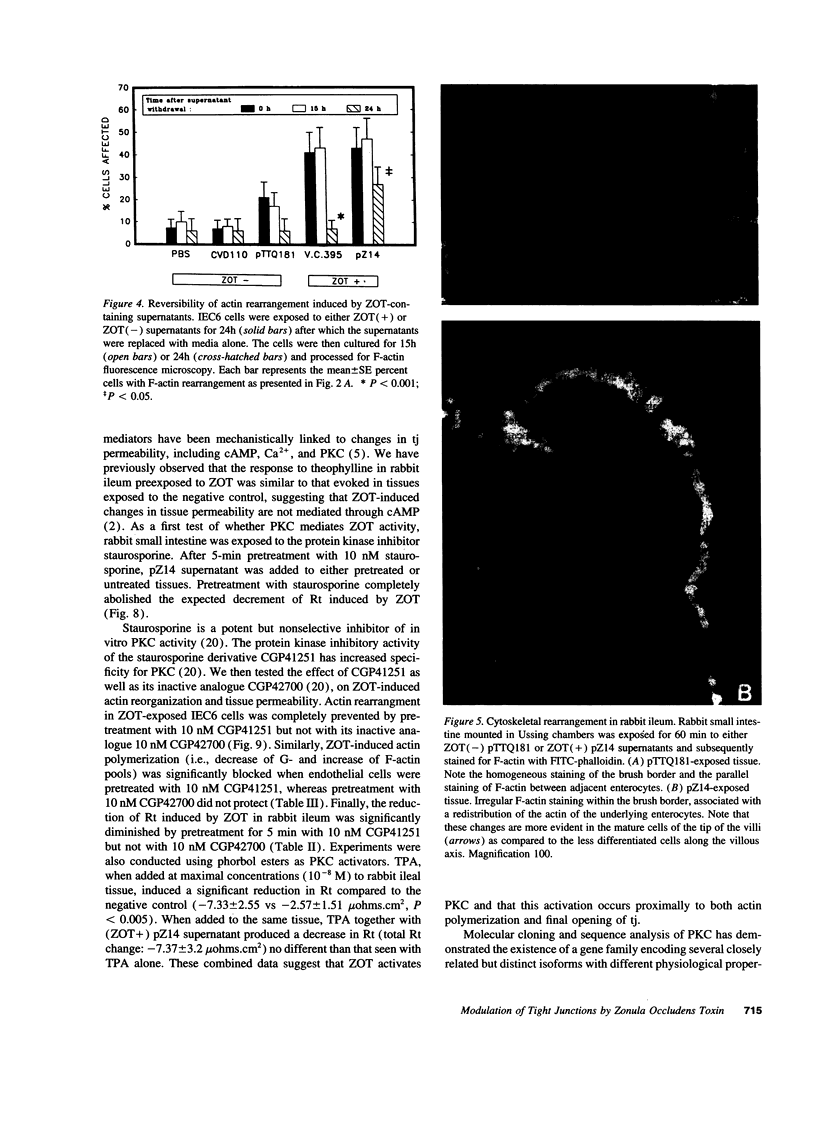
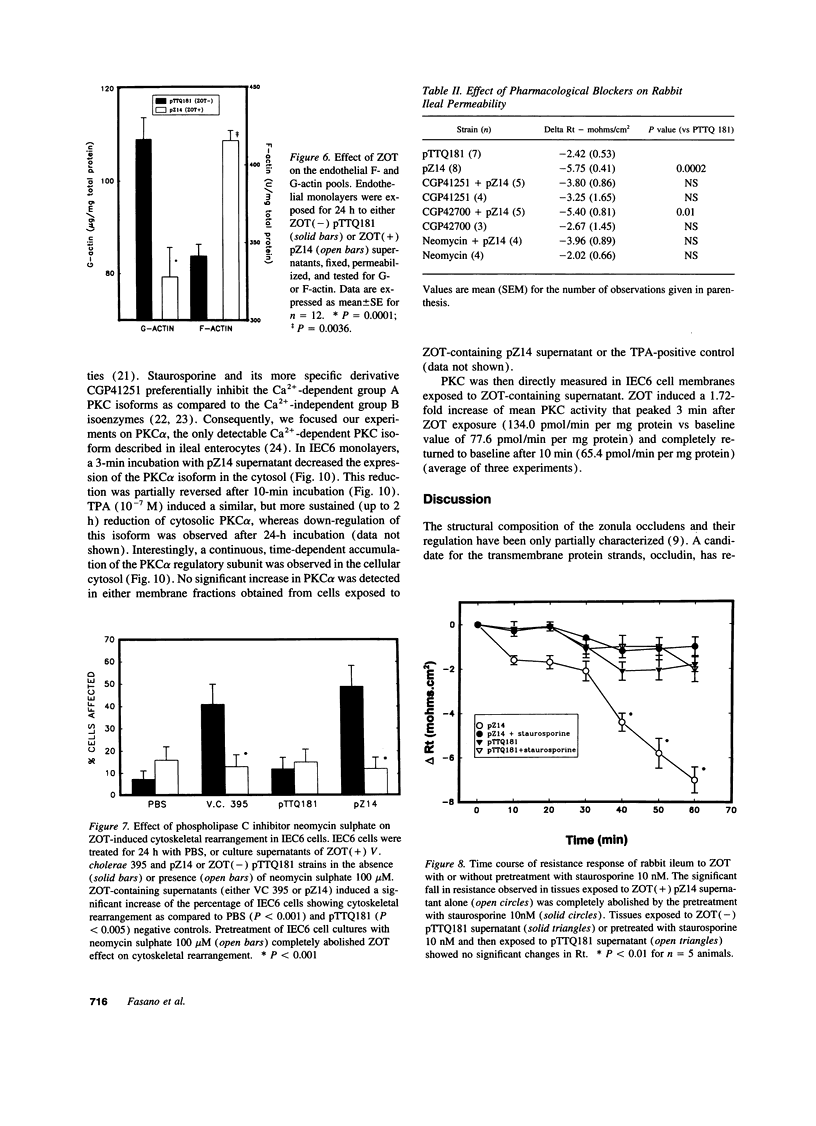
The intracellular signaling involved in the mechanism of action of zonula occludens toxin (ZOT) was studied using several in vitro and ex vivo models. ZOT showed a selective effect among various cell lines tested, suggesting that it may interact with a specific receptor, whose surface expression on various cells differs. When tested in IEC6 cell monolayers, ZOT-containing supernatants induced a redistribution of the F-actin cytoskeleton. Similar results were obtained with rabbit ileal mucosa, where the reorganization of F-actin paralleled the increase in tissue permeability. In endothelial cells, the cytoskeletal rearrangement involved a decrease of the soluble G-actin pool (-27%) and a reciprocal increase in the filamentous F-actin pool (+22%). This actin polymerization was time- and dose-dependent, and was reversible. Pretreatment with a specific protein kinase C inhibitor, CGP41251, completely abolished the ZOT effects on both tissue permeability and actin polymerization. In IEC6 cells ZOT induced a peak increment of the PKC-alpha isoform after 3 min incubation. Taken together, these results suggest that ZOT activates a complex intracellular cascade of events that regulate tight junction permeability, probably mimicking the effect of physiologic modulator(s) of epithelial barrier function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. Signal transduction and the actin cytoskeleton: the roles of MARCKS and profilin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. M., Balda M. S., Fanning A. S. The structure and regulation of tight junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;5(5):772–778. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90024-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzi A., Boscoboinik D., Hensey C. The protein kinase C family. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 15;208(3):547–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker R., Groot J. A. cAMP-mediated effects of ouabain and theophylline on paracellular ion selectivity. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G213–G217. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Fasano A., Ketley J., Kaper J. B. Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.428-434.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Veall N. A persistent defect in intestinal permeability in coeliac disease demonstrated by a 51Cr-labelled EDTA absorption test. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):323–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Twenty-first Bowditch lecture. The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist. 1977 Feb;20(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis B., Schneeberger E. E., Rabito C. A. Cellular variability in the development of tight junctions after activation of protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):F293–F300. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.2.F293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Baudry B., Pumplin D. W., Wasserman S. S., Tall B. D., Ketley J. M., Kaper J. B. Vibrio cholerae produces a second enterotoxin, which affects intestinal tight junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5242–5246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentini C., Thelestam M. Clostridium difficile toxin A and its effects on cells. Toxicon. 1991;29(6):543–567. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frawley B. P., Jr, Tien X. Y., Hartmann S. C., Wali R. K., Niedziela S. M., Davidson N. O., Sitrin M. D., Brasitus T. A., Bissonnette M. TPA causes divergent responses of Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent isoforms of PKC in the nuclei of Caco-2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 30;1222(2):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(94)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi K., Hatano S. Control of actin filament length by phosphorylation of fragmin-actin complex. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1081–1087. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuse M., Hirase T., Itoh M., Nagafuchi A., Yonemura S., Tsukita S., Tsukita S. Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1777–1788. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Ding X., Brann T. W., Campbell-Washington J. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces actin reorganization, intercellular gap formation, and endothelial barrier dysfunction in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells: concurrent F-actin depolymerization and new actin synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Oct;157(1):13–23. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Shalloway D. Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):690–692. doi: 10.1038/358690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Lowenkopf T., Apatira D. Identification of a 160-kDa polypeptide that binds to the tight junction protein ZO-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. Structure, biochemistry, and assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C749–C758. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Thelen M., Rosen A., Janmey P. A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. MARCKS is an actin filament crosslinking protein regulated by protein kinase C and calcium-calmodulin. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):618–622. doi: 10.1038/356618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht G., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Madara J. L. Clostridium difficile toxin A perturbs cytoskeletal structure and tight junction permeability of cultured human intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI113760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht G., Robinson B., Koutsouris A. Reversible disassembly of an intestinal epithelial monolayer by prolonged exposure to phorbol ester. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 1):G214–G221. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.266.2.G214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D. Crohn's disease--a permeability disorder of the tight junction? Gut. 1988 Dec;29(12):1621–1624. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.12.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. N., Cherry W. R., Weaver G. W. The origin and characteristics of a pig kidney cell strain, LLC-PK. In Vitro. 1976 Oct;12(10):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF02797469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyun C. S., Martello L. A., Karl P. I. Identification of protein kinase C-alpha, epsilon and zeta in rabbit ileal enterocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol. 1994 Jul;108(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/1367-8280(94)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Morris J. G., Jr, Kaper J. B. Gene encoding zonula occludens toxin (zot) does not occur independently from cholera enterotoxin genes (ctx) in Vibrio cholerae. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):732–733. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.732-733.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Barenberg D., Carlson S. Effects of cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L. Intestinal absorptive cell tight junctions are linked to cytoskeleton. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C171–C175. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L. Loosening tight junctions. Lessons from the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1089–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI113987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Pappenheimer J. R. Structural basis for physiological regulation of paracellular pathways in intestinal epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02209147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson T., Jacobson J. B., Stackpole C. W. Relationship between intercellular permeability and junction organization in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 1978 Nov;67(1):214–224. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marte B. M., Meyer T., Stabel S., Standke G. J., Jaken S., Fabbro D., Hynes N. E. Protein kinase C and mammary cell differentiation: involvement of protein kinase C alpha in the induction of beta-casein expression. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Mar;5(3):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazariegos M. R., Tice L. W., Hand A. R. Alteration of tight junctional permeability in the rat parotid gland after isoproterenol stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1865–1877. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlynn E., Liebetanz J., Reutener S., Wood J., Lydon N. B., Hofstetter H., Vanek M., Meyer T., Fabbro D. Expression and partial characterization of rat protein kinase C-delta and protein kinase C-zeta in insect cells using recombinant baculovirus. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Jul;49(3):239–250. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240490306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Regenass U., Fabbro D., Alteri E., Rösel J., Müller M., Caravatti G., Matter A. A derivative of staurosporine (CGP 41 251) shows selectivity for protein kinase C inhibition and in vitro anti-proliferative as well as in vivo anti-tumor activity. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):851–856. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalski J., Galen J. E., Fasano A., Kaper J. B. CVD110, an attenuated Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor live oral vaccine strain. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4462–4468. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4462-4468.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikawa K. Studies on proteolysis of protein kinase C with calpain I and II. Kobe J Med Sci. 1990 Apr;36(1-2):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milks L. C., Conyers G. P., Cramer E. B. The effect of neutrophil migration on epithelial permeability. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2729–2738. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Carlson S., Madara J. L. C. difficile toxin A increases intestinal permeability and induces Cl- secretion. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):G165–G172. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.2.G165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S., Stafford J., Madara J. L. The selective and superoxide-independent disruption of intestinal epithelial tight junctions during leukocyte transmigration. Lab Invest. 1988 Oct;59(4):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Denisenko N., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Citi S. The role of phosphorylation in development of tight junctions in cultured renal epithelial (MDCK) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91224-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottlinger M. E., Lin S. Clostridium difficile toxin B induces reorganization of actin, vinculin, and talin in cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):215–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganelli R., Levinsky R. J., Brostoff J., Wraith D. G. Immune complexes containing food proteins in normal and atopic subjects after oral challenge and effect of sodium cromoglycate on antigen absorption. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1270–1272. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palant C. E., Duffey M. E., Mookerjee B. K., Ho S., Bentzel C. J. Ca2+ regulation of tight-junction permeability and structure in Necturus gallbladder. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):C203–C212. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.3.C203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., May R. J. Establishment and characterizaton of intestinal epithelial cell cultures. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21B:403–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen A., Keenan K. F., Thelen M., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Activation of protein kinase C results in the displacement of its myristoylated, alanine-rich substrate from punctate structures in macrophage filopodia. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1211–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Pisam M., Maetz J. The surface epithelium of teleostean fish gills. Cellular and junctional adaptations of the chloride cell in relation to salt adaptation. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):96–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., Parker P. J. Expression, purification, and characterization of protein kinase C-epsilon. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7301–7307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., Lynch R. D. Structure, function, and regulation of cellular tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):L647–L661. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.6.L647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., Walters D. V., Olver R. E. Development of intercellular junctions in the pulmonary epithelium of the foetal lamb. J Cell Sci. 1978 Aug;32:307–324. doi: 10.1242/jcs.32.1.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Winter M., Shasby S. S. Oxidants and conductance of cultured epithelial cell monolayers: inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):C781–C788. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.6.C781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Easom R. A., Riehl T. E., Turk J. Regulation of paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayers by protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):G955–G962. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.5.G955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang D. G., Timar J., Grossi I. M., Renaud C., Kimler V. A., Diglio C. A., Taylor J. D., Honn K. V. The lipoxygenase metabolite, 12(S)-HETE, induces a protein kinase C-dependent cytoskeletal rearrangement and retraction of microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Aug;207(2):361–375. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Regulation by phosphorylation of reversible association of a myristoylated protein kinase C substrate with the plasma membrane. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):320–322. doi: 10.1038/351320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Itoh M., Nagafuchi A., Yonemura S., Tsukita S. Submembranous junctional plaque proteins include potential tumor suppressor molecules. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1049–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berghe N., Vaandrager A. B., Bot A. G., Parker P. J., de Jonge H. R. Dual role for protein kinase C alpha as a regulator of ion secretion in the HT29cl.19A human colonic cell line. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):673–679. doi: 10.1042/bj2850673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]