Abstract
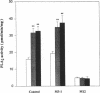
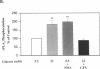
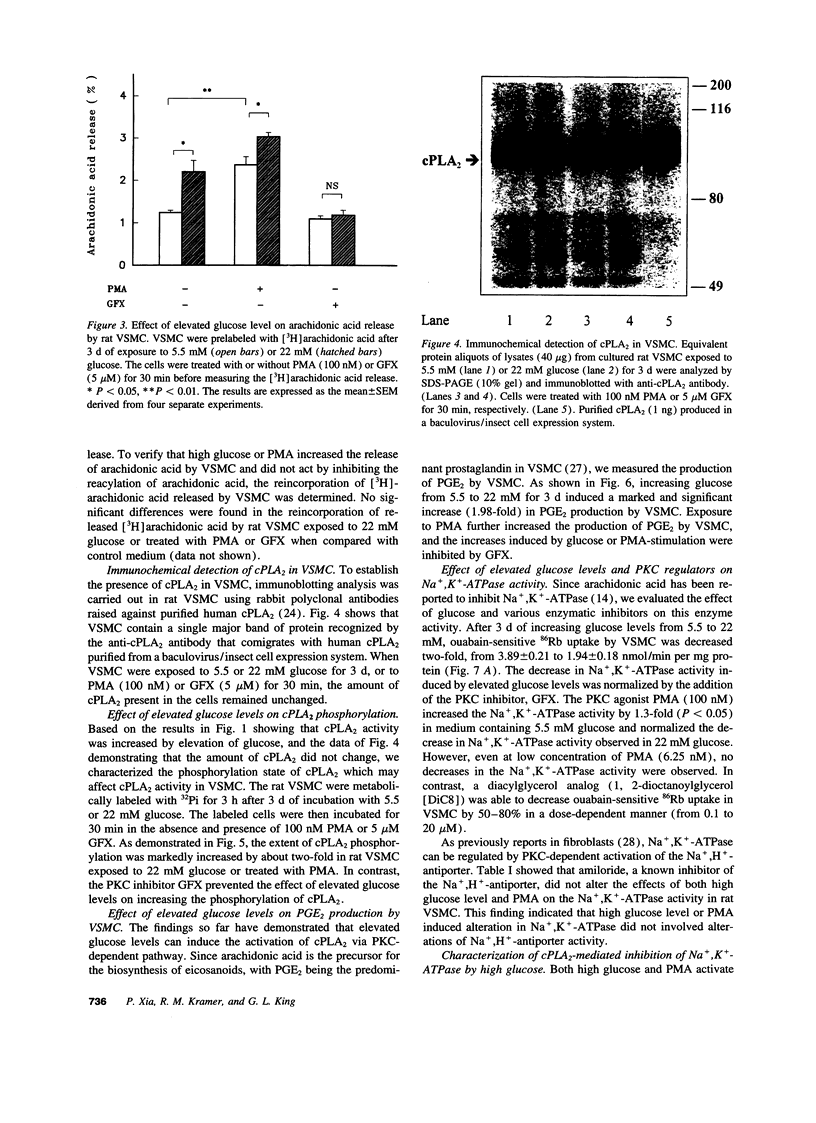
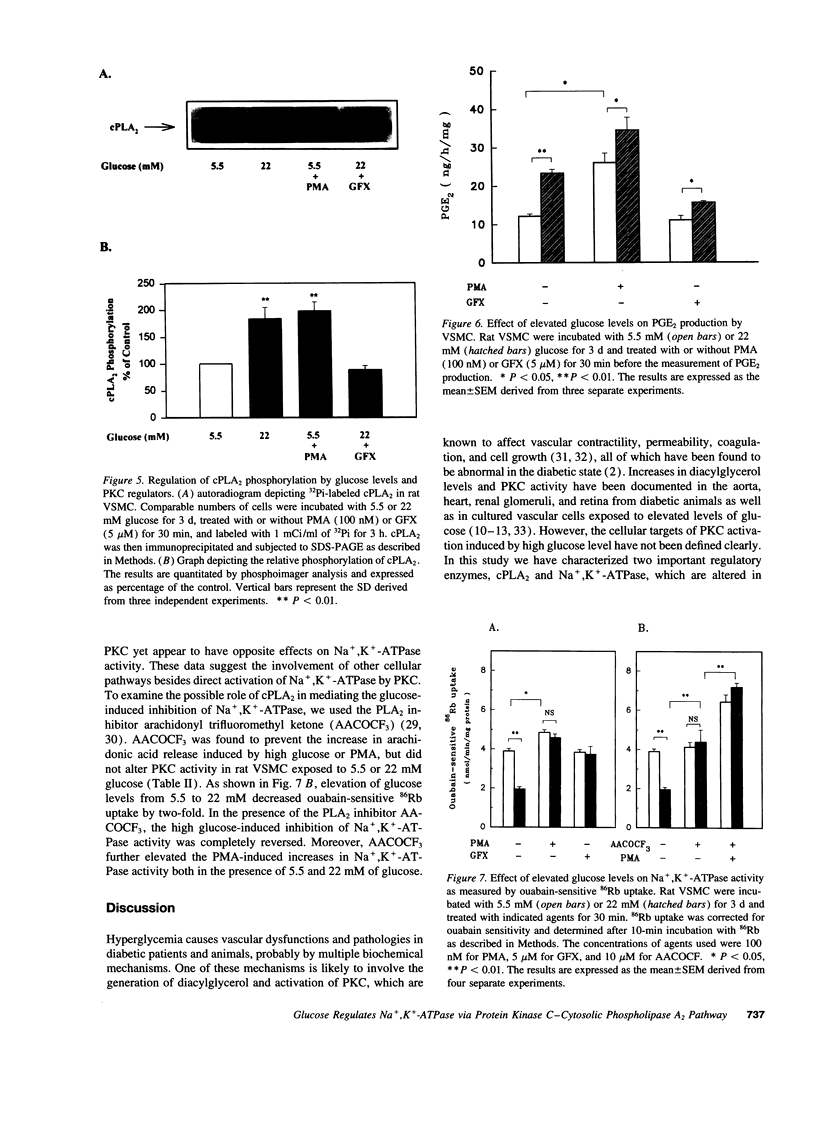
Inhibition of Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity by hyperglycemia could be an important etiological factor of chronic complications in diabetic patients. The biochemical mechanism underlying hyperglycemia's inhibitory effects has been thought to involve the alteration of the protein kinase C (PKC) pathway since agonists of PKC can normalize hyperglycemia-induced inhibition of Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity. Paradoxically, elevated glucose levels and diabetes have been shown to increase PKC activities in vascular cells. The present study tested the hypothesis that the inhibition of Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity is mediated by the sequential activation of PKC and cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2). In cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), increasing glucose levels in the medium from 5.5 to 22 mM elevated cPLA2 activity and increased [3H]arachidonic acid release and PGE2 production by 2.3-, 1.7- and 2-fold, respectively. Similar increases in cPLA2 activity were also induced by elevated glucose levels in human VSMC and rat capillary endothelial cells. The activation of cPLA2 was mediated by PKC since the increases in cPLA2 phosphorylation and enzymatic activity were inhibited by the PKC inhibitor GFX. In contrast, elevation of glucose levels decreased Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity as measured by ouabain-sensitive 86Rb uptake by twofold in rat VSMC. Surprisingly, both PMA, a PKC agonist, and GFX, a PKC inhibitor, were able to prevent glucose-induced decreases in 86Rb uptake. Further, the PLA2 inhibitor AACOCF3 abolished both glucose-induced activation of cPLA2 and the decrease in 86Rb uptake. These data indicated that hyperglycemia is inhibiting Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity by the sequential activation of PKC and cPLA2, resulting in the liberation of arachidonic acid and increased the production of PGE2, which are known inhibitors of Na+,K(+)-ATPase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann E. J., Conde-Frieboes K., Dennis E. A. Inhibition of macrophage Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and trifluoromethyl ketones. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 6;270(1):445–450. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.1.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ager A., Gordon J. L., Moncada S., Pearson J. D., Salmon J. A., Trevethick M. A. Effects of isolation and culture on prostaglandin synthesis by porcine aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jan;110(1):9–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V. Phospholipase A2 and signal transduction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Aug;3(2):128–150. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V32128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borghini I., Geering K., Gjinovci A., Wollheim C. B., Pralong W. F. In vivo phosphorylation of the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit in sciatic nerves of control and diabetic rats: effects of protein kinase modulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6211–6215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. L., Jakubowski J. A., Leventis L. L., Deykin D. Elevated glucose alters eicosanoid release from porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2136–2141. doi: 10.1172/JCI113835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Luria R., Rimon G., Moran A. PGE2 inhibits Na-K-ATPase activity and ouabain binding in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):F61–F65. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.1.F61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feschenko M. S., Sweadner K. J. Conformation-dependent phosphorylation of Na,K-ATPase by protein kinase A and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30436–30444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S. A. Protein kinase C agonists acutely normalize decreased ouabain-inhibitable respiration in diabetic rabbit nerve. Implications for (Na,K)-ATPase regulation and diabetic complications. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):242–245. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A. Sorbitol, phosphoinositides, and sodium-potassium-ATPase in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 5;316(10):599–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703053161007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Sussman I., McArthur C. S., Tornheim K., Cohen R. A., Ruderman N. B. Endothelium-dependent inhibition of Na(+)-K+ ATPase activity in rabbit aorta by hyperglycemia. Possible role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):727–732. doi: 10.1172/JCI115944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halushka P. V., Lurie D., Colwell J. A. Increased synthesis of prostaglandin-E-like material by platelets from patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 15;297(24):1306–1310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712152972402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert R. L., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct by increasing intracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1992–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI115227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoguchi T., Xia P., Kunisaki M., Higashi S., Feener E. P., King G. L. Insulin's effect on protein kinase C and diacylglycerol induced by diabetes and glucose in vascular tissues. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):E369–E379. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.3.E369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen B., Kramer R. M., Hession C., McGray P., Pepinsky R. B. Expression, purification and biochemical comparison of natural and recombinant human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 31;187(1):544–551. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. A., O'Hara D. S., Mitch W. E., Smith T. W. Identification of NaK-ATPase inhibitors in human plasma as nonesterified fatty acids and lysophospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11704–11711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Shiba T., Oliver J., Inoguchi T., Bursell S. E. Cellular and molecular abnormalities in the vascular endothelium of diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Med. 1994;45:179–188. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.45.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Checani G. C., Deykin A., Pritzker C. R., Deykin D. Solubilization and properties of Ca2+-dependent human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 3;878(3):394–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J. V., Hyslop P. A., Jakubowski J. A. Thrombin-induced phosphorylation and activation of Ca(2+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26796–26804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J. V., Sportsman J. R., Jakubowski J. A. Ca(2+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) in human platelets. J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):209–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J., Putnam J. E. The Ca2(+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a 100-kDa protein in human monoblast U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5268–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Wilson P. B., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. The hormone-sensitive hepatic Na+-pump. Evidence for regulation by diacylglycerol and tumor promoters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14551–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor L. C., Matschinsky F. M. Altered retinal metabolism in diabetes. II. Measurement of sodium-potassium ATPase and total sodium and potassium in individual retinal layers. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4052–4058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers T. O., Messina E. J., Rodrigues A. M., Gerritsen M. E. Altered aortic and cremaster muscle prostaglandin synthesis in diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):E374–E379. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.4.E374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Winitz S., Qian N. X., Van Putten V., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1960–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Growth factors activate the bumetanide-sensitive Na+/K+/Cl-cotransport in hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6177–6183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Serum rapidly stimulates ouabain-sensitive 86-RB+ influx in quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4492–4495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Cohen H. T., Katz A. I. Intracellular signaling in the regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase. II. Role of eicosanoids. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):409–415. doi: 10.1172/JCI116215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schambelan M., Blake S., Sraer J., Bens M., Nivez M. P., Wahbe F. Increased prostaglandin production by glomeruli isolated from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):404–412. doi: 10.1172/JCI111714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. A., Hasselbalch S., Farrell P. A., Vestergaard H., Kjeldsen K. Human and rodent muscle Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase in diabetes related to insulin, starvation, and training. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 May;76(5):2140–2146. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.5.2140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman M., Ferreri N. R., Carroll M. A., Songu-Mize E., McGiff J. C. Renal cytochrome P450-related arachidonate metabolite inhibits (Na+ + K+)ATPase. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):620–622. doi: 10.1038/314620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam H., Hülsmann W. C. Effect of fasting and streptozotocin-diabetes on the coronary flow in isolated rat hearts: A possible role of endogenous catecholamines and prostaglandins. Basic Res Cardiol. 1977 Jul-Aug;72(4):365–375. doi: 10.1007/BF02023595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street I. P., Lin H. K., Laliberté F., Ghomashchi F., Wang Z., Perrier H., Tremblay N. M., Huang Z., Weech P. K., Gelb M. H. Slow- and tight-binding inhibitors of the 85-kDa human phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 15;32(23):5935–5940. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer R. K., Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Role for protein kinase C in the mediation of increased fibronectin accumulation by mesangial cells grown in high-glucose medium. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):118–126. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets L. A., Schwarz W. Structure-function relationships of cation binding in the Na+/K(+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 29;1154(2):201–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90012-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley R. E., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M. Lipid metabolism and signal transduction in endothelial cells. Prog Lipid Res. 1990;29(1):45–63. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(90)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B., Schrier R. W. Characterization of glucose-induced in situ protein kinase C activity in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1464–1472. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B., Schrier R. W. Glucose-induced protein kinase C activity regulates arachidonic acid release and eicosanoid production by cultured glomerular mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2889–2896. doi: 10.1172/JCI116911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad A. I. Banting lecture 1986. Does a common mechanism induce the diverse complications of diabetes? Diabetes. 1987 Mar;36(3):396–406. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Williamson J. R., Easom R. A., Chang K., Sherman W. R., Turk J. Diacylglycerol accumulation and microvascular abnormalities induced by elevated glucose levels. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI114988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia P., Inoguchi T., Kern T. S., Engerman R. L., Oates P. J., King G. L. Characterization of the mechanism for the chronic activation of diacylglycerol-protein kinase C pathway in diabetes and hypergalactosemia. Diabetes. 1994 Sep;43(9):1122–1129. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.9.1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]