Abstract
Circulating levels of inflammatory markers can predict cardiovascular disease risk. To identify genes influencing the levels of these markers, we genotyped 1,343 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 1,184 African Americans from the Health, Aging and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study. Using admixture mapping, we found a significant association of interleukin 6 soluble receptor (IL-6 SR) with European ancestry on chromosome 1 (LOD 4.59), in a region that includes the gene for this receptor (IL-6R). Genotyping 19 SNPs showed that the effect is largely explained by an allele at 4% frequency in West Africans and at 35% frequency in European Americans, first described as associated with IL-6 SR in a Japanese cohort. We replicate this association (P≪1.0×10-12) and also demonstrate a new association with circulating levels of a different molecule, IL-6 (P<3.4×10-5). After replication in 1,674 European Americans from Health ABC, the combined result is even more significant: P≪1.0×10-12 for IL-6 SR, and P<2.0×10-9 for IL-6. These results also serve as an important proof of principle, showing that admixture mapping can not only coarsely localize but can also fine map a phenotypically important variant.
Circulating markers of inflammation, particularly C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), are associated with risk of atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, stroke, and the progression of autoimmune disease, although the reasons for these associations remain unclear.1–7 Whereas environmental exposures have a major influence, genetic factors also play a role; for example, CRP, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) have been shown to be heritable in family studies8–10 and twin studies,11–13 motivating searches to find the relevant genetic factors. In the United States, the levels of inflammatory markers are systematically different in European Americans compared with African Americans, with CRP levels higher in African Americans14 and with IL-6 and IL-6 soluble receptor (IL-6 SR) levels higher in European Americans.15 These observations prompted our search for genetic loci that affect these markers and contribute to the epidemiological differences across populations.
The idea of admixture mapping16–26 is to study a population of recently mixed ancestry, such as African Americans, searching for genomic regions where individuals with a specific phenotype have an unusually high proportion of ancestry from one ancestral population. Because of the recent mixture of Europeans and Africans, segments of contiguous European or African ancestry in African Americans have not had much time (only ∼6 generations, on average) to break up by recombination.22–25 Tracking these segments requires genotyping SNPs every couple of million base pairs along the genome, instead of the 100–1,000 times higher density required by whole-genome linkage disequilibrium scans.27
Several recent studies have reported significant associations with the use of admixture mapping. Zhu et al.28 reported two loci for hypertension in African Americans on chromosomes 6 and 21. We reported a locus on chromosome 1 where increased European ancestry is associated with a risk of multiple sclerosis29 and a locus on chromosome 8 where increased African ancestry is associated with a risk of prostate cancer.30 Unfortunately, the regions of association identified by admixture mapping are broad (similar to peaks from linkage studies), and no study has yet moved from an initial peak of admixture association to localizing the exact genetic variant(s) involved. We report an admixture mapping study that first coarsely localizes and then precisely identifies a genetic variant that explains the admixture peak.
Material and Methods
Human Subjects
All biological materials came from Health, Aging and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study participants, a cohort of 3,075 men and women aged 70–79 years and enrolled between April 1997 and June 1998. All participants were Medicare beneficiaries living near Pittsburgh or Memphis. All participants reported no difficulty performing basic physical activities. Of the 3,075 participants enrolled, 1,281 reported their ethnicity as black, and we successfully genotyped 1,184 samples.
Clinical and Phenotypic Information
The eight inflammatory markers we studied are IL-6 (n=1,123 measured samples), CRP (n=1,181), plasminogen-activating inhibitor (PAI1 [n=1,168]), TNF-α (n=1,102), TNF-α SR1 (n=564), TNF-α SR2 (n=576), IL-6 SR (n=583), and IL-2 SR (n=579). The soluble receptors were assayed in only about half the samples. To measure the level of these markers, venipuncture was performed for each of the participants after an overnight fast of at least 8 h, and serum samples were then frozen at −70°C. CRP was measured by colorimetric competitive ELISA (Macy Laboratory) with an intra-assay coefficient of variation (CV) of 5.14%. IL-6 and TNF-α were measured by solid-phase ELISA (R&D Systems) with CVs of 13.1%–18.1% for IL-6 and 14.8%–14.9% for TNF-α. PAI1 was measured by a two-site ELISA (Collen Laboratory) with a CV of 3.47%. TNF-α SR1, TNF-α SR2, IL-6 SR, and IL-2 SR were all measured by ultrasensitive ELISA (R&D Systems) and had CVs of 5.0%–6.7%, 7.8–8.4%, 3.5%–5.2%, and 4.3%–4.9%, respectively.
Seven additional pieces of information were used as covariates because of their known correlation with inflammatory marker levels31: sex, clinic site, age, self-reported status as a smoker, diabetes status (self-reported or based on use of antidiabetes medications or on having a fasting blood glucose level of >126), BMI, and abdominal visceral fat mass (measured at the L4–L5 vertebrae by CT scans).
Genotyping
DNA from the African American samples was whole-genome amplified32 before genotyping at the Broad Institute. We used the Illumina BeadLab platform33 to assay 1,536 SNPs previously identified as highly informative about African versus European ancestry.16,29,30 After performing quality checks identical to those described by Reich et al.,29 we were left with 1,343 SNPs that genotyped well in 1,184 samples. These SNPs had previously been genotyped in an average of 104 West African and 241 European-derived samples,30 and we used these data to improve allele-frequency estimates in the parental populations of African Americans.22,23 For follow-up analysis around the IL-6R gene (MIM 147880), we used the Sequenom MassArray platform34 to genotype an additional 20 SNPs in all the African Americans, of which 18 passed quality checks.29,30 For replication genotyping of rs8192284 in European Americans, we used template-directed dye-terminator incorporation with fluorescence polarization detection (Acycloprime II kit [PerkinElmer])35 on genomic DNA at the University of California–San Francisco.
Reduced SNP Panels
The ANCESTRYMAP software identifies SNPs that appear to be in linkage disequilibrium with one another in the ancestral West African and European American populations or that are not appropriately intermediate in frequency in African Americans between the ancestral West African and European American populations.23 These SNPs were removed before analysis. Since the samples included in each admixture scan were slightly different (depending on the phenotype), the algorithm removed slightly different sets of SNPs for each run, leaving 1,326–1,343 SNPs for analysis (table 1). We present results for the 1,299 SNPs common to all runs in tab-delimited ASCII file data set 1.
Table 1. .
Association Tests for Eight Markers of Inflammation
| Admixture Scansc |
|||||||
| Marker | Median (Range) | No. of Samplesa |
P for Correlation to Ancestryb |
No. of Cases/Controls | No. of SNPs | Genome Score | Best LOD Score |
| IL-6 | 2.0 pg/ml (.3–14.2) | 1,099 | .23 | 230/226 | 1,343 | −.71 | 1.42 |
| CRP | 2.1 mg/liter (.3–63.9) | 1,156 | .0084 | 238/230 | 1,342 | −.57 | 1.55 |
| PAI1 | 21 ng/ml (2–280) | 1,143 | .17 | 234/228 | 1,342 | −.29 | 1.71 |
| TNFα | 3.0 pg/ml (.6–14.2) | 1,082 | .23 | 217/217 | 1,342 | −.62 | 1.23 |
| TNF-α SR1 | 3,296 pg/ml (1,725–6,059) | 569 | .50 | 108/113 | 1,331 | −.43 | 1.16 |
| TNF-α SR2 | 1,394 pg/ml (513–4,428) | 553 | .51 | 115/118 | 1,326 | −.38 | 1.52 |
| IL-6 SR | 30,743 pg/ml (9,010–65,506) | 572 | .00012 | 114/117 | 1,336 | 2.03 | 4.59 |
| IL-2 SR | 1,087 pg/ml (454–4,431) | 571 | .020 | 117/111 | 1,330 | −.40 | 1.47 |
For each phenotype, we analyzed only samples for which information was available for the phenotype of interest and all seven covariates—age, sex, site of collection, smoking status, diabetes status, BMI, and abdominal visceral fat mass.
IL-6 SR is significantly positively associated with European ancestry, and CRP is negatively associated.
Admixture scans compared highest 20% with lowest 20% for each phenotype.
Adjusting for Covariates
The main admixture scans used the raw values of the phenotypes without adjustment for covariates. For tests of association between overall ancestry and the rs8192284 genotype, we adjusted for the seven covariates of age, sex, clinic site (Memphis or Pittsburgh), smoking status, diabetes status, BMI, and abdominal visceral adiposity.
Normalizing Transformations
For the analysis of variance (ANOVA), we needed to obtain normally distributed values for all eight quantitative traits. As reported in tables 1 and 2, we performed a “probit” transformation,36 by rank-ordering all individuals according to their values for each trait and by assigning Z scores corresponding to percentiles in a normal distribution. For example, an individual with CRP in the 97.7th percentile in the population would be assigned Z=2. The probit transformation, although it ensures normality, is based solely on the ordering of samples, and so it loses quantitative information. To quantitatively assess the effect of the rs8192884 genotype on IL-6 and IL-6 SR levels, we replaced the probit transformation with a natural-logarithm transformation.
Table 2. .
Testing SNPs for Their Ability to Explain the Admixture Association[Note]
| ANOVA |
|||||||
| Association at SNP |
AdmixtureAssociationNot Explainedby SNP |
||||||
| SNP | Position on Chromosome 1a | SNP-Specific LOD Score | χ2 | P | χ2 | P | Percentage of Locus-Specific IL-6 SR Association Explained by SNP Genotype Alone |
| rs11582424 | 151177058 | −.9 | 3 | .27 | 38 | 7.7×10−10 | 7 |
| rs11265608 | 151177213 | −.7 | .2 | .90 | 39 | 5.0×10−10 | 0 |
| rs952146 | 151182001 | −.9 | .8 | .67 | 38 | 7.4×10−10 | 2 |
| rs4845615 | 151188350 | −.6 | .8 | .66 | 41 | 1.7×10−10 | 1 |
| rs1552481 | 151189426 | −.5 | 1 | .61 | 46 | 1.4×10−11 | 3 |
| rs4845617 | 151190971 | −.9 | 4 | .13 | 38 | 6.9×10−10 | 10 |
| rs1386821 | 151195122 | −.3 | 6 | .047 | 37 | 9.2×10−10 | 15 |
| rs4845618 | 151213088 | 8.6 | 79 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 34 | 6.1×10−9 | 72 |
| rs7549250 | 151217409 | 5.6 | 59 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 39 | 4.5×10−10 | 63 |
| rs7518199 | 151220492 | 11.0 | 114 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 21 | 4.0×10−6 | 86 |
| rs4845623 | 151228850 | 10.9 | 50 | 1.1×10−11 | 58 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 49 |
| rs4845625 | 151235140 | 8.8 | 48 | 3.9×10−11 | 51 | 1.1×10−12 | 51 |
| rs8192284 | 151240043 | 13.6 | 195 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 2 | .13 | 99 |
| rs11265618 | 151243165 | .6 | 13 | .0015 | 36 | 2.1×10−9 | 27 |
| rs4329505 | 151245493 | −.8 | 2 | .29 | 37 | 1.3×10−9 | 6 |
| rs7526293 | 151257282 | 1.8 | 34 | 3.8×10−8 | 25 | 4.6×10−7 | 59 |
| rs12568083 | 151269022 | 1.0 | 66 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 5 | .025 | 93 |
| rs4845632 | 151272005 | .0 | 24 | 5.2×10−6 | 23 | 1.3×10−6 | 52 |
| rs12740969 | 151300133 | 3.6 | 63 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 3 | .071 | 95 |
Note.— We used a look-up table to convert χ2 statistics to P values: 2 df for the test of genotype association and 1 df for the test for admixture association beyond genotype. We do not present exact P values when P≪1.0×10-12, since it is not clear that the statistics follow an exact χ2 distribution at such extremely significant values. There is no evidence of an ancestry association beyond rs8192284. The SNP genotype explains 99% of the association evidence at the locus, and the P value for additional admixture association not explained by the SNP is .13. All tests reported in this table were uncorrected for covariates.
Position according to build 35 of the human genome reference sequence.
Admixture Mapping
We used the ANCESTRYMAP software23 to screen the genome in the African Americans from Health ABC, searching for association to genomic segments with an increased proportion of European or African ancestry. Since ANCESTRYMAP is optimized for the analysis of dichotomous traits,23 we ran the analysis comparing the 20% of individuals with the highest values as cases and the 20% with the lowest values as controls. To test for association, we prespecified a set of risk models. We tested 18 models and averaged the factors in favor of each model, to assess overall evidence of association.23 The first six models used 2.5-fold, 2-fold, 1.5-fold, 0.67-fold, 0.5-fold, and 0.4-fold increased risk due to European ancestry for cases, with the inverse risk in controls. The next six models used the same set of increased risk for cases, but with a control risk of 1. The last six models specified that cases had risk 1, whereas the controls had risks of 0.4, 0.5, 0.67, 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5. All Markov chain–Monte Carlo runs used 100 burn-in and 200 follow-on iterations, as recommended on the basis of simulation studies.23
Assessing Statistical Significance for the Admixture Scan
The ANCESTRYMAP software produces a score of association at each position in the genome: the LOD10 at that point in the genome indicates that there is an association with disease, versus a model with no disease. The whole-genome score is the average of the local odds ratios for genomewide association; we interpret a score >2 as genomewide significant23 and observe a score of 2.03 for IL-6 SR. As a secondary analysis, the software also searches for a difference in ancestry proportion between cases and controls23 (data set 1).
Credible Interval for the Position of the Disease-Causing Variant(s)
To identify a 99% Bayesian credible interval for the position of the disease-causing variant,23,29,30 we used a uniform prior distribution for its position across the genetic distance span of chromosome 1. We multiplied the factor in favor of association at each point by this prior distribution. The credible interval is defined as the central region with 99% of the area.
Fine-Mapping Strategy around the IL-6R Gene
To follow up the evidence of association to IL-6 SR levels, we picked haplotype-tagging SNPs across the IL-6R gene and the 10 kb of flanking sequence in both directions. The SNPs were chosen using data from the first phase of the International Haplotype Map (HapMap) database (release 16c)37 and the Tagger program.38 To form a comprehensive tag set that was appropriate to both ancestral populations of African Americans, we picked SNPs to tag all haplotypes in West Africans (YRI from HapMap). We then forced these SNPs into the tag set and picked additional SNPs to tag variation in European Americans (CEU from HapMap). We stopped choosing SNPs when all HapMap SNPs with minor-allele frequency ⩾10% in the region were correlated to one of the tag SNPs at r2⩾0.7. Nineteen tag SNPs were thereby selected, to which we added rs8192284, an amino acid–changing SNP that had been identified by Galicia et al.39 as being associated with IL-6 SR in Japan. We also studied another SNP in the vicinity that had been typed in the admixture scan.
Detecting an Allele Contributing to the Admixture Mapping Signal
To test whether a SNP allele contributes more to the phenotype than can be expected from the ancestry association alone, we used a new feature of the ANCESTRYMAP software (appendix A). We calculated an allele-specific LOD score corresponding to the likelihood of a disease model containing a specific contribution of the allele versus no contribution of the allele and found there is only an admixture association. We observe a highly significant score of 13.6 at rs8192284.
How Much of the Admixture Signal Is Explained by an Allele?
To test whether the rs8192284 polymorphism explains the entire admixture signal, we performed nested ANOVA. First, we assessed how much of the variance in probit-transformed IL-6 SR levels can be explained by genotype status (e.g., zero, one, or two copies of the C allele at rs8192284), providing a P value for association to each SNP. Next, we assessed how much the variance increases when we add the local estimate of ancestry from ANCESTRYMAP into the ANOVA. The increase in χ2 produces a P value for there being residual admixture association not explained by the SNP. To assess how much of the evidence of association is attributable to the SNP, we divided the amount of variance explained in the first ANOVA (SNP alone) by the amount in the second (SNP plus local ancestry).
Testing for rs8192284 Associations with Several Inflammatory Markers
To test the association of rs8192284 with each of the inflammatory markers in African Americans as well as in European Americans, we controlled for the seven covariates in ANOVA. For the African Americans, we also added the overall proportion of European ancestry for each individual. To test for rs8192284 association, we used all the samples from the Health ABC Study, not only the top and bottom quintiles.
Quantifying the Contribution of the rs8192284 Genotype to Levels of IL-6 SR and IL-6
IL-6 SR and IL-6 levels were natural-log transformed. We used ANOVA to determine the effect of the rs8192284 genotype on these levels, before and after controlling for covariates. The values that emerged were exponentiated, to evaluate the effect of the different genotypes on absolute levels of IL-6 and IL-6 SR (table 3).
Table 3. .
Quantitative Effect of rs8192284 on Levels of IL-6 SR and IL-6
| No Correction for Covariates |
Correction for Covariatesa |
|||||
| Marker, Genotype at rs8192284, and Population |
No. of Samples | Marker Level (pg/ml ± SD) |
Multiplicative Effect on Level |
P vs. AA Genotype | Multiplicative Effect on Level |
P vs. AA Genotype |
| IL-6 SR: | ||||||
| AA: | ||||||
| African American | 419 | 29,665 ± 5,245 | … | … | … | … |
| European American | 278 | 31,476 ± 5,188 | … | … | … | … |
| AC: | ||||||
| African American | 157 | 38,894 ± 8,735 | 1.29 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 1.28 | ≪1.0×10−12 |
| European American | 400 | 40,790 ± 6,323 | 1.28 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 1.29 | ≪1.0×10−12 |
| CC: | ||||||
| African American | 16 | 46,543 ± 7,286 | 1.53 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 1.65 | ≪1.0×10−12 |
| European American | 127 | 49,371 ± 8,129 | 1.57 | ≪1.0×10−12 | 1.55 | ≪1.0×10−12 |
| IL-6: | ||||||
| AA: | ||||||
| African American | 833 | 2.55 ± 2.14 | … | … | … | … |
| European American | 586 | 2.16 ± 1.87 | … | … | … | … |
| AC: | ||||||
| African American | 290 | 2.71 ± 1.84 | 1.13 | .006 | 1.15 | .006 |
| European American | 802 | 2.25 ± 1.74 | 1.09 | .014 | 1.06 | .095 |
| CC: | ||||||
| African American | 32 | 3.39 ± 2.29 | 1.43 | .002 | 1.43 | .004 |
| European American | 246 | 2.53 ± 1.83 | 1.24 | .000004 | 1.22 | .0001 |
We corrected for the seven covariates; for African Americans, we also corrected for overall percentage of European ancestry.
Testing for a Nonmultiplicative Effect
To assess whether the effect of rs8192284 on a phenotype (IL-6 or IL-6 SR) was appropriately fit by a multiplicative model, we calculated a likelihood ratio. We first calculated the χ2 fit for the data under a one-parameter model in which the log-transformed values of the phenotype increased additively with increasing numbers of copies of the C allele. We then calculated the χ2 fit under a two-parameter model in which a separate increased risk was allowed for one or two copies of the C allele. These analyses controlled for the seven main covariates, and the analyses in African Americans additionally controlled for the overall percentage of European ancestry.
Testing Whether the IL-6 SR Antibody Binds to the Variant Encoded by rs8192284
To determine whether the anti-human IL-6R monoclonal antibody used to assay IL-6 SR levels displays a preferential binding affinity to a specific epitope (particularly the D358A substitution encoded by rs8192284), we synthesized custom peptides corresponding to the entire amino acid sequence (468 residues) and spotted them onto a cellulose membrane. Synthesized spots included 230 overlapping 10-mer peptides with an offset of 2 aa, 115 overlapping 11-mer peptides with an offset of 4 aa, and 39 peptides that specifically focused on tiling the region of the IL-6R protein flanking amino acid 358. We spotted numerous peptides that captured both A allele and D allele variants. Employing a modified protocol from Sigma-Genosys and standard immunoblotting methods,40 we incubated the membrane with the anti–IL-6 SR monoclonal antibody at a concentration of 10 μg/ml in buffer containing 2% milk/TBS-T for 3 h at room temperature (TBS-T is Tris-buffered saline with 0.05% Tween 20, composed of 25 mM Tris, 0.14 M NaCl, and 0.05% Tween 20), followed by incubation with a horseradish peroxidase–conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody at a dilution of 1:10,000 in buffer containing 2% milk/TBS-T for 2 h at room temperature. Positive spots were visualized using Amersham chemiluminescent reagents and were imaged by autoradiographic exposure at 1 h and 16 h.
Lymphoblastoid Cell-Line Experiment
Lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL) from the HapMap Project (269 of 270) were interrogated for cell-surface expression of IL-6R. The LCLs were grown for 7 d in batches of 96 LCLs in RPMI 1640 media with 2 mmol l-glutamine, 1x penicillin and streptomycin, and 10% Fetalplex serum. From each LCL, ∼25,000 cells were incubated with R-Phycoerythrin–conjugated mouse anti-human IL-6R (catalog number 551850 [BD Pharmingen]) at 4°C for 30 min. Cells were washed once with PBS and 1% fetal bovine serum and were fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde. Data on cell-surface expression of IL-6R in each cell line were acquired using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter (BD Biosciences FACSCalibur system). To quantify IL-6R expression for each LCL, we used flow cytometry, requiring at least 500 cells per LCL for it to be reported in our analysis. Fluorescence intensity was measured for both the anti–IL-6R antibody and a control isotype antibody for each cell and was assessed in 1,024 equally sized bins.41,42 The normalized intensity in each bin was defined as the number of anti–IL-6R–labeled cells minus the number of isotype control–labeled cells. To convert into a single measurement of fluorescence intensity, we averaged across all cells (by summing across the bins) and reported the natural logarithm. To test for statistical significance of fluorescence intensity between genotype classes, we used a t test.
Results
We first tested whether the levels of eight inflammatory markers—IL-6, CRP, PAI1, TNF-α, TNF-α SR1, TNF-α SR2, IL-6 SR, and IL-2 SR—were correlated to the proportion of European ancestry in the 1,184 African American participants in the Health ABC Study. After correcting for age, sex, clinic site, smoking status, diabetes status, BMI, and abdominal visceral fat mass, which are known to be correlated to inflammatory marker levels,31 we found evidence of a significant correlation of high IL-6 SR levels with increased European ancestry (P=.00012) and high CRP levels with increased African ancestry (P=.0084). The correlation to ancestry suggests that admixture mapping may find genes underlying these phenotypes.
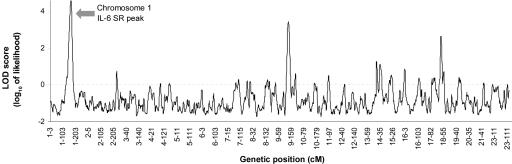
We performed eight admixture scans,23 comparing the 20% of the samples with the highest values of each phenotype with the 20% of samples with the lowest values. Only one scan produced significant evidence of association with IL-6 SR levels. The peak LOD score for this phenotype was 4.59 on chromosome 1, and the genomewide score reaches the threshold of 2.03 for significance23,26 (table 1 and fig. 1). Formally, this does not meet our criterion for statistical significance if we correct for the eight hypotheses we tested. However, the peak appeared to be worthy of further study, especially since the IL-6R gene localizes to the peak.
Figure 1. .
Admixture scan for loci affecting levels of IL-6 SR. The analysis was performed by comparing the 20% of African Americans with the highest levels (n=114) with the 20% with the lowest levels (n=117) of IL-6 SR. A significant signal was contributed by a peak on chromosome 1 (LOD 4.59). Factor-averaging the LOD scores across the genome (to correct for multiple-hypothesis testing) produced a significant genomewide score of 2.03. We also observed a secondary peak with a LOD score of 3.45 on chromosome 9, but this does not reach our published threshold for suggestiveness.26
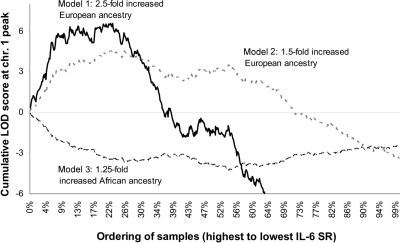
When we repeated the analysis on all 583 samples with measured IL-6 SR levels (not just the samples with the highest and lowest levels), we noticed that the evidence of association to IL-6 SR levels was contributed almost entirely by the individuals with the highest 10%–30% of IL-6 SR levels. To show this, we used the fact that the ANCESTRYMAP software generates a LOD score at each position in the genome not only for all individuals treated together but also for each individual separately. When we rank-ordered all the 583 individuals with a measurement of IL-6 SR, we were able to test which samples were contributing most to association. The score increases to a maximum for the top 10% of IL-6 SR values and drops after the top 30% (fig. 2). This suggests that the association is explained by a major-effect allele at higher frequency in European Americans than in West Africans and carried by 10%–30% of African Americans.
Figure 2. .
The 10%–30% of individuals with the highest IL-6 SR levels contributing most of the association. We rank-ordered 584 African Americans by their measured levels of IL-6 SR, from highest to lowest, not correcting for covariates. We ran ANCESTRYMAP, treating all samples as cases, and calculated the log factor of disease association for each sample under three models: (1) 2.5-fold increased risk for European ancestry associated with case status, the model that provided the strongest contribution to disease risk; (2) 1.5-fold increased risk for European ancestry; and (3) 1.25-fold increased risk for African ancestry. For model 1, the LOD score increased dramatically for the top 10% (peak LOD 6.57) of levels until the 30th percentile and then decreased, indicating that the signal was likely to be contributed only by the individuals with the highest 10%–30% of IL-6 SR levels.
To localize the putative allele affecting IL-6 SR levels, we constructed a 99% credible interval for its position. Both admixture mapping and linkage mapping in families generate coarse initial localizations of a disease-causing locus, in contrast with whole-genome linkage disequilibrium mapping, in which the initial localization is usually within tens of kilobases.26 In this study, the initial localization spans 119.0–151.7 Mb in the human genome reference sequence (human genome reference sequence build 35) and contains dozens of genes. However, we noticed that the peak contains the IL-6R gene (at position 151.19–151.25 Mb), an excellent candidate for containing variants contributing to IL-6 SR levels. A recent candidate-gene study by Galicia and colleagues39 already identified genetic variants in the IL-6R gene that affected levels of IL-6 SR in Japanese (P<.0001 for the most-associated rs8192284 SNP). For follow-up fine mapping, we genotyped rs8192284, as well as 20 other variants surrounding the IL-6R gene that tagged all the common variation of at least 10% minor-allele frequency in both West Africans and European Americans from HapMap.37 A total of 19 SNPs produced usable data.
We employed ANCESTRYMAP,23 to test for association to IL-6 SR levels above and beyond the admixture association. This identified five SNPs with extremely significant associations to IL-6R levels (single-SNP LOD scores all >8) (table 2). All were within an ∼40-kb segment of very strong linkage disequilibrium in both West Africans and European Americans.37 The SNP with the strongest association is rs8192284 (LOD 13.6), the same polymorphism that was associated to IL-6 SR levels in Japanese.39 As Galicia et al.39 pointed out, rs8192284 is an excellent candidate as a SNP that modulates IL-6 SR levels. Since it occurs at the proteolytic cleavage site of IL-6R,39 variability could affect levels of the circulating soluble receptor. Moreover, the variant is highly differentiated in frequency across populations (35% in European Americans and 4% in West Africans in HapMap), which is consistent with it producing a differential risk across populations and explains the admixture signal.
Our statistical analysis suggests that rs8192284 is sufficient to explain the admixture peak. First, when we tested whether there is any evidence of an admixture association above and beyond the contribution of the genotype at rs8192284, we found no significant evidence (P=.13). Of the 19 SNPs we tested, this is the only one consistent with explaining the entire admixture signal (table 2). Second, in ANOVA, the genotype at rs8192284 explains 99% of the total association we have detected to IL-6 SR levels, which is again consistent with ancestry not capturing any additional signal (table 2). Finally, the effect of rs8192284 on IL-6 SR can be seen visually: when we control for genotype—that is, subtract the average IL-6 SR level for each of the three genotype classes—the distribution of absolute IL-6 SR levels becomes approximately Gaussian (data not shown), and its variance is reduced by 33%.
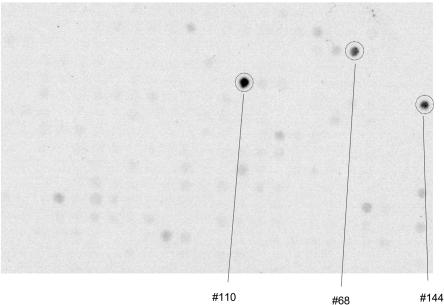
We were concerned that, although the association we detected is real, it might reflect an artifact of the measurement technique rather than genuinely high circulating levels of IL-6 SR. In particular, the epitope of the monoclonal antibody used to measure IL-6 SR levels might contain the rs1892284 polymorphism itself (D358A, changing an aspartic acid to an alanine). A polymorphism within the antibody’s epitope could produce an association of the measurement of IL-6 SR to rs8192284 but would not be biologically interesting (this effect could also be produced by a coding polymorphism in strong linkage disequilibrium with rs8192284, but there is no such polymorphism present in the human HapMap). To rule out the possibility of a binding artifact at rs8192294, we spotted peptides tiling the entire IL-6R protein onto a cellulose array and performed immunodetection with the same monoclonal antibody used to assay IL-6 SR in the Health ABC Study. There was no evidence of binding to peptides encoding either D358 or A358 (fig. 3). IL-6 SR is known to arise by two different mechanisms, either by proteolytic cleavage of IL-6R at the cell surface or by a secreted splice isoform of IL-6R.43 Although the peptide sequences of these two different IL-6 SR forms are slightly different, neither contains residue 358, which adds to the weight of evidence that the effect on levels that we observed is not explained by a polymorphism within the epitope of the anti–IL-6 SR antibody.
Figure 3. .
Immunodetection showing no evidence that the IL-6 SR antibody preferentially binds to D358A. We spotted 10-mer, 11-mer, and 12-mer peptides from the IL-6R protein onto a cellulose array with 384 features and immunodetected with the IL-6 SR monoclonal antibody employed in the ELISA assay to study the subjects in the Health ABC Study. Three potential peptide spots from the 10-mers were detected, including an intense positive signal (spot #110 at amino acids 219–228) and two other positive signals (spot #68 at amino acids 135–144 and spot #144 at amino acids 287–296). No intense spots overlapped amino acid 358, which we spotted in both polymorphic forms and was included in numerous peptides. Results are from a 1-h exposure (similar results were obtained from an overnight exposure [not shown]).
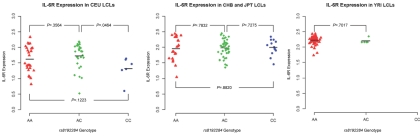
Galicia et al., in their original study of a Japanese cohort, noticed that the DNA polymorphism rs8192284 (protein polymorphism D358A) occurred at the site where IL-6R is cleaved to form IL-6 SR.39 This observation led them to hypothesize that the way the SNP modulates IL-6 SR levels is by affecting the efficiency of cleavage of the circulating receptor from the membrane-bound form. To test this, we quantified the amount of surface IL-6R on the LCLs from the HapMap Project, which should not be substantially affected if the cleavage hypothesis is explaining the high levels in serum. A survey of cell lines from several different ethnic groups shows no evidence of an association of surface IL-6R with the rs8192284 genotype in HapMap cell lines (fig. 4). This supports the hypothesis of Galicia et al. that the mechanism of action of rs8192284 is to affect cleavage efficiency of IL-6 SR from the cell membrane.39
Figure 4. .
rs8192284 does not appear to affect levels of IL-6R protein on the cell surface. We measured expression of surface IL-6R protein on LCLs used in the HapMap Project and found no significant effect of the rs8192284 genotype. We plotted the distribution of IL-6R expression for unrelated European Americans from Utah (CEU), East Asians from Beijing (CHB) and Tokyo (JPT), and West Africans from Ibadan, Nigeria (YRI). The AA homozygotes are represented by red triangles, AC heterozygotes by green diamonds, and CC homozygotes by blue dots. The mean value of each genotype class is represented by a horizontal black line. P values for differences between each genotype class (t test) are reported. The low frequency of the C allele in the YRI samples (4%) limits the power of the analysis in this group (the frequencies are 35% in CEU and 43% in CHB and JPT).
Motivated by the quantitatively profound effect of rs8192284 on IL-6 SR levels and the observation that some of the other markers of inflammation are in the same biological pathway, we next tested for an association of the genotype to levels of the other seven inflammatory markers. We found that rs8192284 is associated not only with IL-6 SR levels (P≪1.0×10-12) but also—a novel finding—with IL-6 levels (P<3.4×10-5).
To replicate both the IL-6 SR and IL-6 associations, we studied 1,674 European Americans for whom we had complete information for the seven covariates and for whom we successfully obtained an rs8192284 genotype. (These samples were a subset of the 1,794 European Americans in the Health ABC Study.) The association with IL-6 SR was extremely significant at P≪1.0×10-12. We also replicated the association with IL-6 (P<8.9×10-6). When the African American and European American samples were combined and when self-declared ancestry and percentage of European ancestry were controlled for in the analysis, both associations were extremely significant (P≪1.0×10-12 for IL-6 SR and P<2.0×10-9 for IL-6).
We next assessed how the AC and CC genotypes at rs81922284 raise inflammatory marker levels, relative to AA (table 3). The rs8192284 genotype explains 33% of the variance in absolute IL-6 SR levels in African Americans and 49% in European Americans. IL-6 SR levels are increased, on average, 1.29-fold per copy of the allele in African Americans and 1.26-fold per copy in European Americans, after correction for covariates. There is no evidence of a nonmultiplicative effect of the allele in African Americans (P=.88) and only marginal evidence in European Americans (P=.05). The effect on IL-6 levels is quantitatively less; the rs8192284 genotype explains 0.8% of the variance in absolute IL-6 levels in African Americans and 0.4% in European Americans. After correction for covariates, IL-6 is increased, on average, 1.17-fold per copy of the allele in African Americans and 1.10-fold per copy of the allele in European Americans. We do not detect a nonmultiplicative effect in either African Americans (P=.60) or European Americans (P=.26) for the association to IL-6 levels.
Discussion
We have used admixture mapping to search for regions of the genome associated with eight acute-phase inflammatory markers and soluble receptors. We identified a 32.7-Mb region on chromosome 1 (including the centromere) at which high levels of European ancestry in African Americans are significantly associated with high levels of IL-6 SR.28,29,30 It is also important to highlight the negative results: seven of the eight phenotypes failed to show associations. One possible explanation is low sample size. The scans in this study included only a couple hundred samples with each extreme phenotype, but our power calculations suggest that >1,000 samples should be studied for admixture mapping to have high statistical power compared with alternative methods such as linkage mapping.23,26 It is important to recognize, however, that admixture scans can have negative results, even with large samples sizes. For example, we have performed scans for BMI and type 2 diabetes, which, despite containing >2,000 samples, fail to detect association (D. Reich and N. Patterson, unpublished data).
The admixture mapping study identified a missense SNP in the IL-6R gene, rs8192284, which was first associated with IL-6 SR levels in 114 Japanese individuals.39 We show that alleles at this SNP fully account for the admixture peak on chromosome 1. Our analysis powerfully replicates the result found by Galicia et al.39 in two additional ethnic groups and also provides quantitative information about the importance of the effect. An association with IL-6 SR is interesting not only because of the association of inflammatory markers to atherosclerosis but also because IL-6 SR has been associated in vivo to the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (MIM 180300), ulcerative colitis, and Crohn disease (MIM 191390).43
A novel result in this study is that rs8192284 is also associated with IL-6 levels in both African Americans and European Americans. There is a 1.06- to 1.15-fold increased level of IL-6 for one copy of the allele and a 1.22- to 1.43-fold increase for two copies, accounting for 0.8% of the variance in IL-6 measurements in African Americans and for 0.4% in European Americans. Although the causative SNP in the IL-6R locus is associated with higher IL-6 levels, admixture mapping did not detect a signal for IL-6 at this locus. The lack of a signal for IL-6 as the phenotype at this locus is not surprising given our limited sample size and the fact that the association between rs8192284 and IL-6 SR (33%–49% of variance explained) is so much stronger than the association with IL-6 (<1% of variance explained). Our previously published power calculations23 suggest that several thousand individuals with extreme values of IL-6 would be necessary to directly detect an association with IL-6 levels at the IL-6R locus in African Americans. High IL-6 levels are biologically important, since they are correlated with risk of coronary heart disease and mobility disability.44 In one study of postmenopausal women,6 individuals in the highest quartile of IL-6 levels have more than double the rate of coronary artery disease of those in the lowest quartile. We do not know whether rs8192284 is associated with coronary heart disease risk, but this study identifies it as a candidate risk variant.
Finally, this study is methodologically significant because it provides the first evidence that admixture mapping can be used to localize and precisely map phenotypically important variants. Past studies have used admixture mapping to provide rough localization.29,30,33 However, no study has followed an initial localization with a successful positional cloning effort. Similar to previous admixture mapping studies,28–30 this study identified a wide region around the peak containing many genes. The presence of IL-6R in this region was fortuitous in allowing us to narrow the search to a small region. However, the strength of the signal we found at multiple tag SNPs around IL-6 SR indicates that mapping would also have been successful (although it would have required more genotyping) if we had instead taken the approach of haplotype tagging across the entire admixture peak. Thus, this study demonstrates that an admixture scan followed by haplotype tagging across a peak can identify causal variants.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank all the volunteers who participated in the Health ABC Study. We thank David Altshuler, John Danesh, Steve Kritchevsky, and Alkes Price, for comments on the manuscript. We thank Emily Kenyon, Hilsa Ayonayon, and Whitney Green, for preparing DNA samples and bioinformatic support. We thank Richard Cook at the MIT biopolymers facility, for spotting the peptide array, and Jacqueline Slavik, Sasha Bonadkar, Cara Wolfish, and Roman Yelensky, for technical and analytical help on the HapMap LCL experiment. The Health ABC Study is funded by National Institute on Aging (NIA) contracts AG62101, AG62103, and AG62106 and is also supported in part by the Intramural Research program of the NIA. Genotyping for the study was performed at the Broad Institute Center for Genotyping and Analysis, which is supported by National Center for Research Resources grant RR020278 and by a subaward (to J.Z.). Further support for genotyping came from a Burroughs Wellcome Career Development Award in the Biomedical Sciences (to D.R.). V.J. is supported by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke grant NS45776. R.F. and J.Z. are supported by NIA grant AG021024. E.Z. is supported by a career transition award from the National Cancer Institute (CA109351), and E.Z., A.R., P.K. and S.C. are supported by NIA grant AG2312201.
Appendix A
We extended our ANCESTRYMAP software23 to allow us to detect not only a locus with increased proportion of European or African ancestry compared with the genomewide average (an admixture peak) but also a variant that contributes more to association than can be explained by the admixture signal alone. As in the original work of Patterson et al.,23 the fine-mapping test for statistical association uses Bayesian statistics.
To review the approach we used to search for an admixture peak in ANCESTRYMAP, we model the risk of disease for an individual due to ancestry at a locus as ψ(a)=ra. Here, a is the number of European ancestry chromosomes (0, 1, or 2) that individual has, and r is the multiplicative risk per European chromosome. To score for association, we calculate L1(i), which can be summed over all individuals to obtain overall evidence of admixture association at the locus,
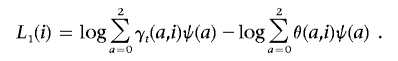 |
Here, γt(a,i) is the estimated probability that an individual has a European chromosomes at the position of interest t, and θ(a,i) is the genomewide proportion of European ancestry. Both of these are calculated by the ANCESTRYMAP software.23
To extend the model to calculate a fine-mapping score at a specific marker, we score for risk as a joint function of ancestry a and genotype g: ψ(a,g). The relevant score is now
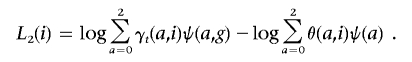 |
A contrast between the main admixture score L1(i) and the fine-mapping score L2(i) is that, for the admixture mapping score, we are comparing the hypothesis that European ancestry at the locus modulates risk of disease with the hypothesis that the locus has nothing to do with disease. For the fine-mapping score, we are comparing the hypothesis that the allele or one in strong linkage disequilibrium with it modulates a phenotype with the hypothesis that the locus is indeed connected with disease but only by an admixture signal. Thus, the fine-mapping score L2(i) gives evidence of association above and beyond the admixture signal L1(i).
All that remains is to specify the joint risk function ψ(a,g). We model it as ψ(a,g)=X(a)Y(g). In this formulation, ancestry and genotype contribute multiplicatively and independently to risk. We specify a regularly spaced mesh on genotype logY(g), to test different models of disease risk. Given a particular Y(g), we then set X(a) such that it reduces to ψ(a) in the case in which genotype makes no additional contribution. Thus, we set X(a) so that E[ψ(a,g)|a]=ψ(a). Our final score is an average of the Bayes factors obtained at each mesh point. This yields a Bayes factor for the compound hypothesis that the genotype is contributing to the score.
Web Resources
The URLs for data presented herein are as follows:
- ANCESTRYMAP software, http://genepath.med.harvard.edu/~reich/Software.htm
- International HapMap Project, http://www.hapmap.org/
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for IL-6R, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn disease)
- UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/ (for human genome reference sequence build 35)
References
- 1.Cesari M, Penninx BW, Newman AB, Kritchevsky SB, Nicklas BJ, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Rubin SM, Ding J, Simonsick EM, Harris TB, et al (2003) Inflammatory markers and onset of cardiovascular events. Circulation 108:2317–2322 10.1161/01.CIR.0000097109.90783.FC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cushman M, Arnold AM, Psaty BM, Manolio TA, Kuller LH, Burke GL, Polak JF, Tracy RP (2005) C-reactive protein and the 10-year incidence of coronary heart disease in older men and women. Circulation 112:25–31 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.504159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tuomisto K, Jousilahti P, Sundvall J, Pajunen P, Salomaa V (2006) C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha as predictors of incident coronary and cardiovascular events and total mortality. Thromb Haemost 95:511–518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kohler HP, Grant PJ (2000) Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 342:1792–1801 10.1056/NEJM200006153422406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Curb JD, Abbott RD, Rodriguez BL, Sakkinen P, Popper JS, Yano K, Tracy RP (2003) C-reactive protein and the future risk of thromboembolic stroke in healthy men. Circulation 107:2016–2020 10.1161/01.CIR.0000065228.20100.F7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N (2000) C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med 342:836–843 10.1056/NEJM200003233421202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, Eda S, Eiriksdottir G, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Pepys MB, Gudnason V (2004) C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 350:1387–1397 10.1056/NEJMoa032804 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pankow JS, Folsom AR, Cushman M, Borecki IB, Hopkins PN, Eckfeldt JH, Tracy RP (2001) Familial and genetic determinants of systemic markers of inflammation: the NHLBI Family Heart Study. Atherosclerosis 154:681–689 10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00586-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Best LG, North KE, Tracy RP, Lee ET, Howard BV, Palmieri V, Maccluer JW (2004) Genetic determination of acute phase reactant levels: the Strong Heart Study. Hum Hered 58:112–116 10.1159/000083032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Austin MA, Zhang C, Humphries SE, Chandler WL, Talmud PJ, Edwards KL, Leonetti DL, McNeely MJ, Fujimoto WY (2004) Heritability of C-reactive protein and association with apolipoprotein E genotypes in Japanese Americans. Ann Hum Genet 68:179–188 10.1046/j.1529-8817.2004.00078.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Maat MP, Bladbjerg EM, Hjelmborg JB, Bathum L, Jespersen J, Christensen K (2004) Genetic influence on inflammation variables in the elderly. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:2168–2173 10.1161/01.ATV.0000143856.01669.e7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Retterstol L, Eikvar L, Berg K (2003) A twin study of C-reactive protein compared to other risk factors for coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 169:279–282 10.1016/S0021-9150(03)00192-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Worns MA, Victor A, Galle PR, Hohler T (2006) Genetic and environmental contributions to plasma C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels—a study in twins. Genes Immun 7:600–605 10.1038/sj.gene.6364330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Khera A, McGuire DK, Murphy SA, Stanek HG, Das SR, Vongpatanasin W, Wians FH Jr, Grundy SM, de Lemos JA (2005) Race and gender differences in C-reactive protein. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:464–469 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.04.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Visser M, Pahor M, Taaffe DR, Goodpaster BH, Simonsick EM, Newman AB, Nevitt M, Harris TB (2002) Relationship of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with muscle mass and muscle strength in elderly men and women: the Health ABC Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 57:M326–M332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rife DC (1954) Populations of hybrid origin as source material for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet 6:26–33 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chakraborty R, Weiss KM (1988) Admixture as a tool for finding linked genes and detecting that difference from allelic association between loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:9119–9123 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stephens JC, Briscoe D, O’Brien SJ (1994) Mapping by admixture linkage disequilibrium in human populations: limits and guidelines. Am J Hum Genet 55:809–824 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McKeigue PM (1997) Mapping genes underlying ethnic differences in disease risk by linkage disequilibrium in recently admixed populations. Am J Hum Genet 60:188–196 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McKeigue PM (1998) Mapping genes that underlie ethnic differences in disease risk: methods for detecting linkage in admixed populations, by conditioning on parental admixture. Am J Hum Genet 63:241–251 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Collins-Schramm HE, Chima B, Operario DJ, Criswell LA, Seldin MF (2003) Markers informative for ancestry demonstrate consistent megabase-length linkage disequilibrium in the African American population. Hum Genet 113:211–219 10.1007/s00439-003-0961-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Smith MW, Patterson N, Lautenberger JA, Truelove AL, McDonald GJ, Waliszewska A, Kessing BD, Malasky MJ, Scafe C, Le E, et al (2004) A high-density admixture map for disease gene discovery in African Americans. Am J Hum Genet 74:1001–1013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Patterson N, Hattangadi N, Lane B, Lohmueller KE, Hafler DA, Oksenberg JR, Hauser SL, Smith MW, O’Brien SJ, Altshuler D, et al (2004) Methods for high-density admixture mapping of disease genes. Am J Hum Genet 74:979–1000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hoggart CJ, Shriver MD, Kittles RA, Clayton DG, McKeigue PM (2004) Design and analysis of admixture mapping studies. Am J Hum Genet 74:965–978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Montana G, Pritchard JK (2004) Statistical tests for admixture mapping with case-control and cases-only data. Am J Hum Genet 75:771–789 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Reich D, Patterson N (2005) Will admixture mapping work to find disease genes? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:1605–1607 10.1098/rstb.2005.1691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Carlson CS, Eberle MA, Rieder MJ, Smith JD, Kruglyak L, Nickerson DA (2003) Additional SNPs and linkage-disequilibrium analyses are necessary for whole-genome association studies in humans. Nat Genet 33:518–521 10.1038/ng1128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhu X, Luke A, Cooper RS, Quertermous T, Hanis C, Mosley T, Gu CC, Tang H, Rao DC, Risch N, et al (2005) Admixture mapping for hypertension loci with genome-scan markers. Nat Genet 37:177–181 10.1038/ng1510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Reich D, Patterson N, De Jager PL, McDonald GJ, Waliszewska A, Tandon A, Lincoln RR, DeLoa C, Fruhan SA, Cabre P, et al (2005) A whole-genome admixture scan finds a candidate locus for multiple sclerosis susceptibility. Nat Genet 37:1113–1118 10.1038/ng1646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Freedman ML, Haiman CA, Patterson N, McDonald GJ, Tandon A, Waliszewska A, Penney K, Steen RG, Ardlie K, John EM, et al (2006) Admixture mapping identifies 8q24 as a prostate cancer risk locus in African-American men. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14068–14073 10.1073/pnas.0605832103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kanaya AM, Wassel Fyr C, Vittinghoff E, Harris TB, Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Tylavsky F, Cummings SR (2006) Adipocytokines and incident diabetes mellitus in older adults: the independent effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Arch Intern Med 166:350–356 10.1001/archinte.166.3.350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hosono S, Faruqi AF, Dean FB, Du Y, Sun Z, Wu X, Du J, Kingsmore SF, Egholm M, Lasken RS (2003) Unbiased whole-genome amplification directly from clinical samples. Genome Res 13:954–964 10.1101/gr.816903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fan JB, Oliphant A, Shen R, Kermani BG, Garcia F, Gunderson KL, Hansen M, Steemers F, Butler SL, Deloukas P, et al (2003) Highly parallel SNP genotyping. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 68:69–78 10.1101/sqb.2003.68.69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tang K, Fu DJ, Julien D, Braun A, Cantor CR, Koster H (1999) Chip-based genotyping by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10016–10020 10.1073/pnas.96.18.10016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kwok PY (2002) SNP genotyping with fluorescence polarization detection. Hum Mutat 19:315–323 10.1002/humu.10058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom [Google Scholar]
- 37.International Haplotype Map Working Group (2005) A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437:1299–1320 10.1038/nature04226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.de Bakker PIW, Yelensky R, Pe’er I, Gabriel SB, Daly MJ, Altshuler D (2005) Efficiency and power in genetic association studies. Nat Genet 37:1217–1223 10.1038/ng1669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Galicia JC, Tai H, Komatsu Y, Shimada Y, Akazawa K, Yoshie H (2004) Polymorphisms in the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) gene: strong evidence that serum levels of soluble IL-6R are genetically influenced. Genes Immun 5:513–516 10.1038/sj.gene.6364120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wiederhold T, Lee MF, James M, Neujahr R, Smith N, Murthy A, Hartwig J, Gusella JF, Ramesh V (2004) Magicin, a novel cytoskeletal protein associates with the NF2 tumor suppressor merlin and Grb2. Oncogene 23:8815–8825 10.1038/sj.onc.1208110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dean PN, Bagwell CB, Lindmo T, Murphy RF, Salzman GC (1990) Introduction to flow cytometry data file standard. Cytometry 11:321–322 10.1002/cyto.990110302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Data File Standards Committee of the Society for Analytical Cytology (1990) Data file standard for flow cytometry. Cytometry 11:323–332 10.1002/cyto.990110303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jones SA, Horiuchi S, Topley N, Yamamoto N, Fuller GM (2001) The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: mechanisms and implications in disease. FASEB J 15:43–58 10.1096/fj.99-1003rev [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kritchevsky SB, Cesari M, Pahor M (2005) Inflammatory markers and cardiovascular health in older adults. Cardiovasc Res 66:265–275 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.12.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.