Abstract
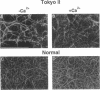
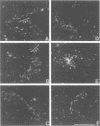
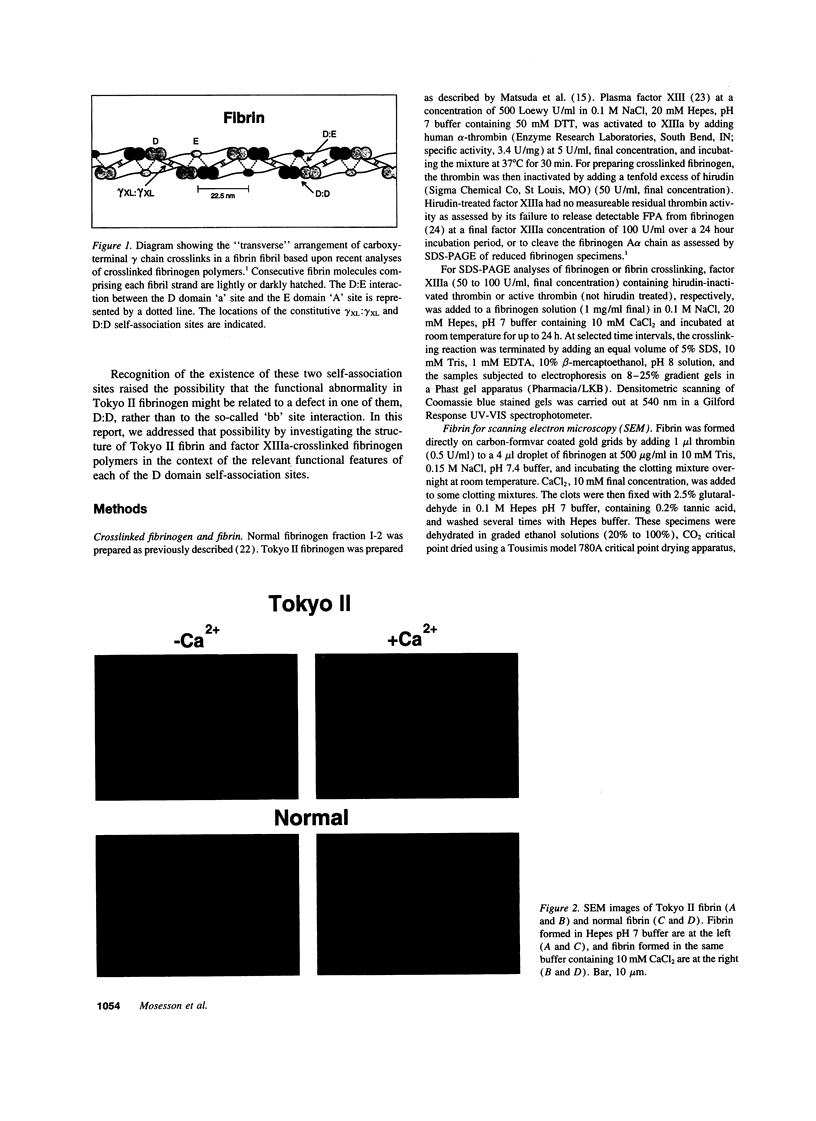
Intermolecular end-to-middle domain pairing between a thrombin-exposed 'A' polymerization site in the central 'E' domain of fibrin, and a constitutive complementary 'a' site in each outer 'D' domain ('D:E'), is necessary but not alone sufficient for normal fibrin assembly, as judged from previous studies of a congenital dysfibrinogen, Tokyo II (gamma 275 arg-->cys), which showed defective fibrin clot assembly and a normal D:E interaction (Matsuda, M., M. Baba, K. Morimoto, and C. Nakamikawa, 1983. J. Clin. Invest. 72:1034-1041). In addition to the 'a' polymerization site, two other constitutive intermolecular association sites on fibrinogen D domains have been defined: between gamma chain regions containing the carboxy-terminal factor XIIIa crosslinking site ('gamma XL:gamma XL'); and between sites located at the outer ends of each molecule ('D:D') (Mosesson, M. W., K. R. Siebenlist, J. F. Hainfeld, and J. S. Wall, manuscript submitted for publication). We evaluated the function of these sites in Tokyo II fibrinogen, and confirmed that there was a normal fibrin D:E interaction, as determined from a normal fibrin crosslinking rate in the presence of factor XIIIa. We also found a normal gamma XL: gamma XL interaction, as assessed by a normal fibrinogen crosslinking rate. Judging from electron microscopic images, factor XIIIa-crosslinked Tokyo II fibrinogen failed to form elongated double-stranded fibrils like normal fibrinogen. Instead, it formed aggregated disordered collections of molecules, with occasional short fibrillar segments. In addition, Tokyo II fibrin formed an abnormal, extensively branched clot network containing many tapered terminating fibers. These findings indicate that the Tokyo II fibrinogen defect results in a functionally abnormal D:D self-association site, and that a normal D:D site interaction is required, in addition to D:E, for normal fibrin or fibrinogen assembly.
Full text
PDF
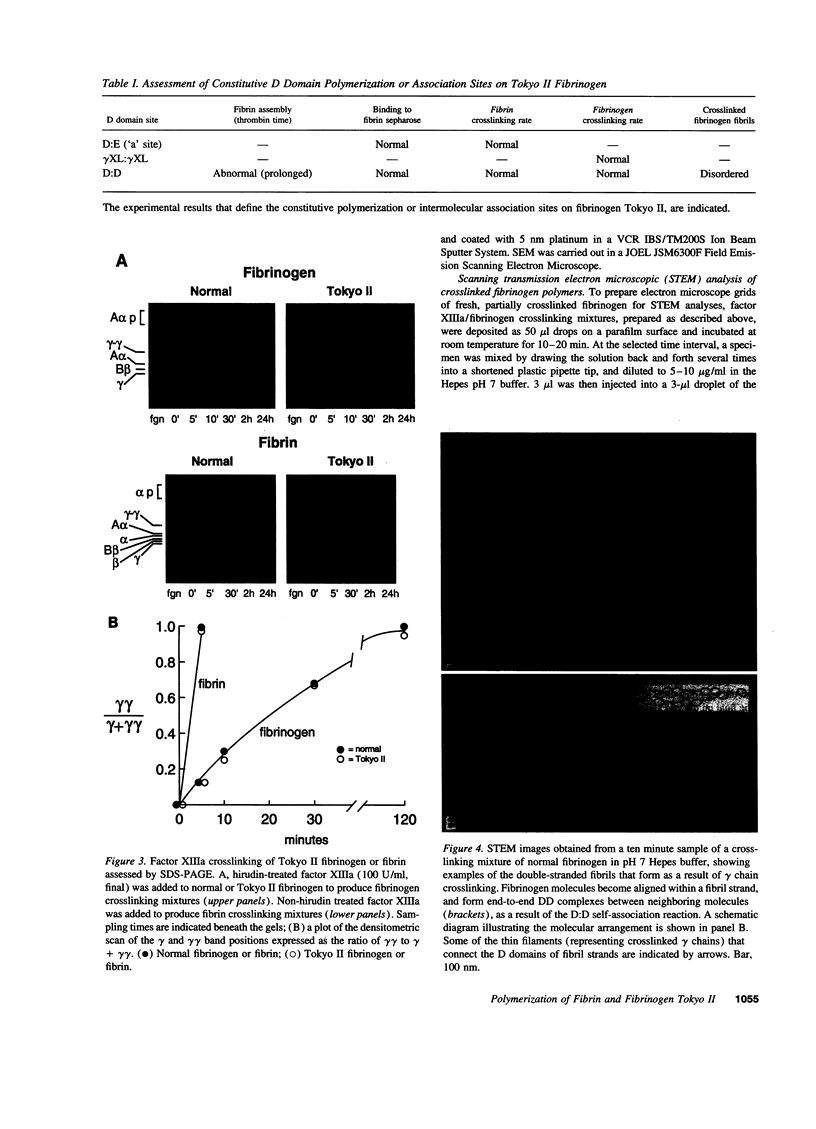



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Hogg D., Therkildsen L. A two-step fibrinogen--fibrin transition in blood coagulation. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):501–505. doi: 10.1038/275501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Olexa S. A., Pandya B. V. Fibrin polymerization sites in fibrinogen and fibrin fragments. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:301–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardik B. N., Shainoff J. R. Crosslinking of monomeric fibrin by factor XIIIa. Thromb Haemost. 1979 Oct 31;42(3):864–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. D. The Mechanism of Polymerization of Fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Jul;38(7):566–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.7.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Hantgan R. R., Hermans J., Erickson H. P. Structure of the fibrin protofibril. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4872–4876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R., McDonagh J., Hermans J. Fibrin assembly. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:344–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaide H., Shainoff J. R. Cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin by fibrin-stablizing factor (factor XIIIa). J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):574–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow W., Endres G. F., Siegel B. M., Scheraga H. A. An electron microscopic investigation of the polymerization of bovine fibrin monomer. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryk B. J., Collen D., Woods K. R., Blombäck B. Evidence for localization of polymerization sites in fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3322–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryk B., Blombäck B., Blombäck M. Fibrinogen Detroit - an abnormal fibrinogen with non-functinal NH2-terminal polymerization domain. Thromb Res. 1976 Jul;9(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Baba M., Morimoto K., Nakamikawa C. "Fibrinogen Tokyo II". An abnormal fibrinogen with an impaired polymerization site on the aligned DD domain of fibrin molecules. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1034–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI111027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., DiOrio J. P., Müller M. F., Shainoff J. R., Siebenlist K. R., Amrani D. L., Homandberg G. A., Soria J., Soria C., Samama M. Studies on the ultrastructure of fibrin lacking fibrinopeptide B (beta-fibrin). Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1073–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., DiOrio J. P., Siebenlist K. R., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F. Evidence for a second type of fibril branch point in fibrin polymer networks, the trimolecular junction. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1517–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., DiOrio J. P., Siebenlist K. R., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F. Evidence for a second type of fibril branch point in fibrin polymer networks, the trimolecular junction. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1517–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. The preparation and properties of human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2829–2835. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Siebenlist K. R., Amrani D. L., DiOrio J. P. Identification of covalently linked trimeric and tetrameric D domains in crosslinked fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1113–1117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. F., Ris H., Ferry J. D. Electron microscopy of fine fibrin clots and fine and coarse fibrin films. Observations of fibers in cross-section and in deformed states. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Evidence for four different polymerization sites involved in human fibrin formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosser R. W., Roberts W. W., Ferry J. D. Rheology of fibrin clots. IV. Darcy constants and fiber thickness. Biophys Chem. 1977 Sep;7(2):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenfel'd M. A., Vasil'eva M. V. Mechanism of aggregation of fibrinogen molecules: the influence of fibrin-stabilising factor. Biomed Sci. 1991;2(2):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G. A., Nair C. H., Dhall D. P. Physiological studies on fibrin network structure. Thromb Res. 1985 Oct 15;40(2):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Dardik B. N. Fibrinopeptide B in fibrin assembly and metabolism: physiologic significance in delayed release of the peptide. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:254–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist K. R., Mosesson M. W., Di Orio J. P., Tavori S., Tatarsky I., Rimon A. The polymerization of fibrin prepared from fibrinogen Haifa (gamma 275Arg----His). Thromb Haemost. 1989 Nov 24;62(3):875–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist K. R., Prchal J. T., Mosesson M. W. Fibrinogen Birmingham: a heterozygous dysfibrinogenemia (A alpha 16 Arg----His) containing heterodimeric molecules. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann C., Bögli C., Jungo M., Lämmle B., Heinemann G., Wermuth B., Redaelli R., Baudo F., Furlan M. Fibrinogen Milano V: a congenital dysfibrinogenaemia with a gamma 275 Arg-->Cys substitution. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994 Aug;5(4):463–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Morphology of bovine fibrinogen monomers and fibrin oligomers. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 15;150(3):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90555-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. K., Waugh D. F. Relations between enzymatic and association reactions in the development of bovine fibrin clot structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 1;211(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]