Abstract
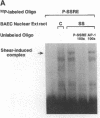
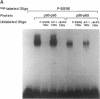
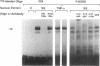
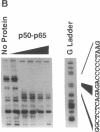
Hemodynamic forces, such as fluid shear stress, that act on the endothelial lining of the cardiovascular system can modulate the expression of an expanding number of genes crucial for homeostasis and the pathogenesis of vascular disease. A 6-bp core element (5'-GAGACC-3'), defined previously as a shear-stress response element is present in the promoters of many genes, including the PDGF B-chain, whose expression is modulated by shear stress. The identity of the nuclear protein(s) binding to this element has not yet been elucidated. Using electrophoretic mobility shift assays and in vitro DNase I footprinting, we demonstrate that nuclear factor-kappa B p50-p65 heterodimers, which accumulate in the nuclei of cultured vascular endothelial cells exposed to fluid shear stress, bind to the PDGF-B shear-stress response element in a specific manner. Mutation of this binding motif abrogated its interaction with p50-p65 and abolished the ability of the promoter to mediate increased gene expression in endothelial cells exposed to shear stress. Transient cotransfection studies indicate that p50-p65 is able to activate PDGF-B shear-stress response element-dependent reporter gene expression in these cells. These findings thus implicate nuclear factor-kappa B in the transactivation of an endothelial gene responding to a defined fluid mechanical force.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando J., Tsuboi H., Korenaga R., Takada Y., Toyama-Sorimachi N., Miyasaka M., Kamiya A. Shear stress inhibits adhesion of cultured mouse endothelial cells to lymphocytes by downregulating VCAM-1 expression. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):C679–C687. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.3.C679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T. Endothelial nuclear factor-kappa B and the initiation of the atherosclerotic lesion. Lab Invest. 1993 May;68(5):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Tripathi S. C. Mechanical stress mechanisms and the cell. An endothelial paradigm. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):239–245. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca L. G., Johnson D. R., Whitley M. Z., Collins T., Pober J. S. cAMP and tumor necrosis factor competitively regulate transcriptional activation through and nuclear factor binding to the cAMP-responsive element/activating transcription factor element of the endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (E-selectin) promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19193–19196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey C. F., Jr, Bussolari S. R., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Davies P. F. The dynamic response of vascular endothelial cells to fluid shear stress. J Biomech Eng. 1981 Aug;103(3):177–185. doi: 10.1115/1.3138276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond S. L., Eskin S. G., McIntire L. V. Fluid flow stimulates tissue plasminogen activator secretion by cultured human endothelial cells. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1483–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.2467379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangos J. A., Eskin S. G., McIntire L. V., Ives C. L. Flow effects on prostacyclin production by cultured human endothelial cells. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1477–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.3883488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Independent modes of transcriptional activation by the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):775–787. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh H. J., Li N. Q., Frangos J. A. Pulsatile and steady flow induces c-fos expression in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Jan;154(1):143–151. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh H. J., Li N. Q., Frangos J. A. Shear stress increases endothelial platelet-derived growth factor mRNA levels. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):H642–H646. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.2.H642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh H. J., Li N. Q., Frangos J. A. Shear-induced platelet-derived growth factor gene expression in human endothelial cells is mediated by protein kinase C. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):552–558. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Schwartz S. M. Pharmacology of smooth muscle cell replication. Hypertension. 1992 Dec;20(6):713–736. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.6.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszubska W., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Ghersa P., DeRaemy-Schenk A. M., Chen B. P., Hai T., DeLamarter J. F., Whelan J. Cyclic AMP-independent ATF family members interact with NF-kappa B and function in the activation of the E-selectin promoter in response to cytokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7180–7190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachigian L. M., Fries J. W., Benz M. W., Bonthron D. T., Collins T. Novel cis-acting elements in the human platelet-derived growth factor B-chain core promoter that mediate gene expression in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22647–22656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan Q., Mercurius K. O., Davies P. F. Stimulation of transcription factors NF kappa B and AP1 in endothelial cells subjected to shear stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jun 15;201(2):950–956. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenfant C. NHLBI funding policies. Enhancing stability, predictability, and cost control. Circulation. 1994 Jul;90(1):1–1. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis H., Kaszubska W., DeLamarter J. F., Whelan J. Cooperativity between two NF-kappa B complexes, mediated by high-mobility-group protein I(Y), is essential for cytokine-induced expression of the E-selectin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):5701–5709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Sedivy J. M. Raf-1 protein kinase activates the NF-kappa B transcription factor by dissociating the cytoplasmic NF-kappa B-I kappa B complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9247–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. C., Brown K., Siebenlist U. Activation of NF-kappa B requires proteolysis of the inhibitor I kappa B-alpha: signal-induced phosphorylation of I kappa B-alpha alone does not release active NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):552–556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek A. M., Greene A. L., Izumo S. Regulation of endothelin 1 gene by fluid shear stress is transcriptionally mediated and independent of protein kinase C and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5999–6003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Sutton C., Gould H. Purification and characterization of Ku-2, an octamer-binding protein related to the autoantigen Ku. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3052–3059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kurihara H., Maemura K., Yoshizumi M., Yazaki Y. Disruption of cytoskeletal structures mediates shear stress-induced endothelin-1 gene expression in cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1706–1712. doi: 10.1172/JCI116757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel T., Resnick N., Atkinson W. J., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Shear stress selectively upregulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):885–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI117410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann M., Scheidereit C. Activation of NF-kappa B in vivo is regulated by multiple phosphorylations. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4597–4607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neish A. S., Read M. A., Thanos D., Pine R., Maniatis T., Collins T. Endothelial interferon regulatory factor 1 cooperates with NF-kappa B as a transcriptional activator of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2558–2569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell C. L., Deisseroth A. B., Lopez-Berestein G. Interaction of nuclear proteins with an AP-1/CRE-like promoter sequence in the human TNF-alpha gene. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Jul;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nollert M. U., Panaro N. J., McIntire L. V. Regulation of genetic expression in shear stress-stimulated endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Oct 13;665:94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb42577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard K., May G. E. An EMSA-based method for determining the molecular weight of a protein--DNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3335–3336. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombella V. J., Rando O. J., Goldberg A. L., Maniatis T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):773–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Agranoff A. B., Pascal E., Nabel G. J. An interaction between the DNA-binding domains of RelA(p65) and Sp1 mediates human immunodeficiency virus gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6570–6583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan V., Diamond S. L. Fluid shear stress induces synthesis and nuclear localization of c-fos in cultured human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 15;196(1):79–84. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. A., Whitley M. Z., Williams A. J., Collins T. NF-kappa B and I kappa B alpha: an inducible regulatory system in endothelial activation. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):503–512. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick N., Collins T., Atkinson W., Bonthron D. T., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor B chain promoter contains a cis-acting fluid shear-stress-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosette C., Karin M. Cytoskeletal control of gene expression: depolymerization of microtubules activates NF-kappa B. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1111–1119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Hambrecht R., Schlierf G., Niebauer J., Hauer K., Neumann J., Hoberg E., Drinkmann A., Bacher F., Grunze M. Regular physical exercise and low-fat diet. Effects on progression of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):1–11. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyy Y. J., Hsieh H. J., Usami S., Chien S. Fluid shear stress induces a biphasic response of human monocyte chemotactic protein 1 gene expression in vascular endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Cogswell P. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3964–3974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Gray J., Chandra G., Talabot F., DeLamarter J. F. An NF kappa B-like factor is essential but not sufficient for cytokine induction of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2645–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley M. Z., Thanos D., Read M. A., Maniatis T., Collins T. A striking similarity in the organization of the E-selectin and beta interferon gene promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6464–6475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]