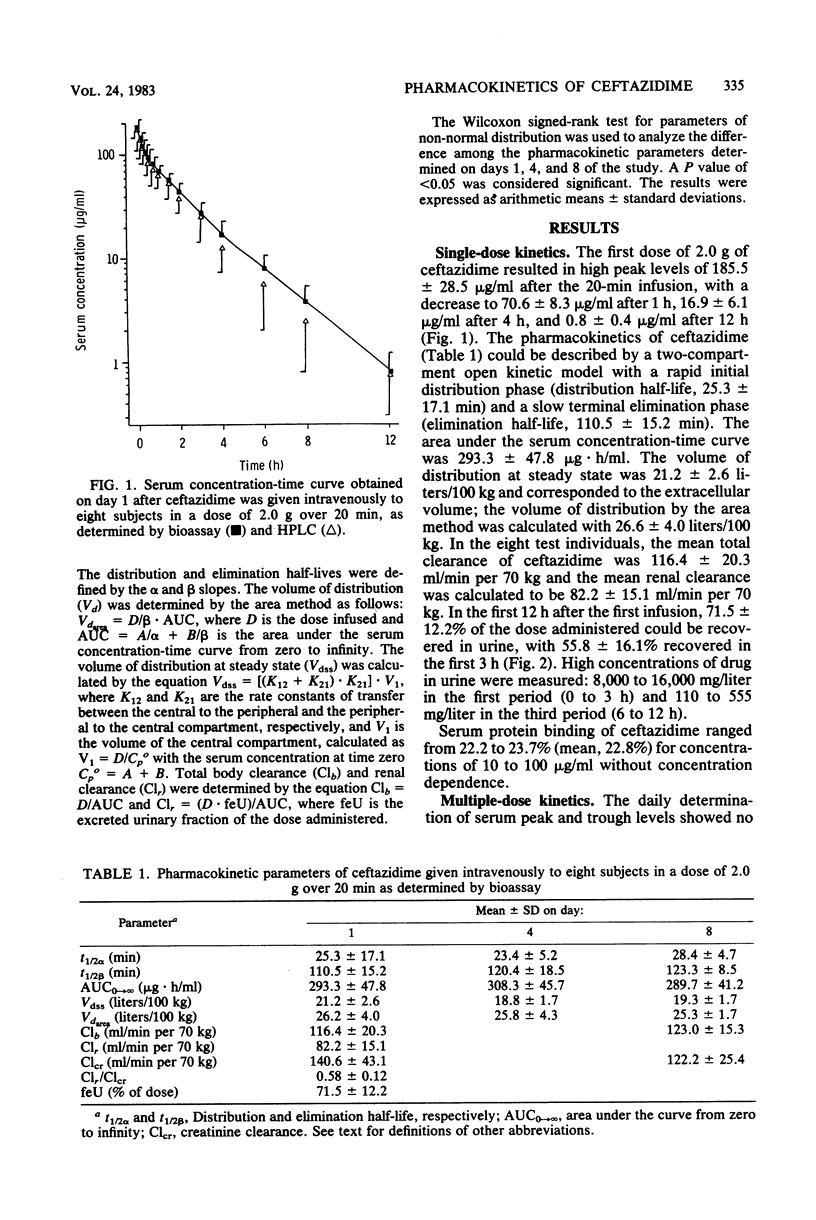
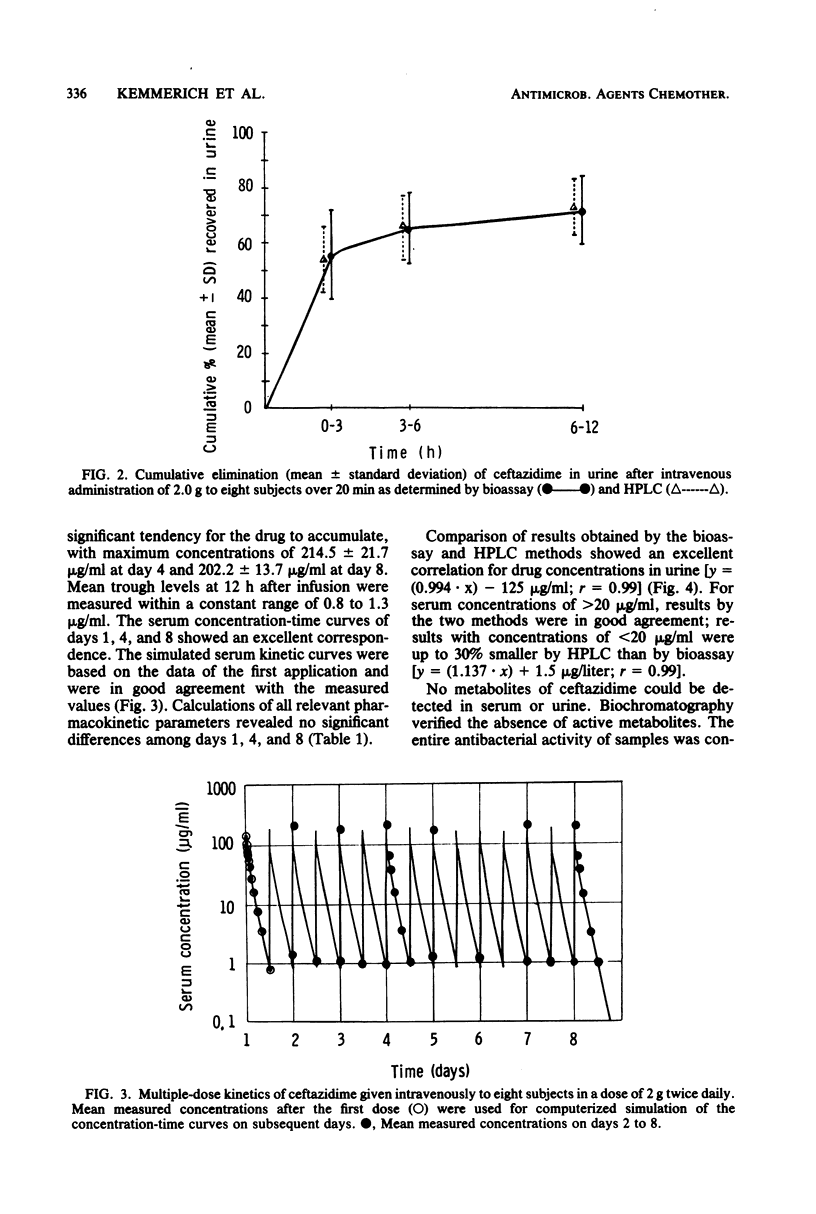
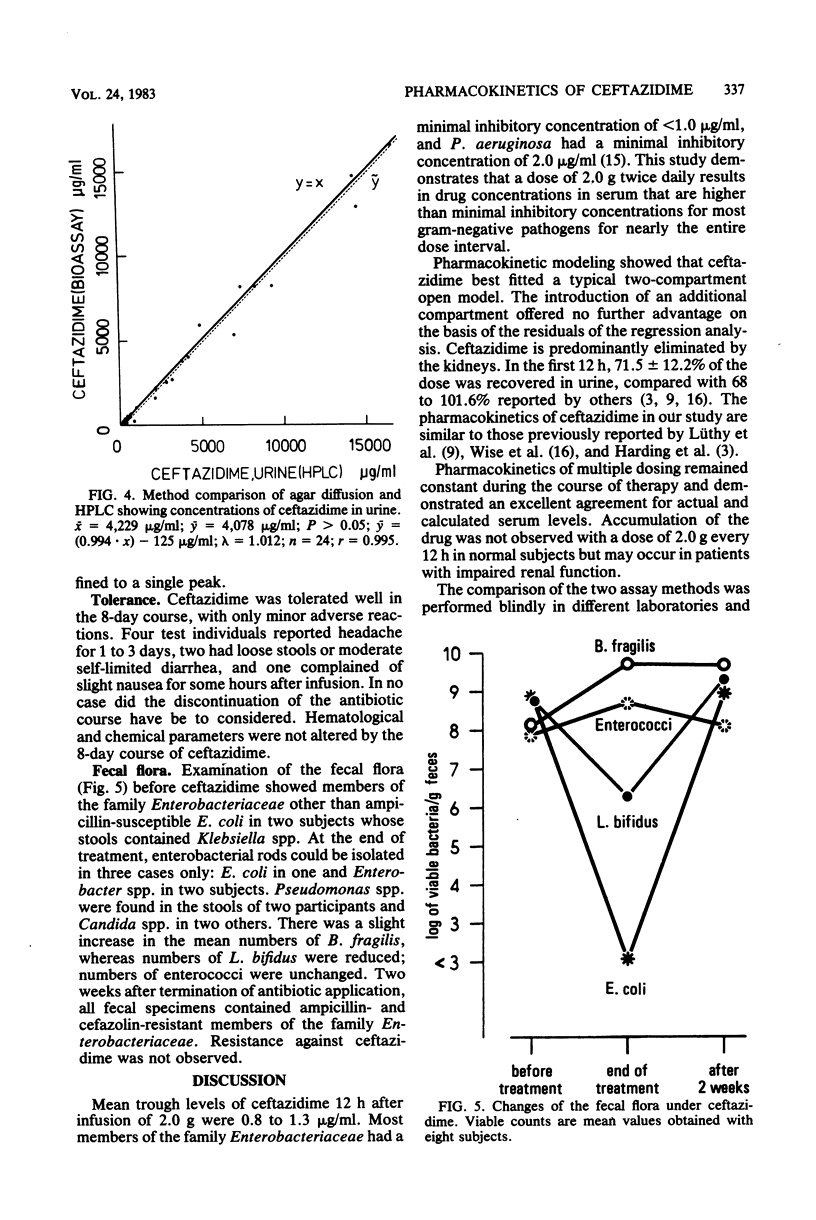
Abstract
Eight healthy volunteers each received 2.0 g of ceftazidime by constant intravenous infusion over 20 min twice daily every 12 h for 8 days. Concentrations of ceftazidime in serum and urine were measured by a microbiological assay and by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Qualitative and quantitative studies on aerobic and anaerobic fecal flora were carried out before, during, and 2 weeks after the end of treatment. The mean (+/- standard deviation) maximum drug concentration in serum at the end of the 20-min infusion (day 1) was 185.5 +/- 28.5 micrograms/ml, decreasing to 0.8 +/- 0.4 microgram/ml after 12 h. The mean recovery of drug in urine at 12 h was 71.5 +/- 12.2%. Pharmacokinetic parameters calculated on the basis of a two-compartment model were as follows: elimination half-life, 110.5 +/- 15.2 min; volume of distribution at steady state, 21.2 +/- 2.6 liters/100 kg; volume of distribution by the area method, 26.2 +/- 4.0 liters/100 kg; area under the serum concentration-time curve, 293.3 +/- 47.8 micrograms X h/ml; total body clearance, 116.4 +/- 20.3 ml/min per 70 kg; renal clearance, 82.2 +/- 15.1 ml/min per 70 kg. The agar diffusion test and high-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis showed a good correlation of results. Metabolites of ceftazidime could not be detected by high-pressure liquid chromatography in serum or urine. No accumulation of ceftazidime could be observed during the 8-day study period. Mean maximum drug levels in serum were 185.5 to 214.5 micrograms/ml, and mean trough levels were 0.8 to 1.1 micrograms/ml (days 1 to 8). No severe side effects were noted. During ceftazidime treatment, anaerobes were left intact, whereas members of the family Enterobacteriaceae could be isolated from stool in only three of eight subjects. Two weeks after discontinuation of the drug, all stool specimens contained ampicillin- and cefazolin-resistant gram-negative rods.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chopra I., Howe T. G., Linton A. H., Linton K. B., Richmond M. H., Speller D. C. The tetracyclines: prospects at the beginning of the 1980s. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jul;8(1):5–21. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaya H., Adnitt P. I., Turner P. Changes in gut flora after cephalexin treatment. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 12;3(5723):624–625. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5723.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Koch-Weser J. Clinical pharmacokinetics (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 6;293(19):964–970. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511062931905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOTHE H. [Intestinal flora and antibiotics with special reference to tetracycline]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1963 Jul 26;88:1469–1477. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1112252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Wiedemann B. Die Wirkung von Ampicillin auf die Darmflora des gesunden Menschen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Aug;197(2):234–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe P., Hamann C. A program for non-linear regression analysis to be used on desk-top computers. Comput Programs Biomed. 1980 Dec;12(2-3):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(80)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Young V. M., Greene W. H., Vermeulen G. D., Moody M. R., Wiernik P. H. Origin of infection in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Significance of hospital acquisition of potential pathogens. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Nov;77(5):707–714. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-5-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


