Abstract
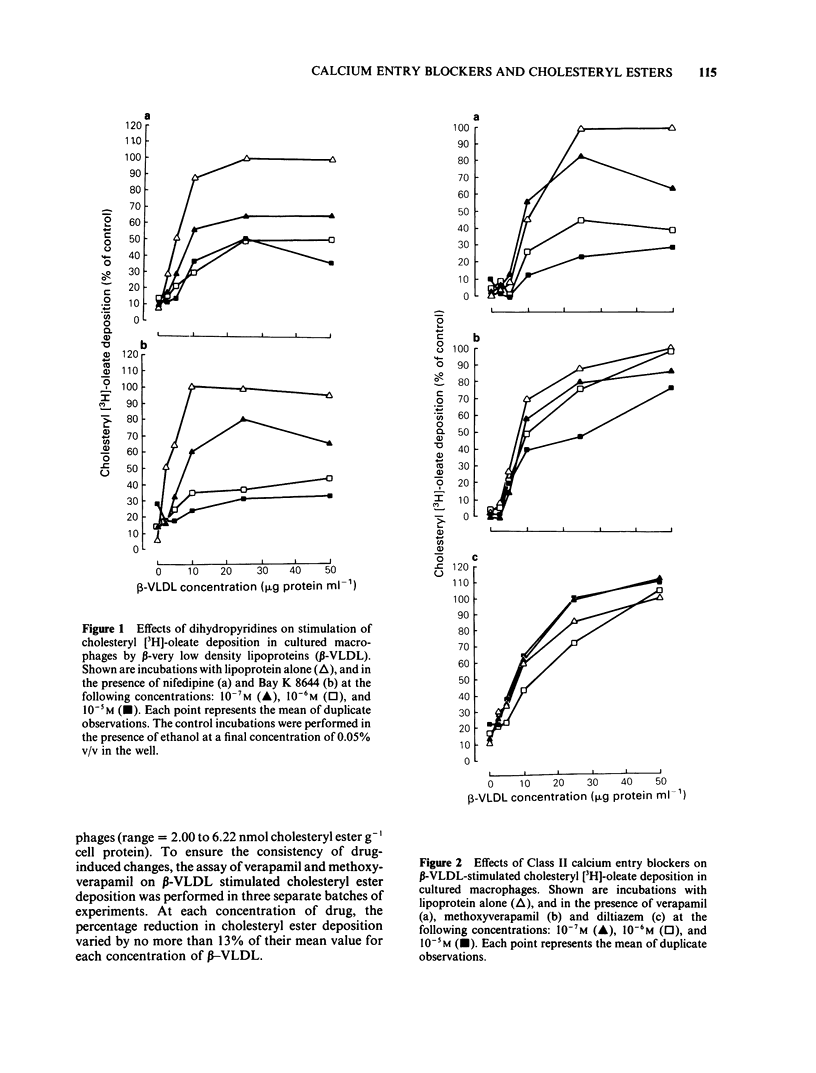
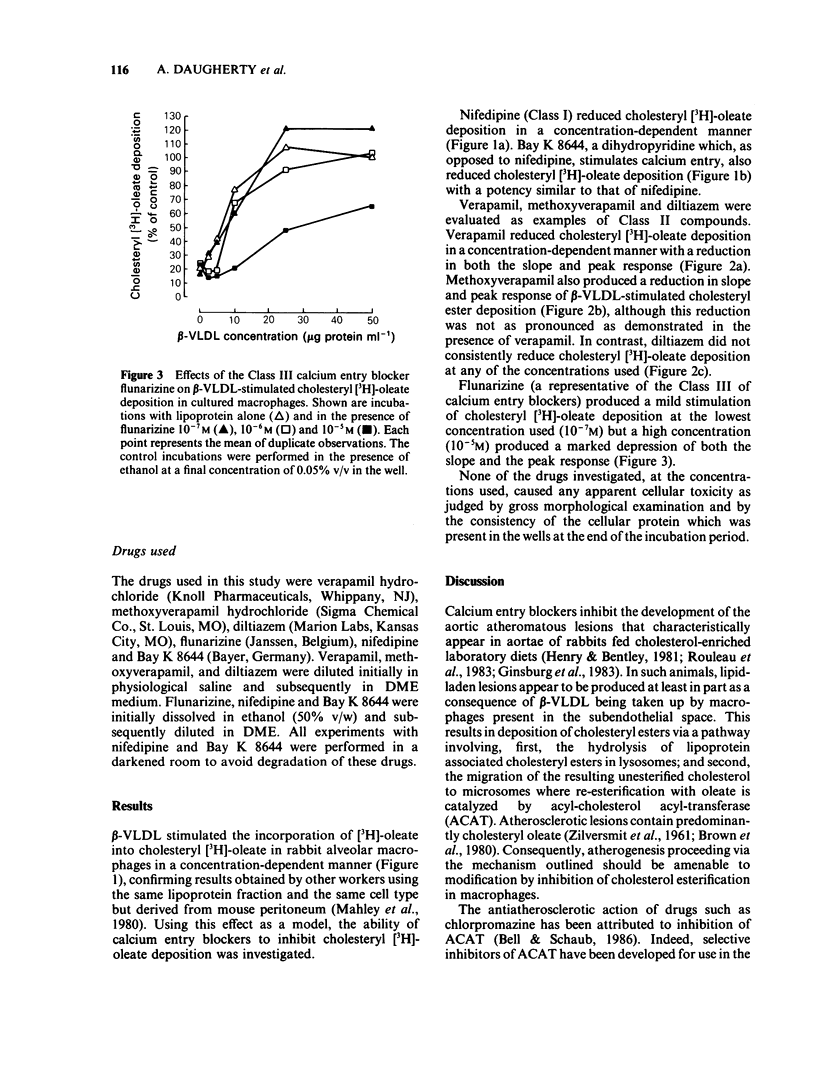
The effects of calcium entry blockers on stimulated cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition in cultured macrophages were characterized in order to elucidate mechanisms underlying possible antiatherosclerotic effects. Stimulation of intracellular cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition was initiated by incubation of macrophages with beta-very low density lipoproteins (beta-VLDL). Nifedipine (Class I) markedly reduced cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition at all concentrations tested. However, Bay K 8644, a dihydropyridine which is known to stimulate calcium entry, also reduced cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition with a similar potency to nifedipine. The effects of three Class II calcium entry blockers were evaluated: verapamil, methoxyverapamil, and diltiazem. Verapamil inhibited cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition in a concentration-dependent manner. Similarly, methoxyverapamil reduced cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition in a concentration-dependent manner although the reduction was not as great as that produced by verapamil. In contrast, diltiazem at any concentration tested did not inhibit cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition. Flunarizine (a Class III calcium entry blocker) produced a modest stimulation of cholesteryl [3H]-oleate deposition at the lowest concentration used (10(-7)M) but marked depression at the highest concentration (10(-5)M). The results indicate calcium entry blockers may exert protective effects on the development of atherosclerosis in animal models of diet-induced hyperlipidaemia by inhibiting intracellular cholesteryl ester deposition, but this effect may not be related to their calcium entry-blocking effects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell F. P., Schaub R. G. Chlorpromazine inhibits arterial ACAT and reduces arterial cholesterol and cholesteryl ester accumulation in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):42–49. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The cholesteryl ester cycle in macrophage foam cells. Continual hydrolysis and re-esterification of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9344–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Lange L. G., Sobel B. E., Schonfeld G. Aortic accumulation and plasma clearance of beta-VLDL and HDL: effects of diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1985 Aug;26(8):955–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R., Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):323–340. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein A. Specific pharmacology of calcium in myocardium, cardiac pacemakers, and vascular smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:149–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg R., Davis K., Bristow M. R., McKennett K., Kodsi S. R., Billingham M. E., Schroeder J. S. Calcium antagonists suppress atherogenesis in aorta but not in the intramural coronary arteries of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Lab Invest. 1983 Aug;49(2):154–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. D., Bentley K. I. Suppression of atherogenesis in cholesterol-fed rabbit treated with nifedipine. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1366–1369. doi: 10.1172/JCI110384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. Cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages: stimulation by beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed animals of several species. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):970–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito M., Kuzuya F., Asai K., Shibate K., Yoshimine N. Ineffectiveness of Ca2+-antagonists nicardipine and diltiazem on experimental atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;51(2-3):343–344. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. C., Go K. J., Heider J. G., Rothblat G. H. Selective inhibition of acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase by compound 58-035. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):815–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau J. L., Parmley W. W., Stevens J., Wikman-Coffelt J., Sievers R., Mahley R. W., Havel R. J. Verapamil suppresses atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Jun;1(6):1453–1460. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):535–537. doi: 10.1038/303535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding M. Activators and inactivators of Ca++ channels: new perspectives. J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct-Dec;16(4):319–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stender S., Stender I., Nordestgaard B., Kjeldsen K. No effect of nifedipine on atherogenesis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):389–394. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano M., Nakashima Y., Matsushima T., Takahara K., Takasugi M., Kuroiwa A., Koide O. Suppression of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits by diltiazem injection. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):237–241. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. L., Nagel B., Churchill V., Whyte M. A., Smith D. L., Mahmud I., Puppione D. L. Antiatherosclerotic effects of nicardipine and nifedipine in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):250–255. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


