Abstract
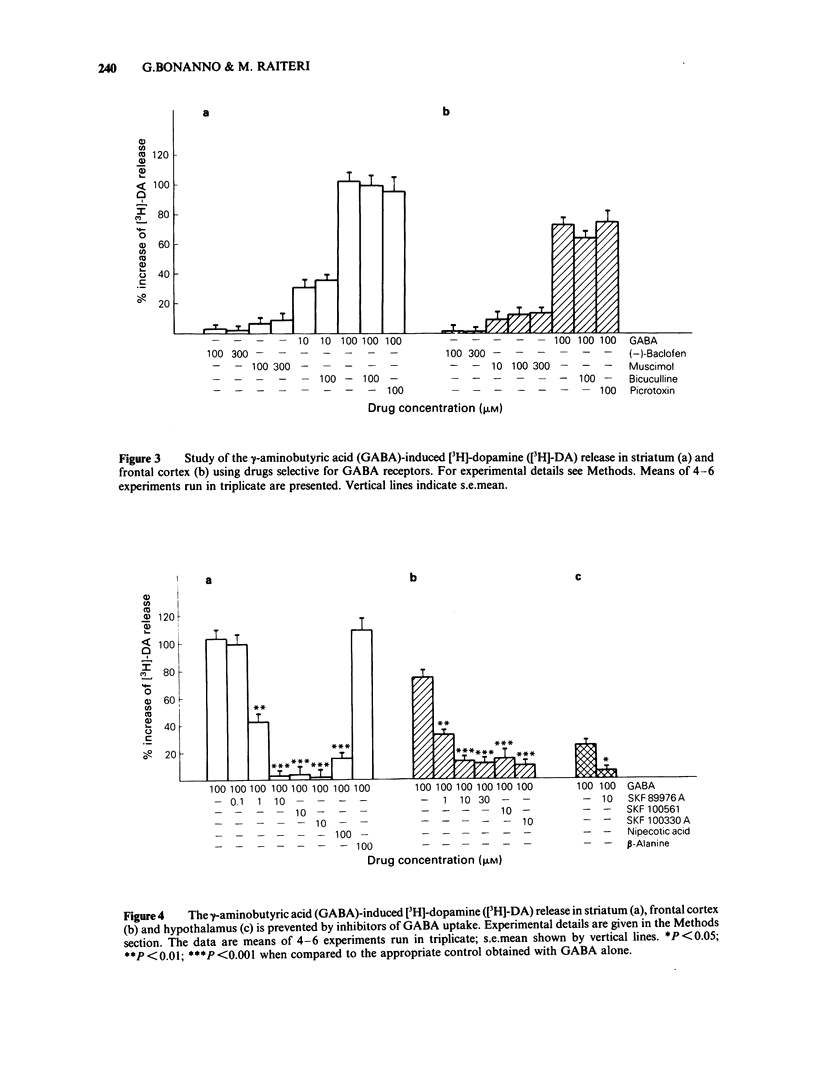
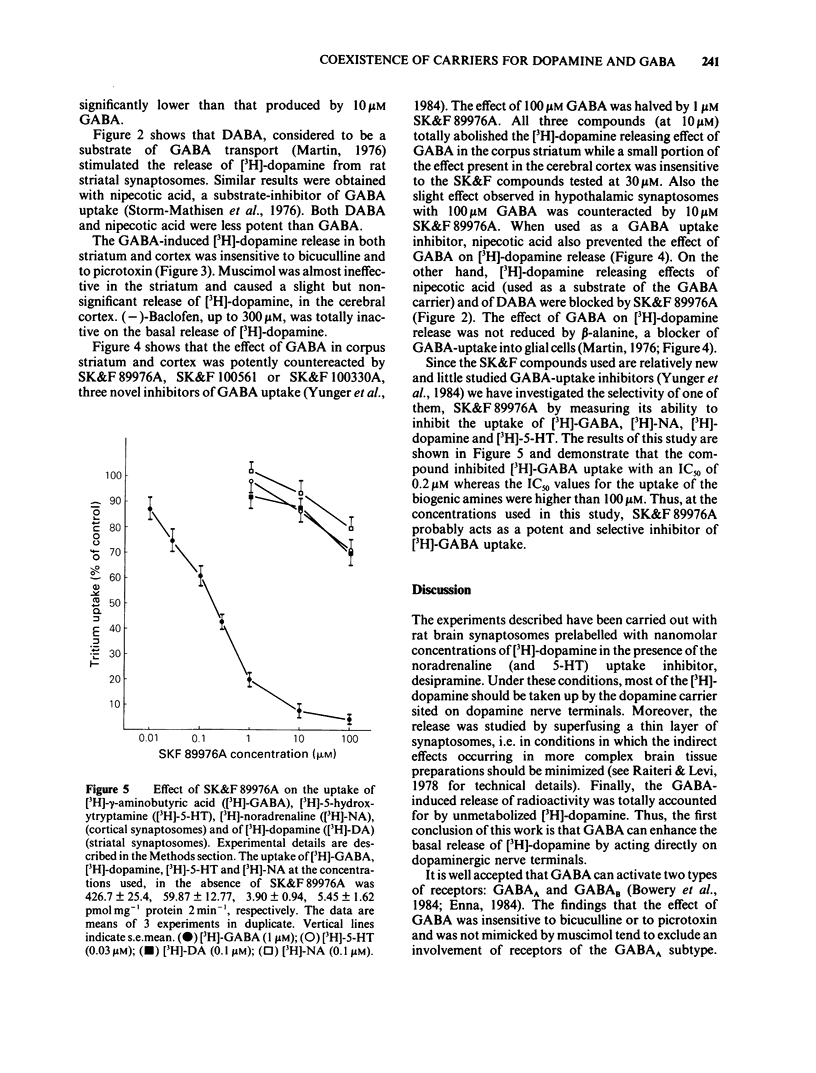
The ability of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) to affect the release of [3H]-dopamine in rat brain synaptosomes prepared from corpus striatum, frontal cortex and hypothalamus and prelabelled with the radioactive catecholamine in the presence of desipramine was examined. GABA (10-300 microM) increased in a concentration-dependent way the basal release of [3H]-dopamine from striatum and cortical synaptosomes; however, its effect was much less pronounced in hypothalamic nerve terminals. 2,4-Diaminobutyric acid (DABA) mimicked GABA although less potently. Neutral amino acids such as leucine, valine or alpha-aminoisobutyric acid (100-300 microM) did not affect or increased minimally the release of [3H]-dopamine. The GABA-induced [3H]-dopamine release was not prevented by the GABAA-receptor antagonists, bicuculline or picrotoxin. The GABAA-receptor agonist, muscimol (10-300 microM), displayed only a very weak, not significant, enhancing effect on [3H]-dopamine release. The GABAB-receptor agonist (-)-baclofen (100 or 300 microM) had no effect. Three novel and selective inhibitors of GABA uptake, N-(4,4-diphenyl-3-butenyl)-nipecotic acid (SK&F 89976A), N-(4,4-diphenyl-3-butenyl)-guvacine (SK&F 100330A) and N-(4,4-diphenyl-3-butenyl)-homo-beta-proline (SK&F 100561) potently counteracted the enhancing effect of GABA on [3H]-dopamine release. Nipecotic acid also reduced the effect of GABA. It is concluded that carriers for the uptake of dopamine and GABA may coexist on the same nerve terminal in the rat brain.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonanno G., Raiteri M. GABA enhances acetylcholine release from hippocampal nerve endings through a mechanism blocked by a GABA uptake inhibitor. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Oct 20;70(3):360–363. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesselet M. F. Presynaptic regulation of neurotransmitter release in the brain: facts and hypothesis. Neuroscience. 1984 Jun;12(2):347–375. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis C., Cox B. GABA enhancement of [3H]dopamine release from slices of rat striatum: dependence on slice size. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 26;70(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorguieff M. F., Kemel M. L., Glowinski J., Besson M. J. Stimulation of dopamine release by GABA in rat striatal slices. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 6;139(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Anderson D. J., Rustad D. G. Glial contamination of synaptosomal fractions. Brain Res. 1976 Jan 16;101(2):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. Catecholamine uptake processes. Br Med Bull. 1973 May;29(2):130–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. The Ferrier Lecture, 1983. Amino acids and peptides: fast and slow chemical signals in the nervous system? Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):245–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Angelini F., Levi G. A simple apparatus for studying the release of neurotransmitters from synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;25(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Bonanno G., Marchi M., Maura G. Is there a functional linkage between neurotransmitter uptake mechanisms and presynaptic receptors? J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Dec;231(3):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann W., Zumstein A., Starke K. Gamma-aminobutyric acid can both inhibit and facilitate dopamine release in the caudate nucleus of the rabbit. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):961–969. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Lane J. D., Shea P. A., McBride W. J., Aprison M. H. A method for concurrent measurement of picomole quantities of acetylcholine, choline, dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, tryptophan, tyrosine, glycine, aspartate, glutamate, alanine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid in single tissue samples from different areas of rat central nervous system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):149–169. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. S. GABA potentiates potassium-stimulated 3H-dopamine release from slices of rat substantia nigra and corpus striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Apr 1;48(3):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. S. GABA-mediated potentiation of amine release from nigrostriatal dopamine neurones in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jan 15;53(3):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Den Breejen E. J., Mulder A. H. GABA modulates the release of dopamine and acetylcholine from rat caudate nucleus slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 15;57(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunger L. M., Fowler P. J., Zarevics P., Setler P. E. Novel inhibitors of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) uptake: anticonvulsant actions in rats and mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


