Abstract
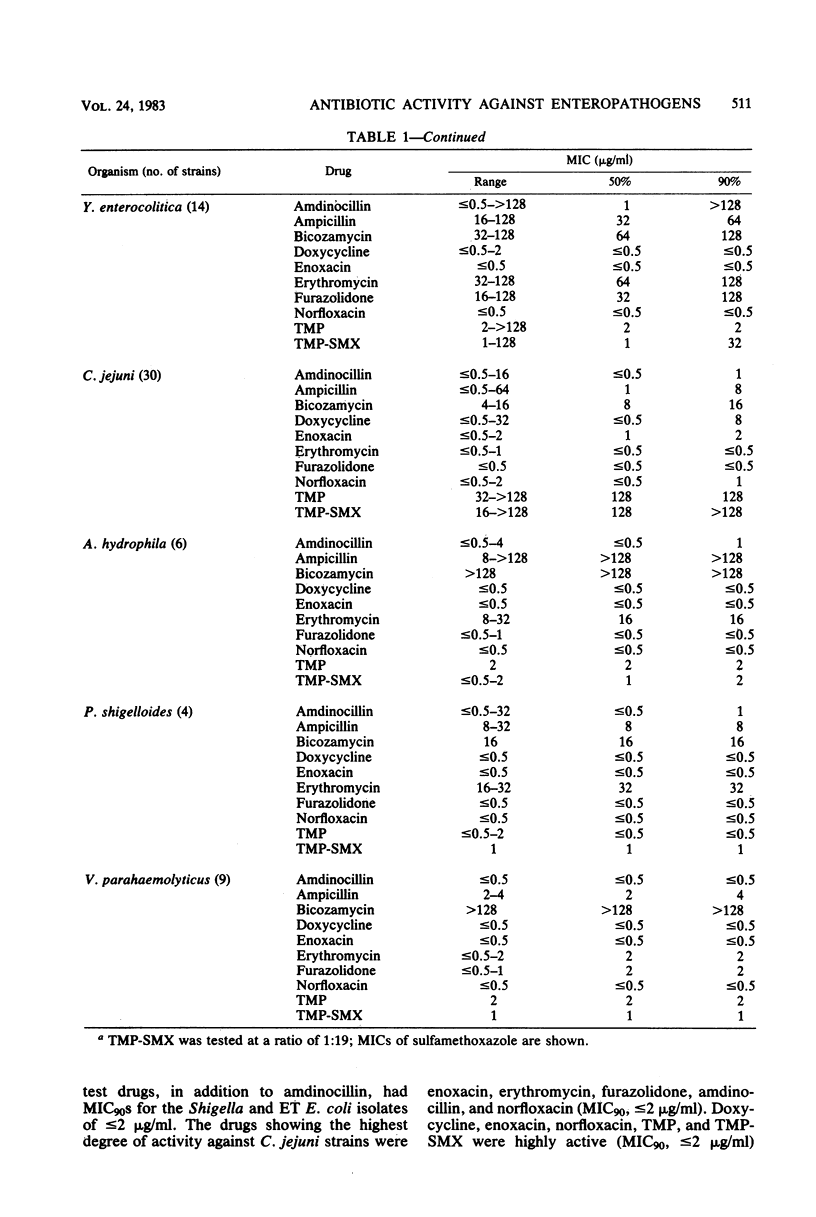
The in vitro susceptibilities of 50 strains of Salmonella spp., 80 strains of Shigella spp., and 50 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, 14 Yersinia enterocolitica, 6 Aeromonas hydrophila, 4 Plesiomonas shigelloides, 9 Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and 30 Campylobacter jejuni strains that were recently isolated from worldwide sources were determined for 10 antimicrobial agents. The antimicrobial agents tested included ampicillin, bicozamycin, doxycycline, enoxacin (CI-919), erythromycin, furazolidone, amdinocillin, norfloxacin, trimethoprim, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Ampicillin resistance occurred frequently in strains of Salmonella and Shigella spp. and enterotoxigenic E. coli strains. The most active agents against all of the bacteria tested were enoxacin and norfloxacin. Furazolidone and amdinocillin were also highly active against the majority of strains. Trimethoprim and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were inhibitory at low concentrations against all test except C. jejuni isolates. The in vitro results of this study confirm the high prevalence of bacterial resistance to ampicillin. However, this work also identifies four antimicrobial agents, enoxacin, furazolidone, norfloxacin, and amdinocillin, that would be appropriate for further testing in clinical trials.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders B. J., Lauer B. A., Paisley J. W., Reller L. B. Double-blind placebo controlled trial of erythromycin for treatment of Campylobacter enteritis. Lancet. 1982 Jan 16;1(8264):131–132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aserkoff B., Bennett J. V. Effect of antibiotic therapy in acute salmonellosis on the fecal excretion of salmonellae. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 18;281(12):636–640. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909182811202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barada F. A., Jr, Guerrant R. L. Sulfamethoxazole- trimethoprim versus ampicillin in treatment of acute invasive diarrhea in adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):961–964. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck G. E., Kelly M. T. Susceptibility testing of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, using broth microdilution panels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):274–277. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. A., Dupont H. L., Goldschmidt M. C. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of shigellae isolated in Houston, Texas, in 1974. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):288–291. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Galindo E., Evans D. G., Cabada F. J., Sullivan P., Evans D. J., Jr Prevention of travelers' diarrhea with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim alone. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jan;84(1):75–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Olarte J., Evans D. G., Pickering L. K., Galindo E., Evans D. J. Comparative susceptibility of latin american and united states students to enteric pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1520–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Reves R. R., Galindo E., Sullivan P. S., Wood L. V., Mendiola J. G. Treatment of travelers' diarrhea with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and with trimethoprim alone. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 30;307(14):841–844. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209303071401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Hinton L. V., Kusmiesz H. T., Sladoje M. Comparison of orally absorbable and nonabsorbable antibiotics in shigellosis. A double-blind study with ampicillin and neomycin. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):708–720. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Weinberger M. H., Grim C. E., Fineberg N. S., Miller J. Z. Sodium sensitivity in normotensive human subjects. Ann Intern Med. 1983 May;98(5 Pt 2):758–762. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-5-758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Gangarosa E. J., Cáceres A., Perera D. R., Mejicanos M. L. Epidemic Shiga bacillus dysentery in Central America. I. Etiologic investigations in Guatemala, 1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):170–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D., Kusmiesz H., Jackson L. H., Woodman E. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy for shigellosis. JAMA. 1976 Mar 22;235(12):1239–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. L., Koster F. T., Alam A. K., Islam M. R. Nutritional status: a determinant of severity of diarrhea in patients with cholera. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):8–14. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Alam AKMJ, Islam M. R. Effects of doxycycline in actively purging cholera patients: a double-blind clinical trial. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):610–612. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Kaminsky D. C., Sack R. B., Itotia J. N., Arthur R. R., Kapikian A. Z., Orskov F., Orskov I. Prophylactic doxycycline for travelers' diarrhea. Results of a prospective double-blind study of Peace Corps volunteers in Kenya. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 6;298(14):758–763. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804062981402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



