Abstract
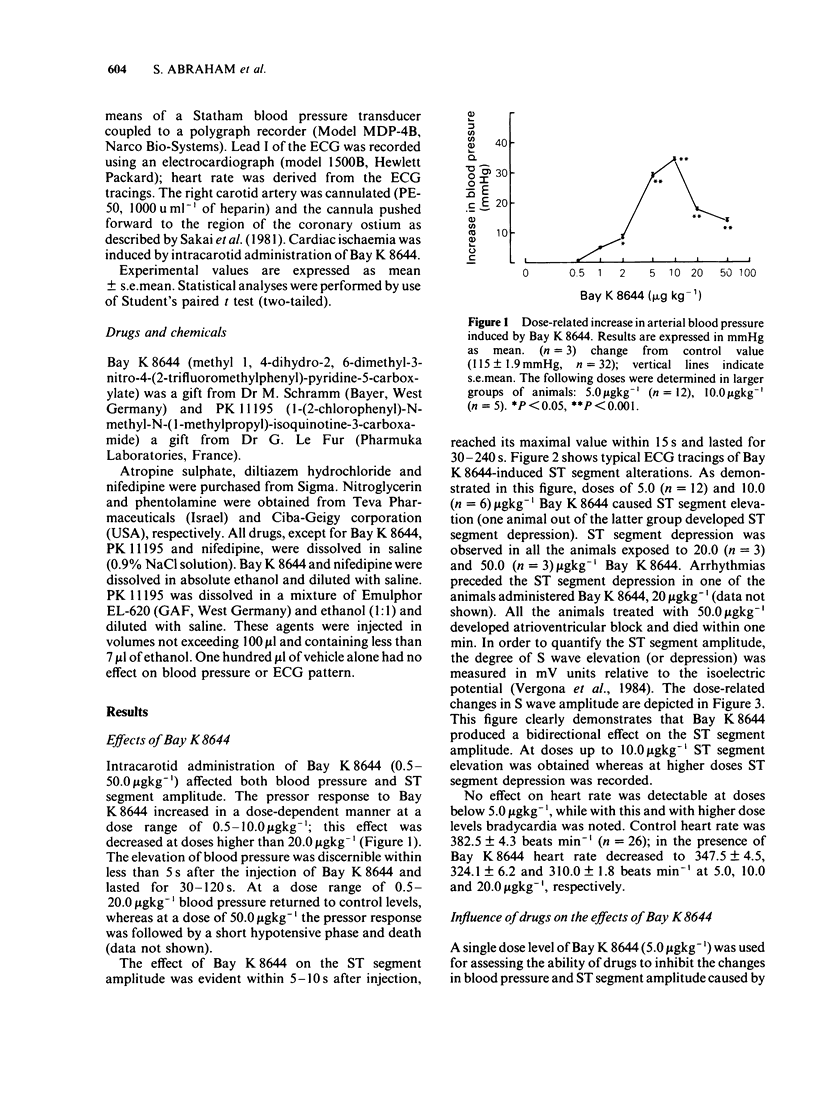
1. The effects of intracarotid administration of Bay K 8644 on the ECG pattern along with their reversal by antianginal drugs were investigated in anaesthetized rats. 2. Intracarotid injections of Bay K 8644 (0.5-50.0 micrograms kg-1) produced a dose-related transient increase in systemic blood pressure. 3. The pressor response was accompanied by ST segment elevation (0.5-10.0 micrograms kg-1), ST segment depression concomitant with the occurrence of arrhythmias (20.0 micrograms kg-1), or A-V block (50.0 micrograms kg-1). 4. ST segment elevation reached its maximal value within 15 s and could be observed for 30-240 s. 5. The increase in blood pressure was immediate (within 5 s) and short lasting (30-120 s). After the initial increase it returned to control levels (0.5-20.0 micrograms kg-1) or dropped below (50.0 micrograms kg-1). 6. The ST segment elevation caused by 5.0 micrograms kg-1 Bay K 8644 (submaximal dose) was blocked by antianginal drugs (e.g. nitroglycerin, nifedipine and diltiazem) and by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor antagonist PK 11195. However, the pressor response was not blocked by any of the drugs used. 7. ST segment elevation (or depression) induced by intracarotid administration of Bay K 8644 provides a useful tool for the evaluation of potential antianginal drugs.
Full text
PDF
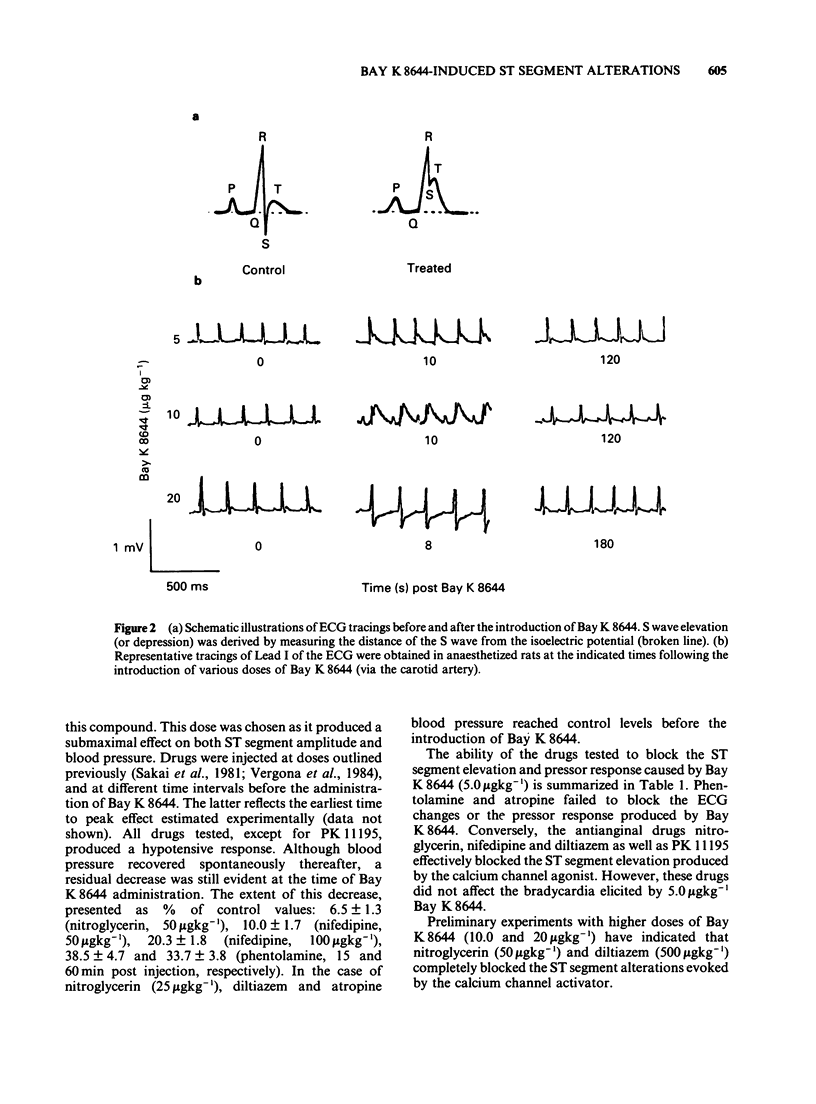
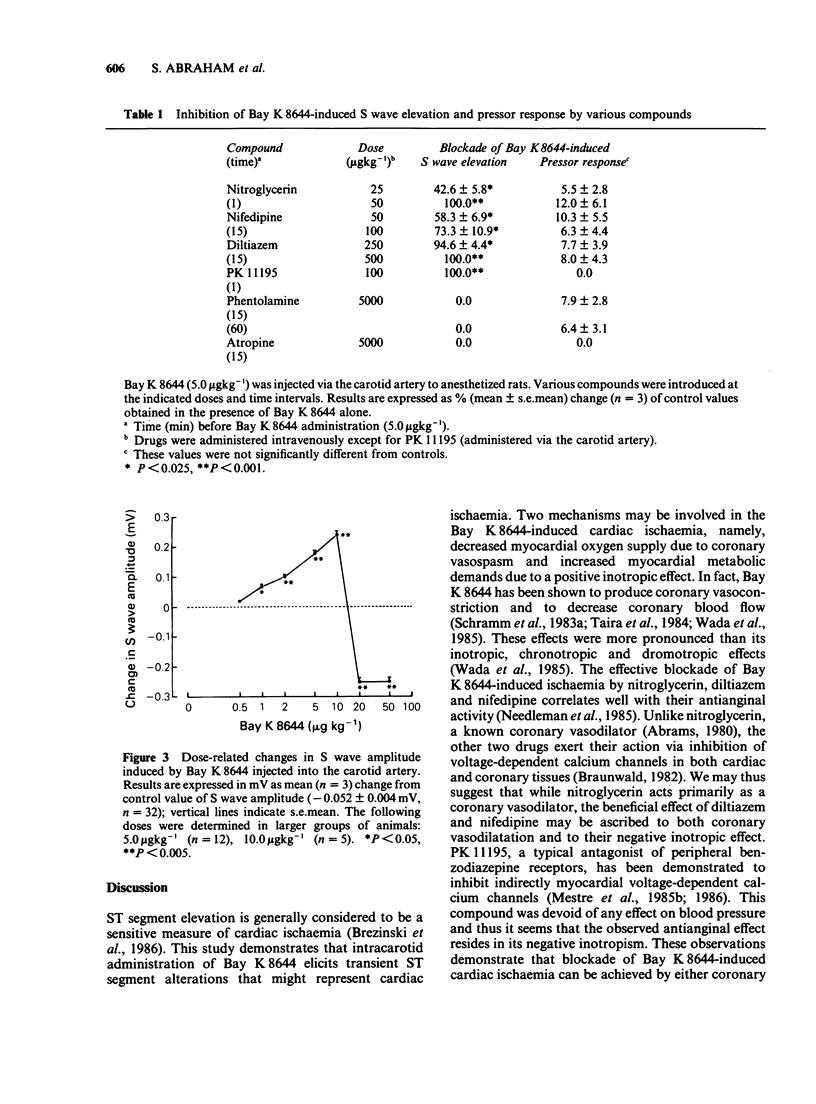


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S., Cantor E. H., Spector S. Atropine lowers blood pressure in normotensive rats through blockade of alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 19;28(3):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90739-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams J. Nitroglycerin and long-acting nitrates. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 29;302(22):1234–1237. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005293022205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunwald E. Mechanism of action of calcium-channel-blocking agents. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 23;307(26):1618–1627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212233072605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezinski M. E., Darius H., Lefer A. M. Cardioprotective actions of a new calcium channel blocker in acute myocardial ischemia. Arzneimittelforschung. 1986 Mar;36(3):464–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubé G. P., Baik Y. H., Schwartz A. Effects of a novel calcium channel agonist dihydropyridine analogue, Bay k 8644, on pig coronary artery: biphasic mechanical response and paradoxical potentiation of contraction by diltiazem and nimodipine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):377–389. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198503000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finet M., Godfraind T., Khoury G. The positive inotropic action of the nifedipine analogue, Bay K 8644, in guinea-pig and rat isolated cardiac preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franckowiak G., Bechem M., Schramm M., Thomas G. The optical isomers of the 1,4-dihydropyridine BAY K 8644 show opposite effects on Ca channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 15;114(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan V., Park L. E., Triggle C. R. The effect of the calcium channel agonist, Bay K-8644 on human vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):447–451. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Kayser M., Schramm M., Taniel R., Thomas G. Cardiovascular effects of the calcium-agonistic dihydropyridine BAY K 8644 in conscious dogs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1985 Oct;277(2):203–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Sato Y., Taira N. Similarity and dissimilarity of the vasoconstrictor effects of Bay K 8644 on coronary, femoral, mesenteric and renal circulations of dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefer A. M., Whitney C. C., 3rd, Hock C. E. Mechanism of the pressor effect of the calcium agonist, BAY k 8644, in the intact rat. Pharmacology. 1986;32(4):181–189. doi: 10.1159/000138168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestre M., Bouetard G., Uzan A., Gueremy C., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Le Fur G. PK 11195, an antagonist of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors, reduces ventricular arrhythmias during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in the dog. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun 7;112(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestre M., Carriot T., Belin C., Uzan A., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Doble A., Le Fur G. Electrophysiological and pharmacological evidence that peripheral type benzodiazepine receptors are coupled to calcium channels in the heart. Life Sci. 1985 Jan 28;36(4):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestre M., Carriot T., Néliat G., Uzan A., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Doble A., Le Fur G. PK 11195, an antagonist of peripheral type benzodiazepine receptors, modulates Bay K8644 sensitive but not beta- or H2-receptor sensitive voltage operated calcium channels in the guinea pig heart. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 28;39(4):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen E. Comparison of effects of a new dihydropyridine, Bay K 8644, and nifedipine on spontaneous mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):383–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen E., Nyborg N. C., Kazda S. A novel 1,4 dihydropyridine, BAY K 8644, with contractile effects on vascular smooth muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1985 Jan;56(1):44–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1985.tb01251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Akima M., Aono J. Evaluation of drug effects in a new experimental model of angina pectoris in the intact anesthetized rat. J Pharmacol Methods. 1981 Jun;5(4):325–336. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(81)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Wada Y., Taira N. Differential effects of Bay k 8644, a presumed calcium channel activator, on sinoatrial nodal and ventricular automaticity of the dog heart. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;326(2):190–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00517319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Activation of calcium channels by novel 1,4-dihydropyridines. A new mechanism for positive inotropics or smooth muscle stimulants. Arzneimittelforschung. 1983;33(9):1268–1272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):535–537. doi: 10.1038/303535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. M., Swamy V. C., Triggle D. J. Calcium channel activation in vascular smooth muscle by BAY K 8644. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1401–1410. doi: 10.1139/y84-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N., Wada Y., Satoh K. Is antagonism by Bay k 8644 of the negative dromotropic effect of nifedipine pharmacological? J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergona R. A., Herrott C., Garippa R., Hirkaler G. Mechanisms of methacholine-induced coronary vasospasm in an experimental model of variant angina in the anesthetized rat. Life Sci. 1984 Oct 29;35(18):1877–1884. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada Y., Satoh K., Taira N. Cardiovascular profile of Bay K 8644, a presumed calcium channel activator, in the dog. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;328(4):382–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00692905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



