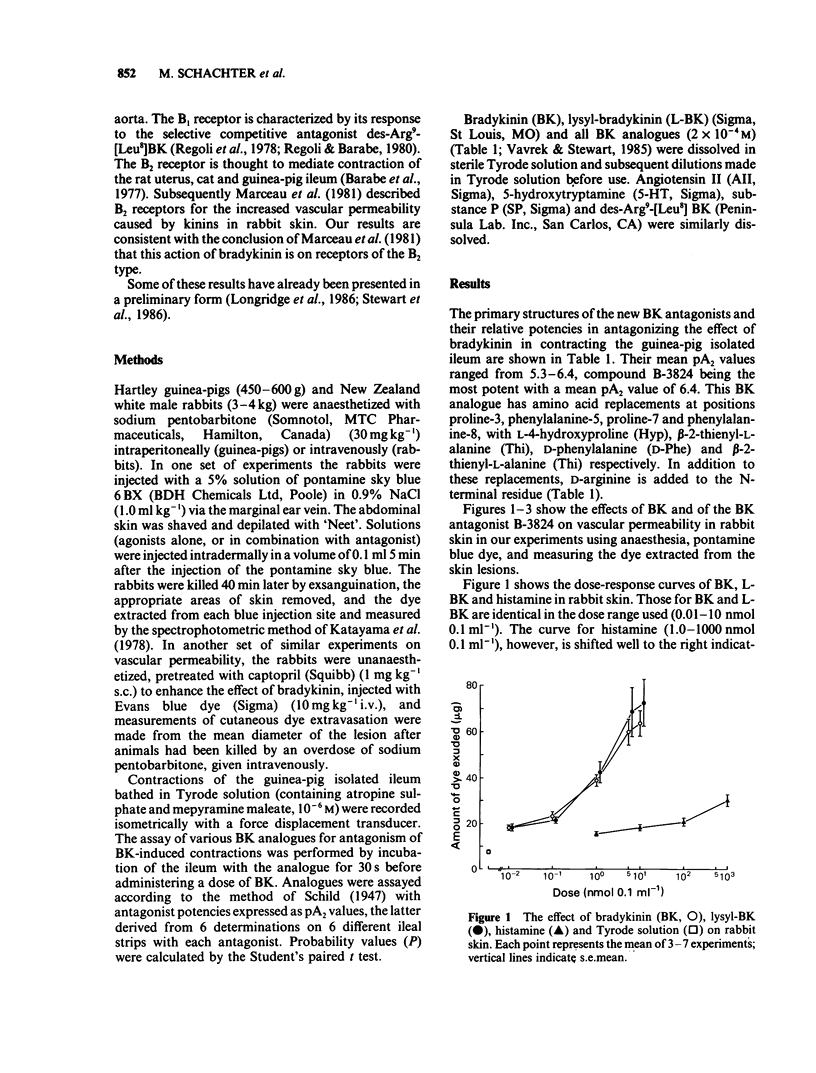
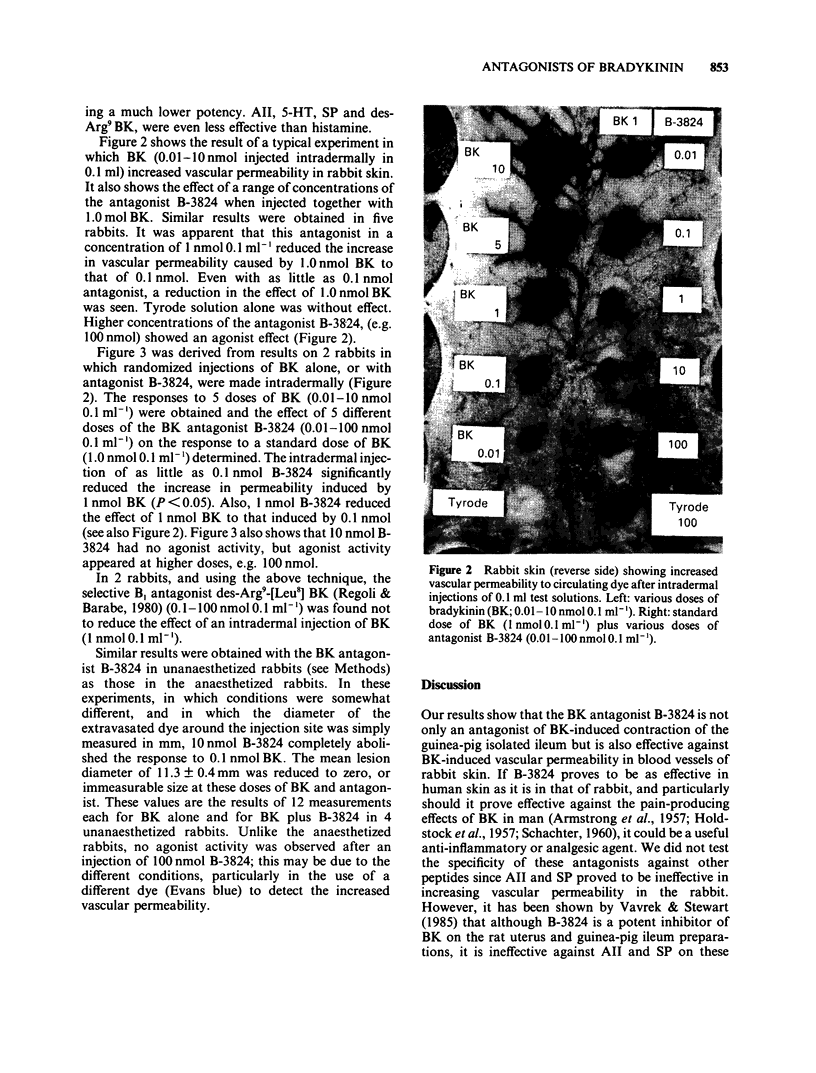
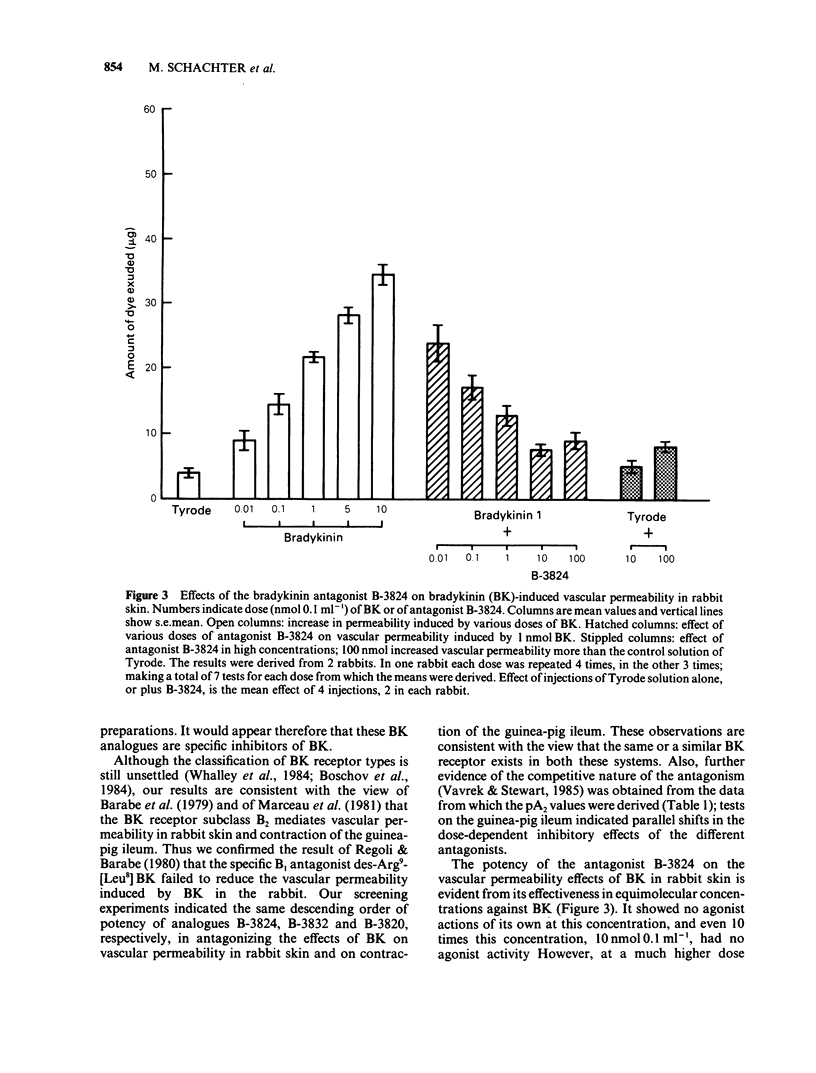
Abstract
1 A new synthetic bradykinin analogue was found to be an antagonist of bradykinin-induced vascular permeability in rabbit skin. It was effective in equimolar concentrations. 2 These analogues also antagonized the action of bradykinin in contracting the guinea-pig isolated ileum. The mean pA2 values of five different antagonists ranged from 5.3-6.4 respectively, on this preparation. 3 Our observations, together with those of others suggest that these antagonists act on the same receptor types, viz., B2, in rabbit blood vessels and in smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum. 4 Our results support the view that the way is now promising for the synthesis of potent specific antagonists of bradykinin for experimental and therapeutic use.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D., JEPSON J. B., KEELE C. A., STEWART J. W. Pain-producing substance in human inflammatory exudates and plasma. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):350–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHOOLA K. D., CALLE J. D., SCHACHTER M. The effect of bradykinin, serum kallikrein and other endogenous substances on capillary permeability inthe guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;152:75–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISSET G. W., LEWIS G. P. A spectrum of pharmacological activity in some biologically active peptides. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Aug;19:168–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabé J., Marceau F., Thériault B., Drouin J. N., Regoli D. Cardiovascular actions of kinins in the rabbit. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;57(1):78–91. doi: 10.1139/y79-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschcov P., Paiva A. C., Paiva T. B., Shimuta S. I. Further evidence for the existence of two receptor sites for bradykinin responsible for the diphasic effect in the rat isolated duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabé J., Drouin J. N., Regoli D., Park W. K. Receptors for bradykinin in intestinal and uterine smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;55(6):1270–1285. doi: 10.1139/y77-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSTOCK D. J., MATHIAS A. P., SCHACHTER M. A comparative study of kinin, kallidin, and bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Jun;12(2):149–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama S., Shionoya H., Ohtake S. A new method for extraction of extravasated dye in the skin and the influence of fasting stress on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in guinea pigs and rats. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(2):89–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Knap M., Regoli D. Pharmacological characterization of the vascular permeability enhancing effects of kinins in the rabbit skin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;59(9):921–926. doi: 10.1139/y81-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Marceau F., Barabé J. De novo formation of vascular receptors for bradykinin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;56(4):674–677. doi: 10.1139/y78-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Tanaka K., Harada Y., Ueno A., Katori M. Activation of plasma kallikrein-kinin system and its significant role in pleural fluid accumulation of rat carrageenin-induced pleurisy. Inflammation. 1983 Jun;7(2):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00917817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Competitive antagonists of bradykinin. Peptides. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley E. T., Sampaio C. A., Fritz H., Edwards G. The effect of kinins on paw oedema and uterus in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;328(2):202–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00512073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]