Abstract
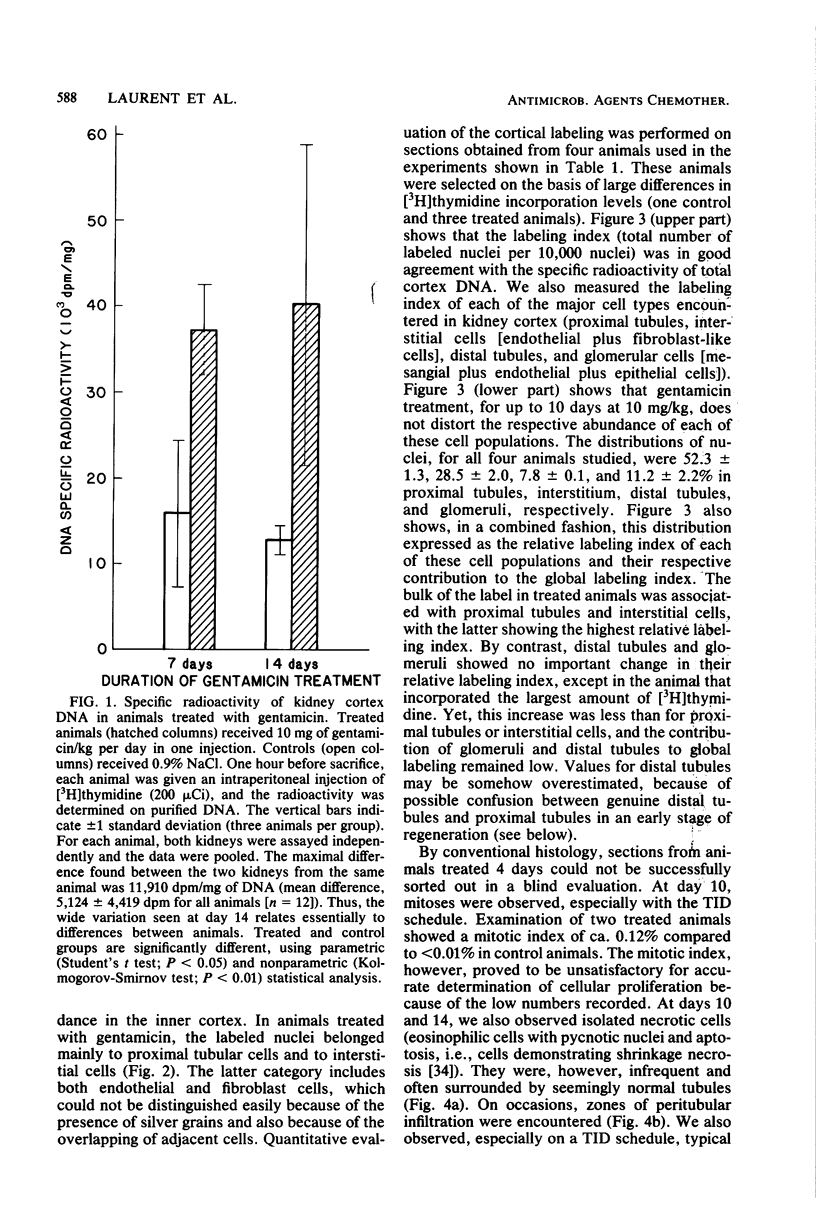
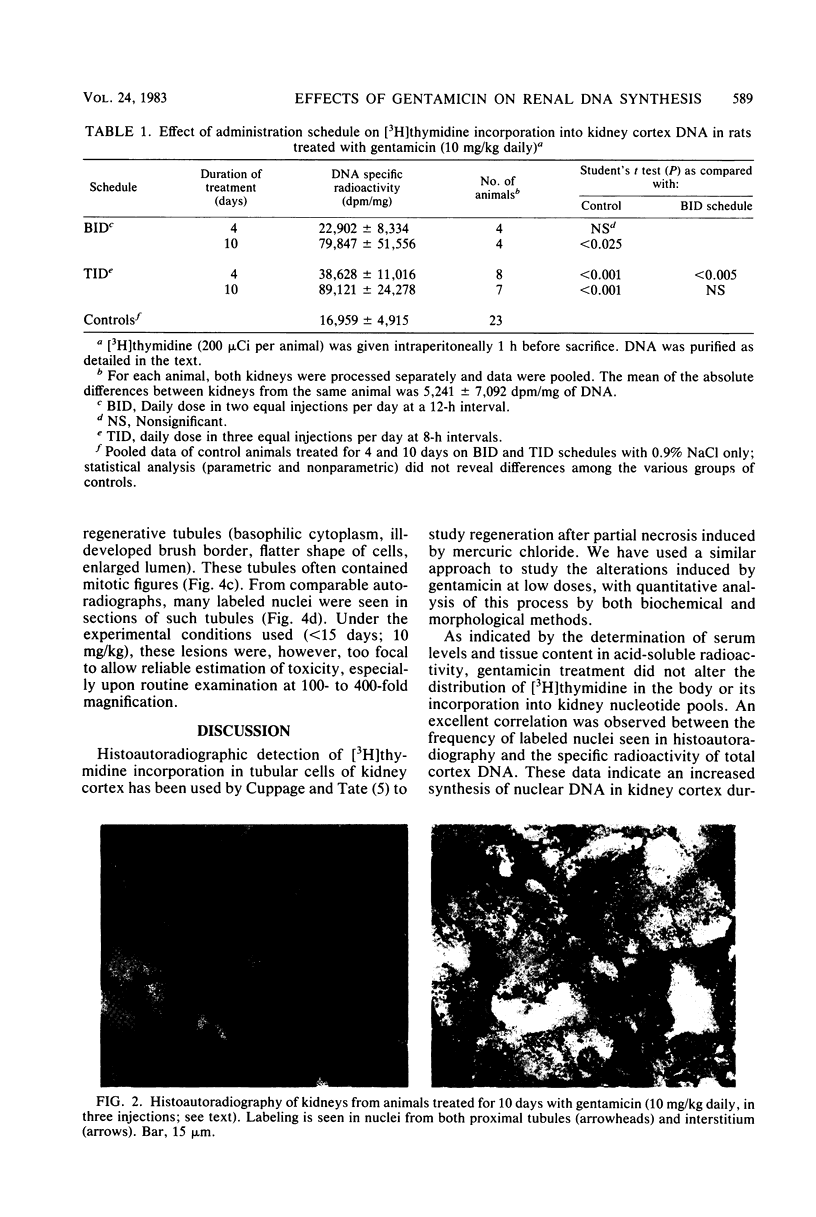
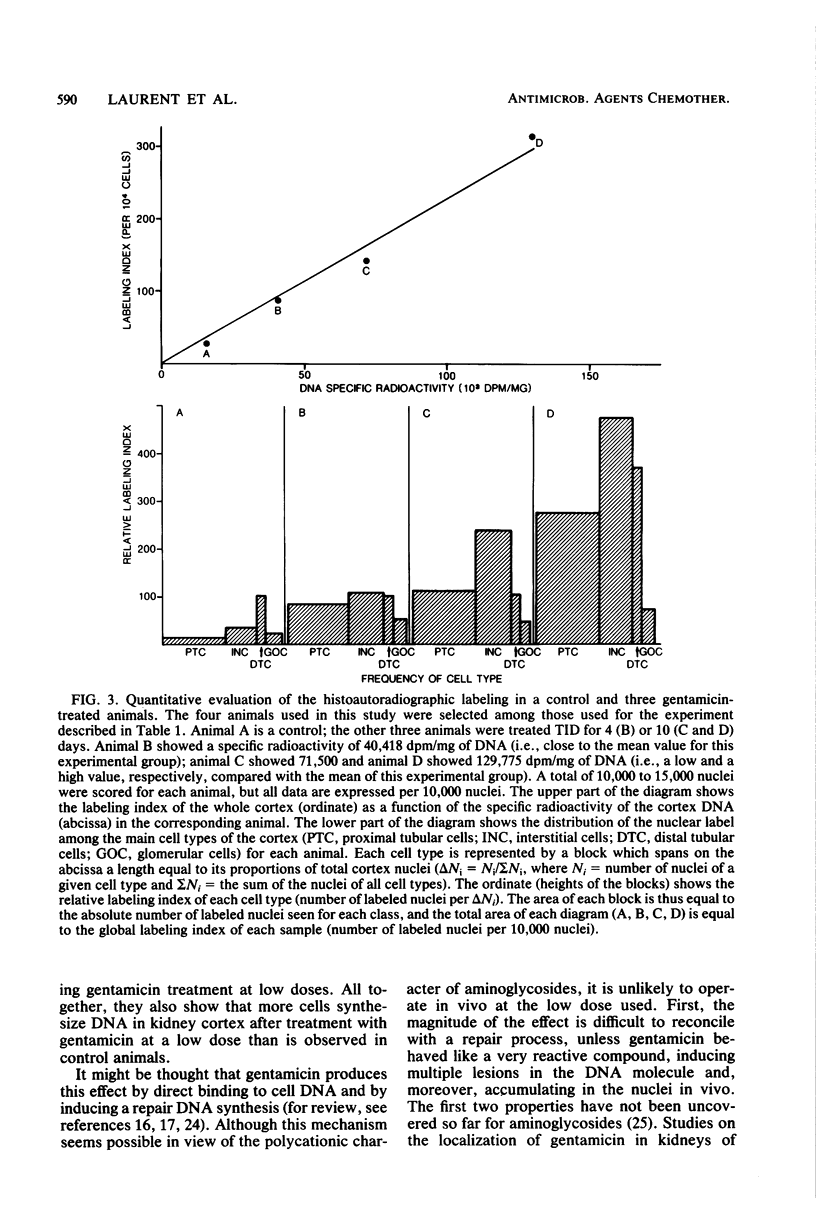
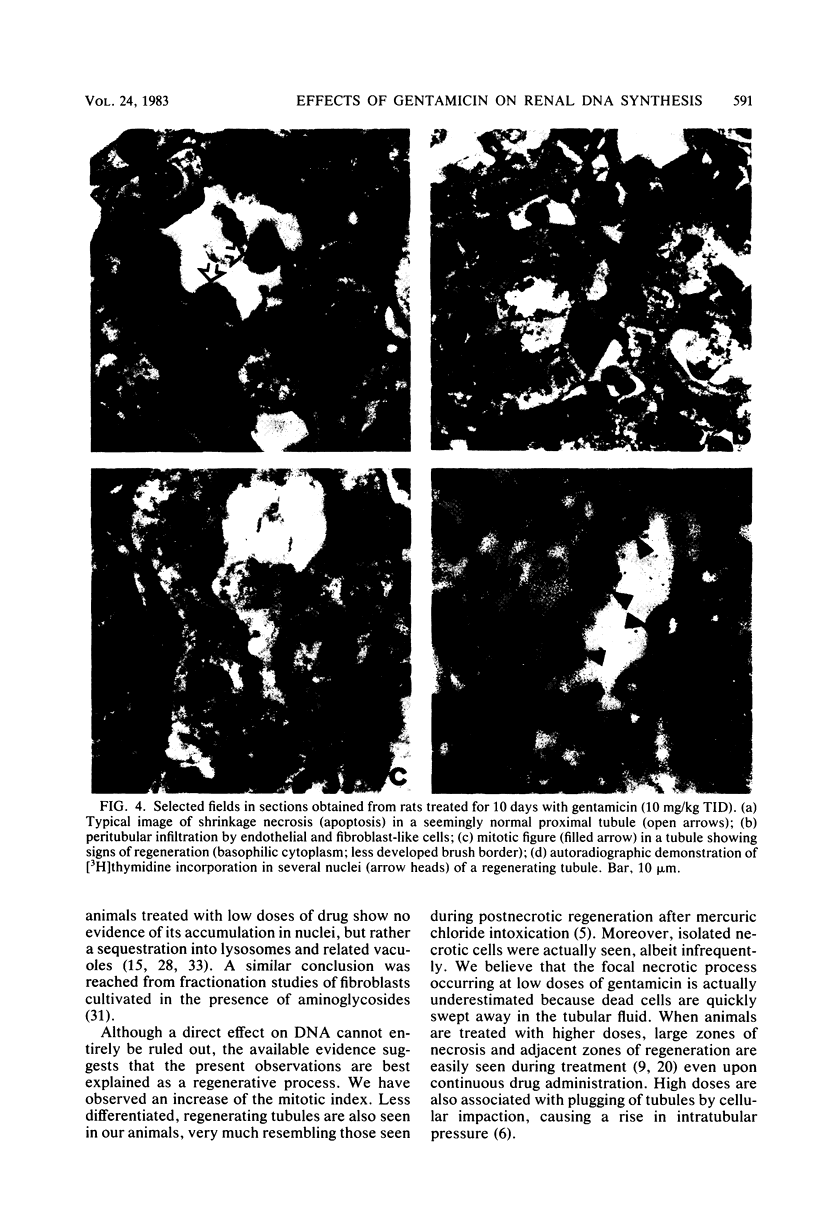
Kidney cortex DNA synthesis was studied in female rats treated with a low dose of gentamicin (10 mg/kg) up to 14 days. Synthesis was measured by incorporation of [3H]thymidine into DNA 1 h after intraperitoneal injection of the labeled precursor (200 muCi per animal). Gentamicin given in one injection per day resulted in a greater incorporation of [3H]thymidine into DNA after both 7 and 14 days of treatment as compared with control animals. When the daily dose was divided into three equal injections given at 8-h intervals, a statistically significant increase in thymidine incorporation was observed as early as 4 days after starting gentamicin administration. Excellent agreement was found between DNA specific radioactivity and kidney cortex nuclear labeling, as measured by histoautoradiography. The greatest amount of [3H]thymidine incorporation occurred within proximal tubular cells and interstitial cells. We conclude that a finite duration of gentamicin treatment at low dosage induces an increased DNA synthesis in vivo in rat kidney cortex. We suggest that this reaction results from cellular proliferation and could reflect a regenerative process after focal necrosis induced by gentamicin at low doses. The demonstrated early increase in DNA synthesis could be a useful tool to measure kidney cortex alterations caused by various aminoglycosides at low, therapeutic doses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel G. B., Neu H. C. Gentamicin in 1978. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):528–538. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Gilbert D. N., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. The influence of dosage regimen on experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: dissociation of peak serum levels from renal failure. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppage F. E., Setter K., Sullivan P., Reitzes E. J., Melnykovych A. O. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity. II. Physiological, biochemical and morphological effects of prolonged administration to rats. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977 Jun 24;24(2):121–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppage F. E., Tate A. Repair of the nephron following injury with mercuric chloride. Am J Pathol. 1967 Sep;51(3):405–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong I. W., Fenton R. S., Bird R. Comparative toxicity of gentamicin versus tobramycin: a randomized prospective study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):81–88. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame P. T., Phair J. P., Watanakunakorn C., Bannister T. W. Pharmacologic factors associated with gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):952–956. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C., Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Reger K., Porter G. A. Reversibility of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats: recovery during continuous drug administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jan;160(1):99–103. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hottendorf G. H., Barnett D., Gordon L. L., Christensen E. F., Madissoo H. Nonparallel nephrotoxicity dose-response curves of aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1024–1028. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hottendorf G. H., Gordon L. L. Comparative low-dose nephrotoxicities of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton D. C., Hartnett M., Campbell-Boswell M., Porter G., Bennett W. A light and electron microscopic analysis of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):589–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes H. D., Weinberg J. M., Knauss T. C. Clinical and pathophysiologic aspects of aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Am J Kidney Dis. 1982 Jul;2(1):5–29. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(82)80039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josepovitz C., Pastoriza-Munoz E., Timmerman D., Scott M., Feldman S., Kaloyanides G. J. Inhibition of gentamicin uptake in rat renal cortex in vivo by aminoglycosides and organic polycations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Erdmann G., Habermann E. The renal handling of polybasic drugs. 1. Gentamicin and aprotinin in intact animals. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00505080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosek J. C., Mazze R. I., Cousins M. J. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Carlier M. B., Rollman B., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P. Mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis: in vitro and in vivo studies with gentamicin and amikacin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3861–3870. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Rankin L. I., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N. Recovery from aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity with continued drug administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):284–287. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. The determination of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1966;14:113–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470110324.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter G. A., Bennett W. M. Nephrotoxic acute renal failure due to common drugs. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F1–F8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Bloxham D. D., Thompson W. L. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin given once daily or continuously in dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4 (Suppl A):85–101. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_a.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. J. Cellular responses to carcinogen-induced DNA damage and the role of DNA repair. Br Med Bull. 1980 Jan;36(1):25–31. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schentag J. J., Plaut M. E., Cerra F. B. Comparative nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin: pharmacokinetic and clinical studies in 201 patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):859–866. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N., Ichikawa I., Rennke H. G., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Pathophysiology of altered glomerular function in aminoglycoside-treated rats. Kidney Int. 1981 Feb;19(2):288–296. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Lipsky J. J., Laskin O. L., Hellmann D. B., Mellits E. D., Longstreth J., Lietman P. S. Double-blind comparison of the nephrotoxicity and auditory toxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 15;302(20):1106–1109. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005153022002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P., Trouet A. The uptake and intracellular accumulation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in lysosomes of cultured rat fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 15;27(4):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen R. P., Batuman V., Cheeks C., Marquet E., Sobel H. Transport of gentamicin in rat proximal tubule. Lab Invest. 1983 Feb;48(2):212–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rougemont D., Oeschger A., Konrad L., Thiel G., Torhorst J., Wenk M., Wunderlich P., Brunner F. P. Gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in the rat. Effect of dehydration, DOCA-saline and furosemide. Nephron. 1981;29(3-4):176–184. doi: 10.1159/000182352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Urk H., Malamud D., Soler-Montesinos L., Malt R. A. Compensatory hyperplasia with increasing loss of renal mass. Lab Invest. 1978 Jun;38(6):674–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]