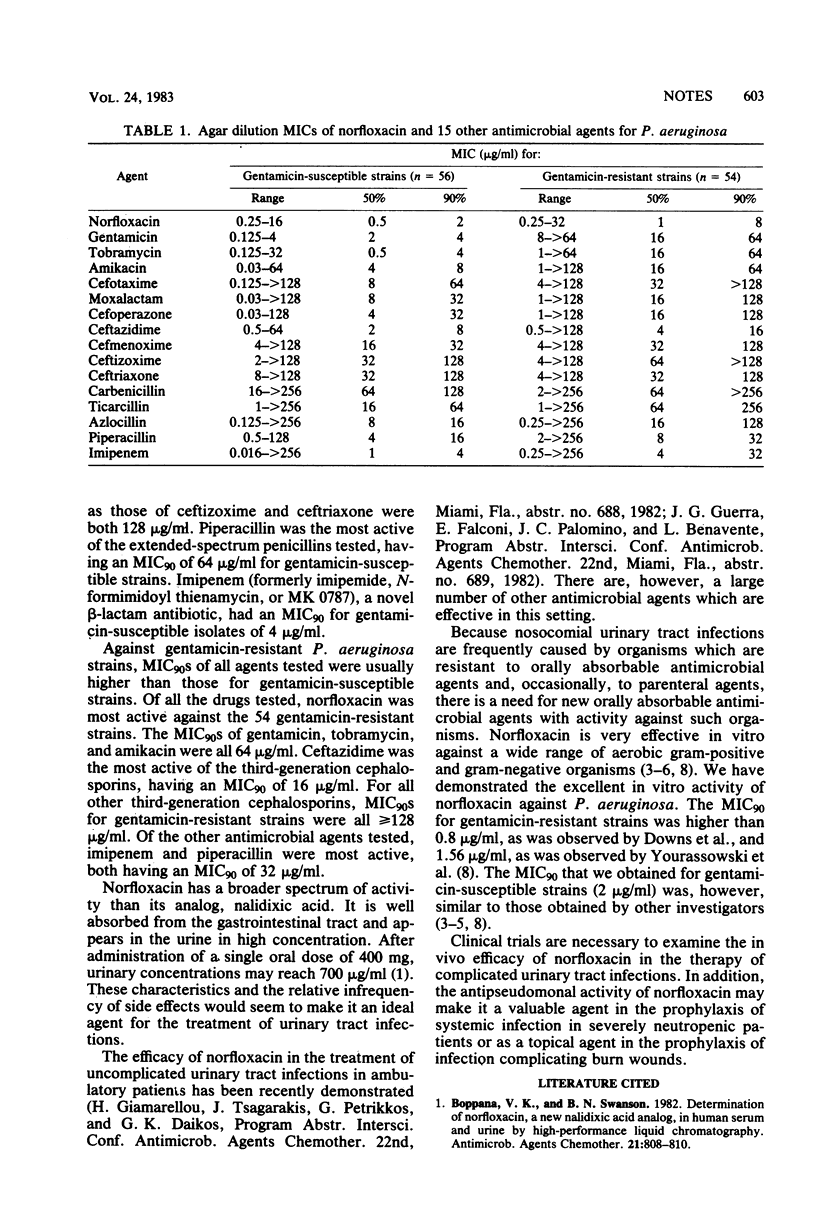
Abstract
We compared the activity of norfloxacin (MK-0366), a new orally absorbable derivative of naladixic acid, with those of other antipseudomonal agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Norfloxacin was the most active against both gentamicin-susceptible and gentamicin-resistant strains, having 90% minimal inhibitory concentrations of 2 and 8 micrograms/ml, respectively. This excellent in vitro activity may make norfloxacin effective for oral therapy of P. aeruginosa urinary tract infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boppana V. K., Swanson B. N. Determination of norfloxacin, a new nalidixic acid analog, in human serum and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):808–810. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Waterworth P. M. Carbenicillin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical material. Br Med J. 1969 Jul 19;3(5663):141–143. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5663.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs J., Andriole V. T., Ryan J. L. In vitro activity of MK-0366 against clinical urinary pathogens including gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):670–672. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. Y., Gruninger R. P., Nelson S. M., Klicker R. E. Comparative in vitro activity of norfloxacin (MK-0366) and ten other oral antimicrobial agents against urinary bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):848–851. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom S. W., Matthews J., Amphlett M., Warren R. E. Norfloxacin and the antibacterial gamma pyridone beta carboxylic acids. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jul;10(1):25–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby S. R., Jonsson M. Antibacterial activity of norfloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):15–18. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



